Contents
- Closed and open fracture of the humerus
- Displaced fracture of the humerus
- Humerus fracture without displacement
- Fracture of the greater tubercle of the humerus
- Other types of fracture of the humerus
- Comminuted fracture of the humerus
- First aid for a fracture of the humerus
- Humeral fracture treatment
- Immobilization for fracture of the humerus
- Rehabilitation after a fracture of the humerus
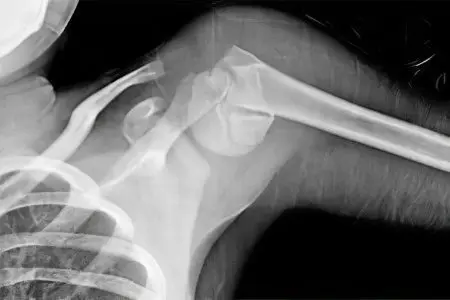
A fracture of the humerus is an injury resulting from an applied force that the bone tissue was not able to withstand. This injury is widespread. It often occurs in both young people and those of retirement age. But the latter still prevails.
The statistics depending on the location of the fracture are as follows:
Proximal fractures account for the majority of injuries. Injuries to the bones of the upper sections occupy a leading position and account for about 7% of all fractures of the skeleton of the human body.
Diaphyseal fractures are less common. The share of bone damage in the middle part of the shoulder accounts for up to 3% of cases.
The most rare are distal fractures, that is, those that affect the lower sections of the shoulder. They account for about 1 – 2%.
If we turn to the anatomical structure, then the following bones are part of the shoulder:
The surgical neck and head of the bone are located under the articular bag and are its components, they belong to the so-called “upper” part of the shoulder.
The longest section of the shoulder is its body or diaphysis.
The lower part of the shoulder, which is called the condylar or distal region, is responsible for the connection with the elbow joint.
Closed and open fracture of the humerus
Closed fracture
A closed fracture may occur in the upper shoulder. There, the head of the bone, the small and large tubercle, the surgical and anatomical neck are subject to injury.
Symptoms that bother a patient who has received a closed injury to this part are as follows:
Pain in the joint area.
If the injury is impacted in nature, then the edema is not too pronounced, it grows slowly. The pain intensifies when trying to actively move the limb. Passive movements are not too limited.
If a displacement is observed during a closed fracture, then the deformation of the hand is more often visible, other symptoms, including pain, appear brighter.
If a closed fracture of the shoulder occurred in the middle section, then most often the cause is a fall or a blow to the shoulder. The injury may be comminuted, may be oblique, transverse and helical. A fracture of this part often entails damage to the nerve bundle, namely the radial nerve. In addition, the brachial arteries and veins suffer.
The main symptoms that allow us to talk about a closed fracture of the body of the shoulder include:
Strong pain.
Deformation, in the presence of displacement.
Decreased limb length.
Fragment crepitation.
Puffiness and hematoma, which can occupy a vast area, up to the hand.
Movements are limited mainly in the elbow and in the shoulder joint.
If the nerves were damaged, then there is a violation of the movements of the fingers and their sensitivity.
The brush cannot be kept in a raised state, it hangs limply.
Open fracture
The main features of an open fracture include:
An open wound will be visible on the surface of the skin. Most often, a bone peeps through it.
There is severe bleeding, which must be stopped by applying a tourniquet. Its location is the upper third of the shoulder.
The wound site is treated with any available antiseptic, after which the application of a sterile dressing is shown.
Only after processing and stopping the bleeding, the hand should be immobilized.
Displaced fracture of the humerus
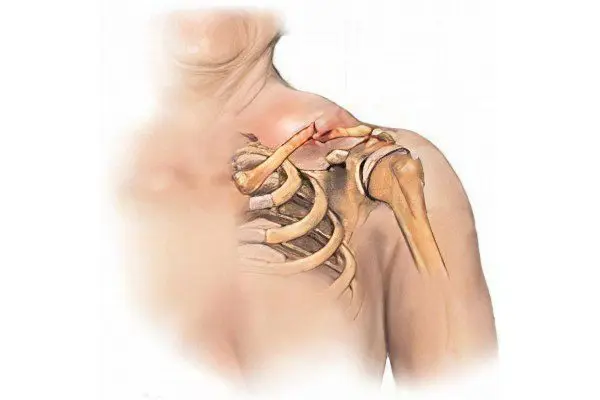
Displaced fractures are characterized by the following symptoms:
The occurrence of a sharp pain that appears when trying to move the arm or when probing the body of the humerus.
Swelling, often with severe hematoma.
The impossibility of performing active actions to abduct and raise the limb.
With active probing, crepitations are heard.
The deformity is visible even when the bones have not broken through the soft tissues. Especially if the displacement of fragments is pronounced.
The final diagnosis can be made only after the doctor sees x-rays, which should be made in two projections. If there is a pronounced displacement of the head of the shoulder, then the prognosis is unfavorable. Since she will experience a nutritional deficiency, this will lead to her necrosis or even resorption. In the same way, fractures are also dangerous, the line of which passes through the tubercles. Restoration of the full functioning of the limb is rare.
When the surgical neck is injured, the displacement occurs according to the impacted type with the formation of a chip. The fragment can move to the side (when the fracture occurs with the shoulder adducted) or to the middle (when the shoulder is abducted). At the same time, the decisive factor in where it will be directed is played not only by the position of the shoulder when injured, but also by muscle contraction, which occurs reflexively.
It is important not to confuse a fracture with a dislocation and dislocation of the shoulder. A distinctive feature of such fractures is the ability to freely move the shoulder (not at the joint), with the help of passive force. There will be no springing effect. These signs are especially relevant for obese people, since it can be difficult to conduct a full-fledged x-ray examination from a dense fatty layer.
Humerus fracture without displacement
If no displacement occurred during a fracture of the shoulder bone, then the signs of a fracture may be somewhat blurred:
Depending on the location of the injury, the person will feel pain in the upper or lower arm. But its intensity is not as pronounced as in a fracture with displacement of fragments. It gets worse when you try to move.
Edema may not form immediately, but within a few hours. This is due to the fact that the soft tissues around the bone will not be damaged by fragments.
A hematoma is observed, but it also manifests itself after some time, its size and severity depends on the cause of the fracture.
Shortening of the limb is not noticeable without special measurements.
There is no hand deformity.
It is important to properly provide first aid to the victim so that the fragments do not shift, and the injury does not become more serious. More often, fractures of the bones of the shoulder without displacement are observed in children, due to the peculiarities of the structure of their bone tissue.
Fracture of the greater tubercle of the humerus
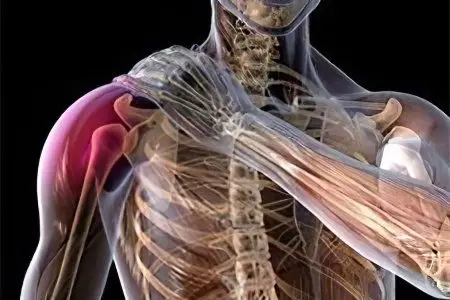
Fractures of the greater tubercle of the humerus are not uncommon. If it was damaged in isolation, then the injury occurs in a tear-off type. Often, the separation of the tubercle is accompanied by dislocation of the shoulder. Due to the fact that the muscles responsible for the abduction of the shoulder and its rotation are attached to it, the detached fragment always shifts due to their tension force.
Signs of detachment of a large tubercle are as follows:
Swelling at the site of injury.
Pain that manifests itself locally, over the shoulder joint.
Impaired mobility of the shoulder joint.
Due to muscle retraction, there is a violation of the external rotation of the shoulder. This is one of the main symptoms indicating damage to the tubercle.
If it is absolutely impossible to remove the hand, then this is a sign of damage to the tendons.
After a fracture of the greater tubercle, there is a risk that movement disorders in the shoulder joint may be expressed. This is due to damage to the supraspinatus muscle. Sometimes a full recovery is not possible.
Other types of fracture of the humerus
Separately, it should be said about the fracture of the surgical neck, transcondylar and comminuted fracture. Each of them has certain characteristics. In the treatment of them, you need to adhere to certain tactics.
Surgical fracture of the humerus
If the mechanism of injury is indirect, then the surgical neck of the shoulder often suffers. Fractures are divided into adduction and abduction fractures, depending on the position of the arm at the time of injury. The first occurs if the limb is adducted, and the second if it is retracted. When the hand is in the middle position, then the introduction of the distal fragment into the proximal one occurs more often. This is called a surgical impacted fracture.
If we consider the symptoms of this type of injury, then it is as follows:
The pain will be localized at the fracture site, it becomes more intense when you try to make circular movements.
It is uncomfortable for a person to hold a limb on weight, he tries to support it under the elbow.
If attempts are made to move, then the large tubercle will move towards the head.
There is swelling and a hematoma is observed.
When displaced, crepitations will be heard.
Pathological mobility is observed.
The shoulder will become shorter than healthy.
A surgical fracture of the neck of the shoulder is dangerous because at the time of injury, the integrity of the neurovascular bundle often occurs. The same damage can occur with improper reposition. This violation will lead to the fact that the function of the hand will not be fully restored.
Transcondylar fracture of the humerus
Such injuries are rare, due to the location of the bone. Damage is considered intra-articular, which means that the fracture line runs through the joint cavity. It runs transversely, from one condyle towards the other.
Symptoms of a transcondylar fracture include:
Painful sensations that radiate to the elbow and forearm.
The presence of swelling. Sometimes the swelling is pronounced.
If there is a displacement, then the deformation of this area will be visible.
When you try to feel a crunch is heard.
Movement of the elbow, if not completely blocked, is largely limited.
A characteristic feature of a transcondylar fracture is trauma to the brachial artery. This increases the risk of gangrene of the hand. If the artery is damaged, then the pulse on the forearm cannot be felt.
In order for both condyles to be broken, the application of impressive force is necessary. This may be a fall on the elbow from a height, accidents at work, for example, a mine collapse. X-rays often show fractures that form the letter V or T.
The external condyle is more likely to break in children. The offset will be directed outwards and upwards. The internal and external epicondyles are rarely affected and are accompanied by dislocation of the elbow.
Comminuted fracture of the humerus
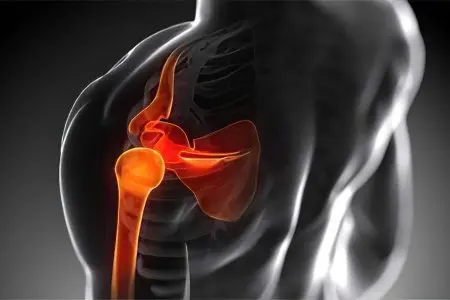
The most severe of all types of shoulder fracture is comminuted, with displacement. The difficulty lies in the fact that not only nerves are damaged, but also blood vessels. Therefore, surgical intervention is required for treatment.
This injury is typical for the adult population.
Depending on the nature and location of the fracture, the following types of comminuted shoulder injury are distinguished:
Fracture of the upper part, it is accompanied by swelling and deformity of the joint. For recovery, surgical intervention is necessary, an obstacle for which may be either advanced age or the presence of a serious illness.
A shoulder fracture in the middle part is dangerous because the radial nerve, veins and arteries can be damaged by fragments. For their fixation, it is necessary to use metal pins or plates, or the Ilizarov apparatus.
If the injury occurred in the lower part of the humerus and there is no displacement of the fragments, then it is advisable to apply a plaster cast. With significant displacement of the fragments, an operation is needed.
First aid for a fracture of the humerus
First aid for trauma is as follows:
To begin with, a person needs to be calmed and offered an anesthetic. As an analgesic, analgin, nimesulide, ketorol can act. If a person has a panic, then you can give him a tincture of valerian, 20 drops will be enough, or one tablet of tazepam or triocazine. Valocordin or cordiamine can be used as a cardio-vascular agent.
Then you need to limit the movements of the hand as much as possible. For this purpose, immobilization is carried out. As improvised means, you can use small boards. One of them should be tightly bandaged to the shoulder, and the other to the forearm. If there are not even planks, then it is advisable to put your hand on a scarf bandage. She throws herself over an uninjured shoulder. In this case, the bend of the arm should be carried out at a right angle at the elbow. To avoid displacement, it is best to tie such a bandage as tightly as possible to the body.
When transporting, it is desirable that the person sits.
Humeral fracture treatment
Three methods are used to treat a shoulder fracture: surgical, conservative, and skeletal traction. If the fracture is not complicated by displacement or it can be corrected by performing a one-stage reposition, then it is enough to apply a plaster or other fixative.
If we consider therapy at the fracture site, then the following features can be distinguished:
The treatment of a large tubercle occurs by applying a plaster, sometimes it can be supplemented with a diverting splint. This is necessary in order to prevent the development of stiffness in the joint and ensure proper fusion of the supraspinatus muscle. If the fragment of the tubercle has moved, then it must be fixed in the correct position with knitting needles or a screw. After about 1,5 months, the structure will be removed.
If the surgical neck was injured, but there was no displacement, then you can do with the imposition of gypsum for a month. When reduction was required, and it was successful, the plaster will have to be carried for two weeks more. If it was not possible to set the bone fragments, then surgical intervention is necessary. Fixation inside the bone is carried out with the help of plates. If the fracture occurred according to the impacted type, then it is advisable to use either a diverting pillow or a special scarf. The duration of treatment can be extended up to 3 months.
When the fracture is localized on the body of the shoulder and displacement is observed, then the most common way to treat it was skeletal traction. In an immobilized position, a person will have to spend up to a month. After another gypsum will be applied for the same time period. Recently, the method of skeletal traction has faded into the background, it is replaced by osteosynthesis, which does not chain a person to bed for such a long time.
Transcondylar fractures are almost always accompanied by displacement of fragments. Their comparison is carried out under anesthesia, and then it is advisable to apply plaster for up to two months.
If, as a result of fractures, vessels or nerves were damaged, then a special operation is necessary, which consists in suturing them. This increases the duration of treatment and it is not always possible to fully restore the functionality of the limb. As for drugs, it is advisable to use calcium preparations, as well as analgesics and antibiotics.
Immobilization for fracture of the humerus
When complete immobilization of the limb is required, it is advisable to apply a thoraco-brochial bandage.
The overlay technique is as follows:
The victim should sit on a high stool or on a table. His limb must be flexed to 80°C for an injury to the upper shoulder and 45°C for a fracture of the lower bones.
A layer of cotton wool should be applied to the body, which is fastened with bandages.
The joints of the hand, such as the wrist, elbow and shoulder, are also lined with cotton.
Gypsum splints are applied horizontally to the body, and on the sides they are attached vertically.
One splint should be passed over the injured shoulder. It should be attached to the body with bandages.
Then additional splints are applied along the body, shoulder girdle, forearm, up to the hand. All this is again fixed with bandages.
A special spacer is inserted between the arm, which will be in the cast and the torso, so that the limb cannot adhere to the body.
Thus, the limb will be immobilized, and the fusion of the bones will proceed correctly.
Rehabilitation after a fracture of the humerus
After the bandage is removed, it is necessary to proceed to rehabilitation measures. They are an integral part of bone restoration and play no less important role than adequate therapy.
Rehabilitation necessarily includes:
Physiotherapy treatment – you will need to take several courses, which consist of 10 procedures. Electrophoresis with novocaine, calcium chloride may be recommended. Ultrasound treatment has proven itself well.
Massage, which, if it is impossible to visit a specialized office, you can perform on your own. To accelerate healing and stimulate blood circulation, you can use specialized ointments and oils.
Performing a set of special exercises.
Exercise therapy for a fracture of the humerus
It is advisable to carry out exercises from the very first days of treatment, while the plaster cast has not yet been removed.
They are as follows:
After waiting a couple of days, from the moment of the fracture, you need to start moving your fingers. Don’t do things that cause pain.
When a week has passed, you can make the first attempts to tighten the shoulder muscles. This should be done in such a way that the joint remains motionless. Approaches need to be done per day at least 10, while each of them should have 15 stresses. A healthy hand should not be ignored, as it also needs to maintain muscle tone.
When the plaster is removed, you can move on to active movements in the joints: shoulder and elbow.
There are certain exercise therapy, which are developed by traumatologists.
They include the following exercises:
Hand movements like a pendulum. In this case, it is necessary to stand with your legs apart shoulder-width apart, and tilt your torso forward.
Without changing position, you need to rotate your hands in a circle.
Mahi limbs in front of the chest.
Performing the exercise “lock” behind the shoulder blades.
Throwing hands back, behind the head.
Using a gymnastic stick to perform exercises.
Exercises can vary, you need to perform them daily. The number of times is up to 15. When the muscles are strengthened, you can start using dumbbells. But not earlier than 1,5 months after the removal of the plaster. If contractures are formed, or the function of the hand is restored with difficulty, then it is advisable to undergo rehabilitation courses in specialized centers or in sanatoriums.









