Contents
The depth of the foundation is a design value that depends on the type of building or structure, the climatic zone, the soil on the site and the level of groundwater. This value is also influenced by the design of the building (with or without a basement), the principle of its use (with or without heating), the number of storeys and weight.
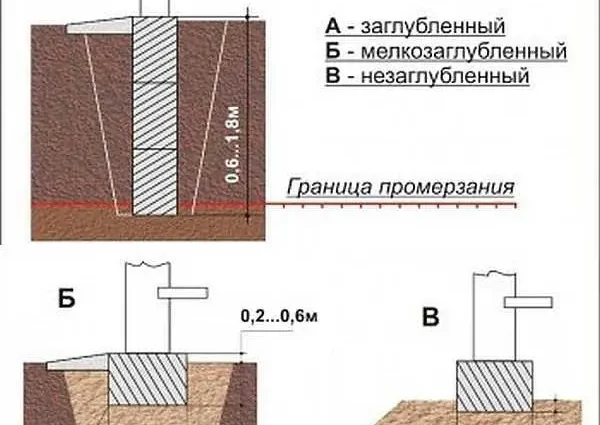
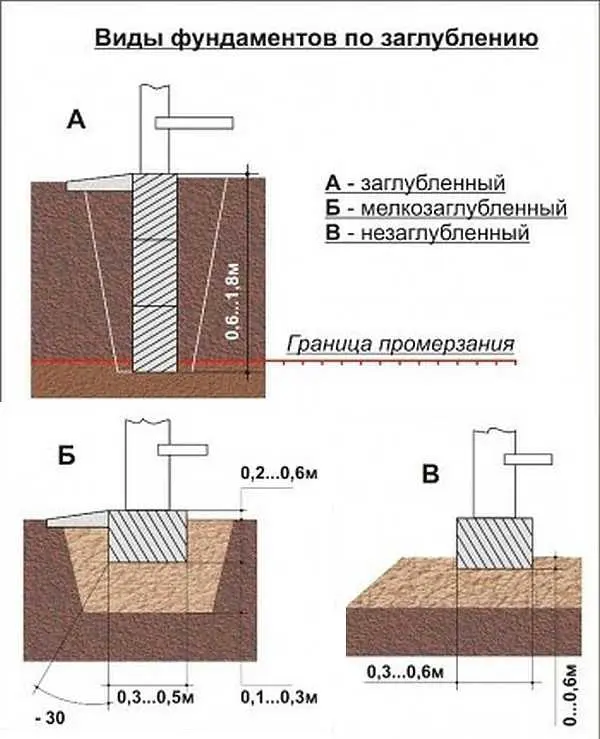
Speaking objectively, this is the amount by which the foundation will need to be buried in order for it to provide a stable support for the structure. They are of two types:
- deep laying;
- shallow or not buried.

Types of strip foundations by depth of penetration
According to building codes, in order to withstand the forces of frost heaving, the sole must be deepened 15-20 cm below the freezing level for the soil. When this condition is met, the foundation is called “deep” or “deep”.
With a freezing depth of more than 2 meters, earthworks have very large volumes, the consumption of materials is also high and the price is very high. In this case, other types of foundations are considered – pile or pile-grillage, as well as the possibility of laying above the standard freezing point. But this is possible only if there are soils with a normal bearing capacity, the obligatory insulation of the basement and foundation, as well as the installation of an insulated blind area. In this case, the laying depth decreases several times and is usually less than a meter.
Sometimes the foundation is poured directly on the surface. This is an option for outbuildings, and most likely made of wood. Only she, in such conditions, is able to compensate for the resulting distortions.
Preliminary survey
Before you start planning your house, you must decide where on the lot you want to put the house. If there are already geological studies, take into account their results: in order to have fewer problems with the foundation, it has a minimum cost, it is advisable to choose the “driest” site: where the groundwater is as low as possible.

Further, geological studies of the soil are carried out in the selected place. To do this, pits are drilled to a depth of 10 to 40 meters: it depends on the structure of the layers and the planned mass of the building. Wells are made at least five: at those points where corners are planned and in the middle.
The average cost of such a study is about $ 1000. If a large-scale construction is planned, the amount will not greatly affect the budget (the average cost of a house is 80-100 thousand dollars), but it can save you from many problems. So in this case, order a study from professionals. If you want to put up a small building – a small house, a summer house, a bathhouse, a gazebo or a platform with a barbecue, then it is quite possible to do the research yourself.
We explore geology with our own hands
To check the geological structure of soils with our own hands, we arm ourselves with a shovel. At all five points – at the corners of the future structure and in the middle – you will have to dig deep holes. Size: meter per meter, depth – at least 2,5 m. We make the walls even (at least relatively). After digging a hole, we take a tape measure and a piece of paper, measure and record the layers.

What can be seen in the cut:
- Above is the darkest layer – fertile. Its thickness is from 10 cm to 1,5 meters, sometimes more. This layer must be removed. Firstly, it is loose, and secondly, different animals / insects / bacteria / fungi live in it. Therefore, immediately after marking the foundation, this layer is first removed.
- Below is natural soil. So it was before “processing” by animals and microorganisms. There may be such soils;
- Dense sand (coarse, medium, with gravel). An excellent foundation for building a house: the water drains quickly and the foundation is reliable. On such soils, you can put the house on a shallow foundation (laying depth from 50 cm).
- Loose sands (fine and dusty). If groundwater is located deep, it is possible to build. But these soils are dangerous because they float when saturated with water.
- Clay, loam, sandy loam. They behave in the same way as silty sands: when wet, they float if there is little water, but their bearing capacity is high. Here you also need to look at the amount of precipitation in the region.
- Peatlands. The most unreliable bases. They can only be built using columnar foundations. And then, only on condition that a layer of soil with good bearing capacity is not very deep.

It is necessary to determine what kind of soils are in each layer
Often difficulties arise when trying to distinguish clay-containing soils. Sometimes it is enough just to look at them: if sand predominates and there are inclusions of clay, you have sandy loam in front of you. If clay predominates, but there is also sand, it is loam. Well, the clay does not contain any inclusions, it is hard to dig.
There is another method that will help you make sure that you have determined the soil correctly. To do this, a roller is rolled up from the moist soil (between the palms, as once in kindergarten) and bent into a bagel. If everything crumbled – it is low-plastic loam, if it fell into pieces – plastic loam, if it remained intact – clay.
Having decided on what soils you have in the selected area, you can begin to choose the type of foundation.
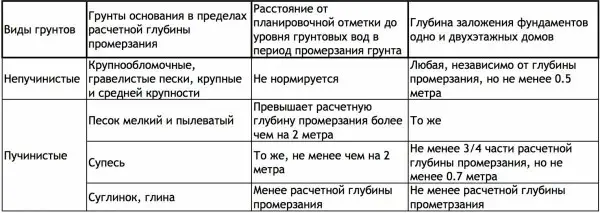
The depth of the foundation, depending on the level of groundwater
All design features are described in SNiP 2.02.01-83*. In general, everything can be reduced to the following recommendations:
- When planning on rocky, sandy large and medium sizes, gravelly, coarse-clastic soils with sandy aggregate, the depth of the foundation does not depend on the level of groundwater.
- If there are fine or silty sands under the base of the foundation, then at the level of groundwater located 2 meters below the freezing level of the soil, the depth of the foundation can be any. If the waters are above this mark, then the foundation must be laid below the freezing level.
- If there are clays, loams, coarse-grained soils with dusty or clay aggregates under the sole, then the foundation must definitely be below the freezing level (it does not depend on the level of groundwater).

Table with the recommended foundation depth depending on the type of soil and groundwater level (to increase the size of the image, click on it with the right mouse button)
As you can see, basically the level of laying the foundation of the foundation is determined by the presence of groundwater and how much the soils in the region freeze through. It is frost heaving that causes problems with foundations (or a change in the level of groundwater).
Soil freezing depth
To roughly determine to what level the soils freeze in your area, just look at the map below.
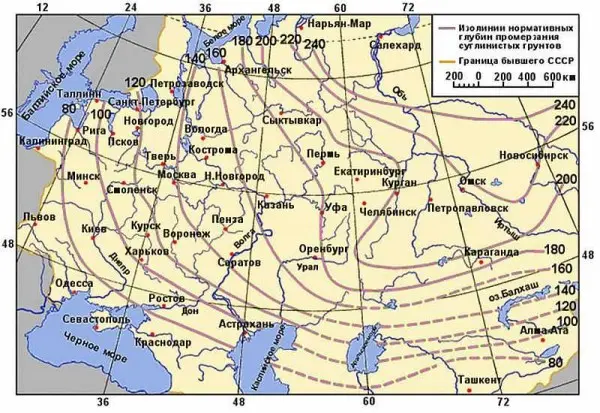
But this is averaged data, so for a particular point it is possible to determine the value with a very large error. For inquisitive minds, we present a method for calculating the depth of soil freezing in any area. You will only need to know the average temperatures for the winter months (those with negative monthly averages). You can calculate for yourself, the formula and calculation example are posted below.
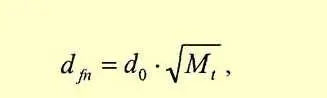
Dfn is the depth of freezing in a given region,
Do is a coefficient that takes into account soil types:
- for coarse soils, it is 0,34;
- for sands with good bearing capacity 0,3;
- for loose sands 0,28;
- for clays and loams, it is 0,23;
Mt – the sum of the average monthly negative temperatures for the winter in your area. Find metrology service statistics for your region. Choose the months in which the average monthly temperature is below zero, add them up, find the square root (there is a function on any calculator). Substitute the result into the formula.
For examplewe’re going to build on clay. Average winter temperatures in the region: -2°C, -12°C, -15°C, -10C, -4°C.
The calculation of soil freezing will be as follows:
- Mtu2d 12 + 15 + 10 + 4 + 43 u43d 6,6, we find the square root of XNUMX, it is XNUMX;
- Dfn= 0,23*6,6= 1,52 m.
We got that the estimated depth of freezing according to the given parameters: 1,52 m. That’s not all, consider whether heating will be necessary, and, if so, what temperatures will be maintained in it.
If the building is unheated (bathhouse, cottage, construction will take several years), a multiplying factor of 1,1 is applied, which will create a margin of safety. In this case, the foundation depth is 1,52 m * 1,1 = 1,7 m.
If the building is heated, the soil will also receive a portion of its heat and it will freeze less. Therefore, in the presence of heating, the coefficients are decreasing. They can be taken from the table.
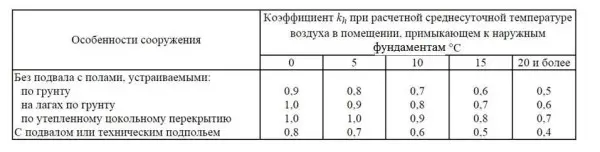
So, if the temperature in the premises is constantly maintained above + 20 ° C, the floors are with insulation, then the depth of the foundation will be 1,52 m * 0,7 = 1,064 m. This is already a lower cost than deepening by 1,52 m.
The tables and maps show the average level for the last 10 years. In general, it is probably worth using data for the coldest winter in the last 10 years in the calculations. Abnormally cold and snowless winters occur with approximately the same frequency. And in the calculations it is desirable to focus on them. After all, it will not calm you down if, after standing for 9 years, on the 10th your foundation will crack due to a too cold winter.
How deep to dig the foundation
Armed with these figures and the results of the study of the site, you need to select several options for foundations. The most popular are tape and columnar or pile. Most experts agree that with the normal bearing capacity of the soil, their sole should be 15-20 cm below the freezing depth. How to calculate it, we told above.
In doing so, keep the following recommendations in mind:
- The sole should rest on the ground with good bearing capacity.
- The foundation must sink into the bearing layer by at least 10-15 cm.
- It is desirable that groundwater is located lower. Otherwise, it is necessary to take measures to divert water or lower its level, and this requires very large funds.
- If the bearing soil is too deep, it is worth considering the option of a pile foundation.
Having chosen several types of foundation, having determined the depth of laying for them, an approximate calculation of the cost of each is carried out. Choose the one that is more economical.
Also note that to reduce the depth of the foundation, you can use an insulated blind area. During the construction of a shallow strip foundation, a blind area is required.
shallow foundation
Sometimes a deep foundation is very expensive to build. Then consider the pile (pile-grillage) or shallow foundations (shallow). They are also called “floating”. There are only two types of them – a monolithic slab and tape.
The slab foundation is considered the most reliable and easily predictable. It has such a design that it can receive significant damage only with gross miscalculations in the design. However, it can also be corrupted.
However, developers do not like slab foundations: they are considered expensive. They take a lot of material (mainly reinforcement) and time (for knitting the same reinforcement). But sometimes a slab foundation is cheaper than a deep-laid tape or even a pile foundation. So don’t discount it right away. It is optimal if they want to build a heavy building on heaving or loose soils.
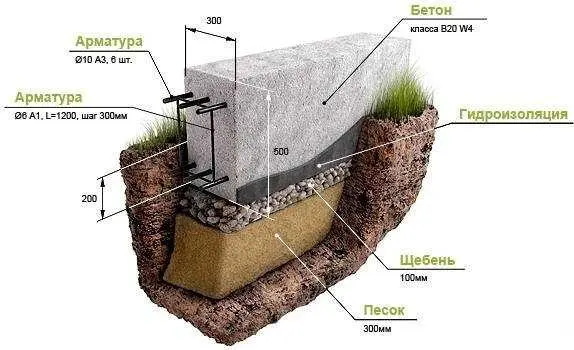
A shallow tape can have a depth of 60 cm or more. At the same time, it must rest on soil with normal bearing capacity. If the depth of the fertile layer is greater, then the depth of the strip foundation increases.
With shallow strip foundations for light buildings, everything is very simple: they work well. A combination with a log cabin or timber frame is an economical and at the same time reliable option. If there are bends in the tape, then elastic wood copes with them perfectly. A frame house feels almost as good on such a basis.
It is necessary to calculate more carefully if they are going to build rear ones from light building blocks (aerated concrete, foam concrete, etc.) on a shallow strip foundation. They react to changes in geometry not in the best way. Here you need the advice of an experienced and, of course, a competent specialist with extensive experience.
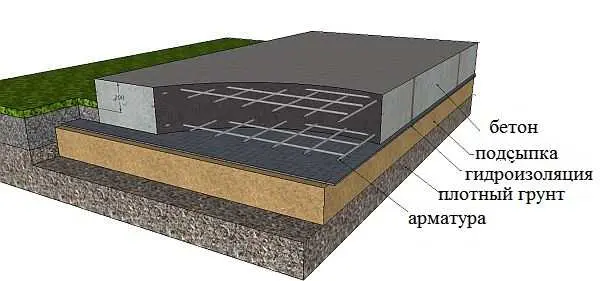
But under a heavy house, it is unprofitable to put a shallow strip foundation. To transfer the entire load, it must be made very wide. In this case, most likely, slab will be cheaper.
How shallow foundation works
This type is used when it is too expensive to deal with heaving forces and does not make sense. In the case of shallow foundations, they are not fought. You could say they are being ignored. They just make the foundation and the house rise and fall along with the swollen soil. Because they are also called “floating”.
All that is needed is to ensure a stable position and a rigid connection of all parts of the foundation and elements of the house. And for this you need the right calculation.