Contents
Gone are the days when, at the word “cottage”, a plot of 6 acres, overgrown with raspberries around the perimeter, with a small shed for storing a pair of shovels and a rake with a chopper, and so many beds that you could move only by jumping. Times are changing, many gardeners have enlarged their plots, houses have grown, but the desire to grow as many vegetables and fruits as possible on their land has been preserved. Each amateur gardener seeks to place fruit trees, various berries, and more vegetables on his land.

Many gardeners grow tomatoes on their plots and want to get a big harvest in a limited area. We will tell you how to increase the productivity of a tomato by forming a tomato bush in two stems, but first you need to understand the whole variety of species and varieties of this crop. Learn the rules for forming tomatoes in two stems. A video on this topic will help you master all the intricacies of forming a tomato in two stems, and from the article you will gain knowledge about the species differences of tomatoes.
Selection of tomato seeds
When choosing seeds, people pay attention to bright inscriptions: a high-yielding tomato variety, early ripeness of fruits, great taste, but these are advertising slogans. To choose the right variety of tomatoes, you need to know what variety they belong to, buy seeds depending on the climate and the method of cultivation: in open ground or in a greenhouse. Selection should be made according to the characteristics of the tallness of the bush and the timing of fruiting. This information is indicated on the packaging.
Many tomato seed producers, in order not to confuse the consumer, write “tall” or “short” varieties.
Varieties of tomatoes
In the wild, tomatoes are a herbaceous perennial liana, they creep along the ground, their growth is unlimited. As a result of serious selective work, tomato varieties with limited growth and uniform ripening of fruits were bred. Modern tomato varieties are divided by growth strength into two large groups: indeterminate and determinant (they are also called bush). The latter can be divided into three subgroups:
- Superdeterminate or standard ones are characterized by short stature, even dwarfism.
- Actually determinant – these are medium-sized varieties.
- Semi-determinant – varieties are tall, with a growth force above average.
Indeterminate varieties and hybrids
The main stem has no growth restrictions. These tomatoes begin to bloom after the formation of 9-12 leaves, after every three leaves a new flower brush is laid. In a warm climate and in a heated greenhouse, it can grow all year round, forming 40-50 fruit clusters. It requires the breakage of all stepchildren, it is formed into one stem, the formation of a tomato into two trunks is impractical. For the southern regions, indeterminate varieties are suitable for growing in the ground and in a greenhouse, the main condition is the possibility of tying to a high support or growing on a trellis. In the middle lane, such tomatoes can be grown in a greenhouse. In even more northern regions, it is unlikely that it will be possible to grow indeterminate varieties even in a greenhouse, the fruits will not have time to ripen.

Determinantant tomatoes
Grow to limited height. The first flower brush is formed at the level of 5-7 leaves, subsequent brushes appear after 1-2 leaves. Having tied 4-5 brushes, the determinant tomato is completed, that is, it forms a brush at the top, stopping vertical growth. Further development of the bush occurs on stepchildren (side shoots), their growth is also limited by the development of the brush. Determinate tomatoes are characterized by early yields and low yields. They need pinching and shaping a bush.
Determinate tomatoes can be grown outdoors in the southern regions and in the middle lane. In the northern regions, these varieties are suitable for growing in greenhouses. The mass of the plant, especially if it is formed into two stems, is very high. The bush needs to be tied up.
Semi-determinant varieties of tomatoes
They are a tall variety of determinant varieties, and can also be completed. Grows well in mid-latitude greenhouses. Suitable for formation in two stems.
Standard varieties of tomatoes
Virtually no maintenance required. Low-growing plants, with a strong thick stem. They do not need to be tied up, stepchildren do not need to be cut off either. The first flowering brush is formed after 4-5 leaves, and then after 1-2 leaves.

Pros and Cons of Determinate Tomatoes
In order to make a decision about growing one or another type of tomato, you need to have an accurate idea of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbtheir strengths and weaknesses, how to use the first to benefit, and minimize the second.
Positive points in comparison with tall varieties
- Early fruiting results from faster laying of the first flower cluster;
- Early ripeness of fruits occurs due to the laying of subsequent brushes through a smaller number of leaves;
- A friendly harvest is due to the almost simultaneous laying of several brushes.
Negative points in comparison with tall varieties
- Less yield from the bush due to the topping of the plant;
- Increased demands on fertilizers are associated with more frequent planting of brushes;
- A high degree of attention to the formation of the bush is due to the constant need to break stepchildren;
- The risk of diseases is increased due to the low resistance of the bush loaded with fruits.

Features of the formation of tomato bushes
All types of tomatoes, with the exception of standard ones, give a large number of side shoots (stepchildren). If stepchildren are not removed in time, then the green mass of the tomato bush grows, taking minerals from the soil, and there are not enough nutrients to form fruits. The result is a lush bush with a minimum of fruit. Excessive thickening of the bushes interferes with good ventilation, and increases the risk of developing tomato diseases. By cutting off stepchildren, you will get a neat, unthickened bush that will direct all its forces to fruiting. You need to understand well where the leaf is, where the brush is, and where the stepson is, so as not to mistakenly remove leaves or fruit brushes.
The leaf grows first, and from almost the same point, a lateral shoot (stepson) stretches, that is, you need to break off the upper sprout.
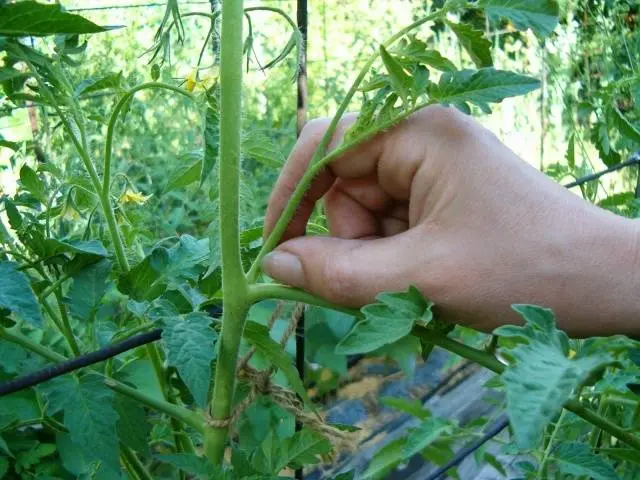

It is most difficult to distinguish between the stepson and the main stem at the first fork, it seems that the stem simply bifurcates. Focus on the location of the flower brush. It is located above the stepson, leaving his sinus, the main stem continues behind the brush. In the figure, the number 1 indicates the main stem, the number 2 leaves, the number 3 indicates the stepson, and the number 4 indicates the fruiting brush. The basic rule for removing stepchildren is regularity. Inspect the plants every week – one and a half, do not let the side shoots grow more than 5 cm, otherwise they will draw nutrients onto themselves and their removal will be traumatic for the tomato bush.
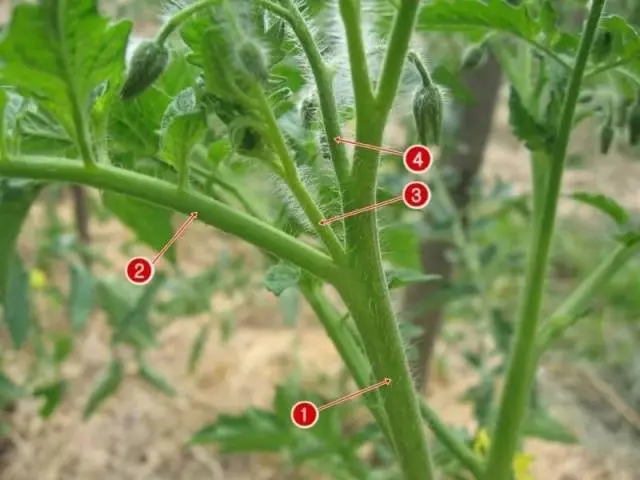
Pinching technique
Stepsons need to be removed by hand. When using the tool, there is a risk of infection transmission from bush to bush. Prepare thin rubber gloves and a weak solution of potassium permanganate, in which you will rinse your hands, moving on to the next plant. Start pinching with the strongest and healthiest plants. Those that are in doubt, leave in the end, and better for another day. Plan the pasynkovanie procedure in the morning hours of a fine day. After watering or top dressing, it is impossible to pinch tomatoes, wait 2-3 days, at which time the plant actively absorbs water and nutrients.
In this video you can see how to stepchild tomatoes correctly:
Grab the stepson with your fingers from above and pinch it. You can powder the place of the stepson’s cliff with ash or crushed coal. Throw the removed sprout under the bush, decomposing, it will fertilize the soil.
When removing the stepson, do not pull it down; together with the stepson, you can tear the skin from the stem. In addition to the stress of injury, an infection can get into the open wound of the bush. After pinching, you can water by the evening of the next day.

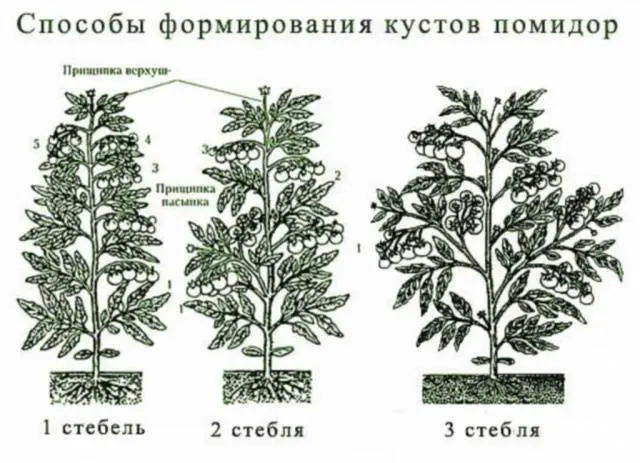
Formation of determinant varieties of tomato in two stems
Armed with basic knowledge, we can move on to mastering the skills of forming tomatoes in two trunks, increasing yields. Often, a tomato bush is formed, leaving a stepson at the leaf, which is located below the first brush. Inspect the ovaries, and pinch the growth point after 6-8 inflorescences. As a rule, both stepchildren and inflorescences begin to grow after seedling acclimatization has occurred. If the seedlings were overexposed, then the inflorescences may still appear in the seedling pots.
Formation at the seedling stage
It is even easier to form a tomato in two stems – pinch the top of the seedling over the second true leaf. After this action, two shoots begin to grow from the axils of 1 and 2 leaves, and they will become the basis for a bush with two trunks. The early pinching method is less traumatic for the tomato bush.
Formation of tomatoes in the greenhouse
When growing tomatoes in a greenhouse, that is, with a growing season of more than three months, grow determinant varieties in one stem, and leave a reserve stepson. You can leave the side shoot after the formation of 4-5 fruit brushes, leaving it in the leaf axil under the upper inflorescence. When the main stem stops growing, the spare stepson will continue to grow, it will be a continuation shoot, and stepchildren will also grow on it, remove them too. If the central trunk has not stopped its growth, then grow another brush on it, and then pinch it.
To correctly regulate the load on the determinant tomato bush, pinching the trunk, follow the rule: the lateral replacement shoot should be located under the second brush from the top. The reserve shoot will take over the function of the stem, and the two upper brushes on the former main trunk will go down under the weight of the fruit. The stepson will need to be pinched after the formation of 4-5 inflorescences. If you did the stepson incorrectly and left the lateral shoot in the axil of the last leaf, it will lag behind in development. If your determinate tomato is single-stemmed, always leave a backup shoot.
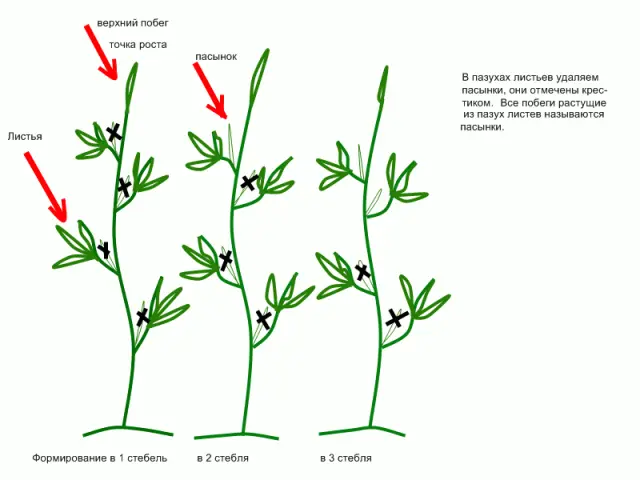
The second option for the formation of tomatoes in two stems is suitable for long periods of vegetation. You will receive the harvest a little later, but it will be more friendly. Leave a stepson under the first inflorescence, form a short continuation shoot from it, literally two brushes. After two brushes and several leaves grow, this shoot should be pinched. The presence of fruits on the lower floor of the bush delays the growth of the upstream stem and slows down the formation of inflorescences higher up the stem.
Keep an eye on your plants. A large load requires enhanced nutrition, it weakens plants, reduces disease resistance. Tie up both the main stem and reserve trunks, the fruits should not touch the ground, otherwise they will rot. Look at fruit-bearing bushes. Remove small fruits, let the nutrients get more promising. In the second half of summer, remove the extra ovaries, if the fruits are tied on them, they will not have time to ripen, and they will only take nutrients from the ripening tomatoes.

Conclusion
As you can see, there is nothing complicated in the formation of tomatoes in two trunks. Do not be afraid to purchase determinant varieties, experiment with the formation of bushes, and you are guaranteed big tomato crops.









