Contents
Forest champignon belongs to the Champignon family. The mushroom was discovered by mycologist Jacob Schaeffer, who gave a complete description of the fruiting body in 1762 and gave it the name: Agaricus sylvaticus. In the common people, forest champignon is called a blessing or a cap.
What does wild champignon look like?
The cap at the fruiting body grows up to 7-12 cm in diameter, less often up to 15 cm. In small mushrooms, it has the shape of a dome, but as it grows, it expands and straightens, becoming almost flat.
In the grown-up goodies, the hat is slightly wavy, on the part of the forest mushrooms you can find pieces of the bedspread. Its surface is light, brown with a reddish tinge. It is brighter in the center than at the edges. When viewed from the cap, you can find small scaly plates of a fibrous type. They are pressed in the center, but slightly lag behind at the edges. Between them, the skin is translucent, on which cracks appear during the drought period.
According to the photo and description, the pulp of the forest champignon is quite thin, but dense. When collecting the fruiting body on the cut, you can notice a change in shade to red. After time, the light red color changes to brown.
The plates at the cap are frequent, located freely. In young fruiting bodies, before the veil breaks, they are creamy in color or almost white. As the fungus grows, the color changes to dark pink, then to red, then to red-brown.
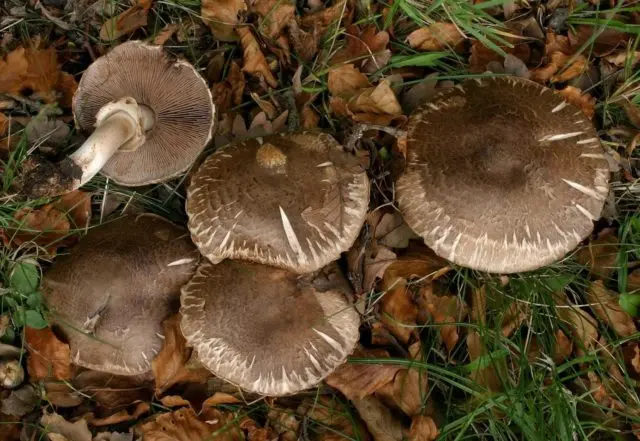

A photo of forest champignons in a section allows you to study the stem of the fungus: it is central, 1-1,5 cm in diameter. Outwardly, the stem looks flat or slightly curved, reaches a height of 8-10 cm, with a thickening at the base. Its color is lighter than that of the hat: white with gray or brownish.
Above the annulus, the stalk is smooth, below it it has a coating of brownish scales, which are larger in the upper third than in the lower one. In most mushrooms, it is solid, but in some specimens it is also hollow.
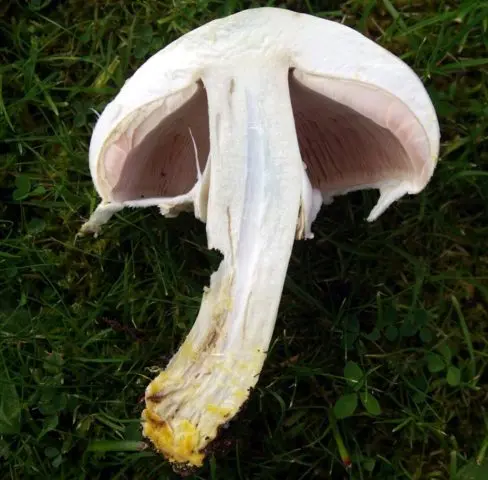
The pulp in the leg is presented in the form of fibers, but dense. It turns red when pressed, but gradually the redness disappears.
The ring of forest champignons is solitary and unstable. On the underside, the color is light, almost white. In adults, the ring on top has a reddish-brown color.
Where does wild mushroom grow?
The fungus is distributed throughout Europe and Asia. The places of growth of fruiting bodies are different: most often blashushki are found in coniferous and mixed forest plantations. You can find forest champignons in deciduous plantings. Occasionally, the cap grows in large forest parks or recreation areas, on the edges or near anthills.
The fruiting process begins in July, peaks in August and continues until mid-autumn. If climatic conditions are favorable, then harvesting is possible until the end of November.
Forest champignon edible or not
The cap belongs to the edible fruit bodies. Mushroom pickers prefer to collect young specimens: adult forest champignons break easily, which makes it difficult to process the harvest.
The blessing does not have a pronounced mushroom taste and smell, which is considered by culinary experts for its dignity. This allows you to add fruiting bodies to dishes without fear of interrupting the taste of other ingredients.
False forest champignons
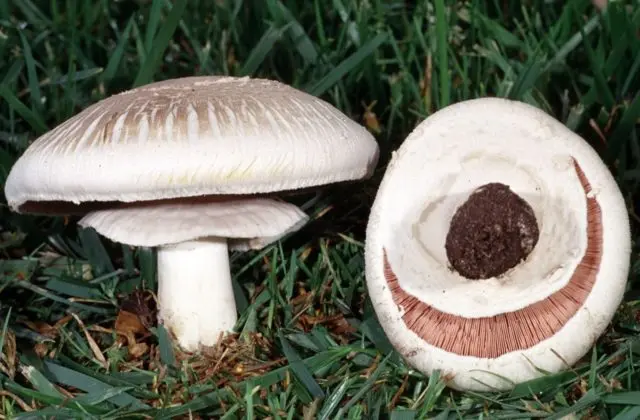
It is necessary to distinguish the cap from the yellow-skinned stove. The mushroom has a brownish color with patches in the center of the cap. In adult specimens, it is bell-shaped, and in young representatives it is round. The flesh of the double is brownish, prone to yellowing.
To distinguish yellow-skinned pecheritsa from forest champignon, it is enough to press on the fruiting body: when touched, it changes color to yellow and begins to smell unpleasant. The scent is similar to phenol.
This twin of the wild mushroom is poisonous, so it should not be eaten or harvested.

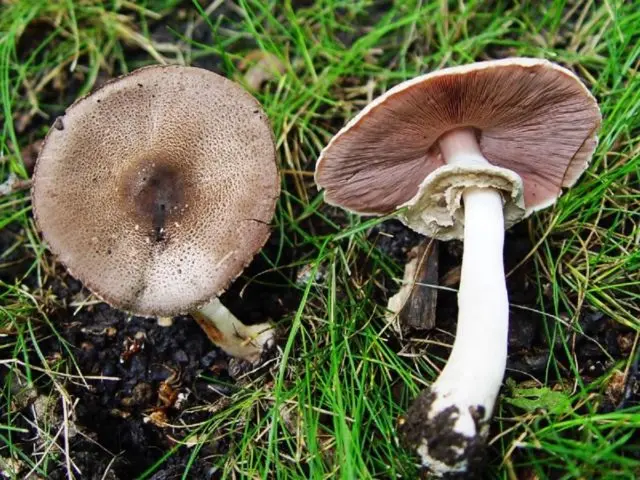
The false twin of the blessing is the flat cap champignon. Its cap reaches a diameter of 5-9 cm, has a small tubercle in the center. It is dry to the touch, whitish or grayish in color, with many gray-brown scales merging into a dark spot.
The forest mushroom looks like an edible champignon: the plates are slightly pink in color, but gradually their shade changes to black-brown. The flesh is thin, when damaged it changes color from whitish to yellow and then brown. But the smell of the flat-cap species is unpleasant, it can be described as a pharmacy, the aroma of iodine or ink, phenol.
In most sources, the flat cap champignon is listed as conditionally edible.

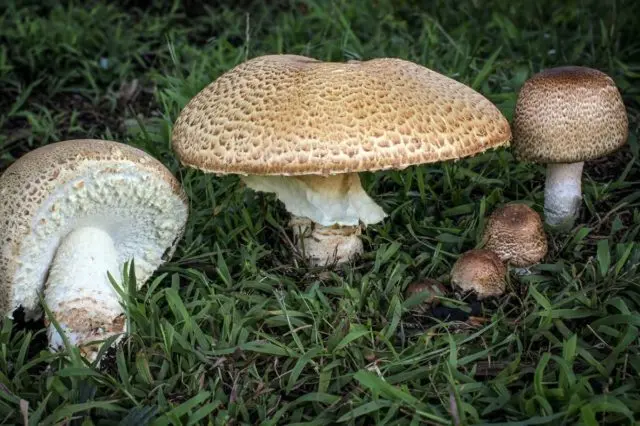
Among other types of forest champignons, with which you can confuse the blessing, is the August champignon. Its hat reaches 15 cm in diameter, at first it has a spherical shape, then it is half-spread, of a dark brown hue. As it grows older, it cracks, as a result of which it becomes scaly. The color of the plates is pinkish-red, changing to brown with age. The wild mushroom has an almond smell and a pungent taste. This species is edible.

Rules for collection and use
When visiting the forest, it is necessary to collect only familiar mushrooms. The selected specimen should be carefully cut, reducing the risk of damage to the mycelium. It is best to collect young fruiting bodies.
Harvest must be processed before use. To do this, all fruiting bodies are sorted out, cleaned of debris and dirt, and then washed under running water.
Use forest champignons in boiled, fried or baked form. Fruiting bodies are distinguished by a pleasant mild mushroom aroma and mild taste.
Cooks add them to sauces and side dishes, preserve them for the winter. Freezing or drying of forest champignons is possible.
Conclusion
Forest champignon is a beautiful, mild-tasting edible mushroom found in coniferous and mixed forest plantations. Despite its wide distribution, it has hard-to-distinguish twins that are unsuitable for food: flat-capped and yellowing champignons.









