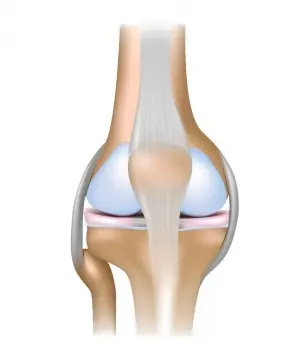
One of the most common diseases of civilization nowadays are diseases of the joints. Research shows that as many as 8 million Poles are affected by this problem. Its cause may be an incorrect lifestyle, but also genetic conditions. This disease significantly impairs physical fitness and even mobility in humans, which is why it is very burdensome.
That’s why you should take care of your joints before they start to bother you. One of the most common causes of joint disease is obesity. Therefore, you should take care of a proper, healthy lifestyle and do not avoid exercise.
Scientists say that degenerative changes in the joints are also affected by poor nutrition. These are, for example, diets low in chondrocytes, i.e. nutrients that are part of the building blocks of joint cartilage. They synthesize collagen and proteoglycans, which are extremely important for the efficiency of joints.
Collagen is so important to our joints because it is found in articular cartilages and is their most important protein component. It is responsible for the strength and resistance of cartilage, thanks to which they are flexible and well cushioned. Taking undenatured collagen makes the cartilage responsible for bone stretching and strength recreate in the body.
The action of collagen on the joints has been proven by scientists. They noticed that this ingredient inhibits the attack of the joints by the human immune system. Currently, there are many dietary supplements on the market enriched with this ingredient.
People who suffer from joint ailments should remember about a few basic rules so as not to burden them additionally. These are primarily regular exercise, avoiding heavy lifting and, when necessary, distributing the weight evenly. It is also very important not to ignore every, even the smallest, infection, such as a runny nose, which can stimulate the immune system and consequently lead to joint diseases. First of all, however, you need to take care of proper supplementation of your diet. Consume foods enriched with glucosamine, chondroitin, and type II collagen.









