Contents
- The effectiveness of chemical methods of dealing with the Colorado potato beetle
- Tactical and technical characteristics of the Colorado potato beetle and the fight against it with folk remedies
- How to deal with the Colorado potato beetle folk remedies
- Conclusion
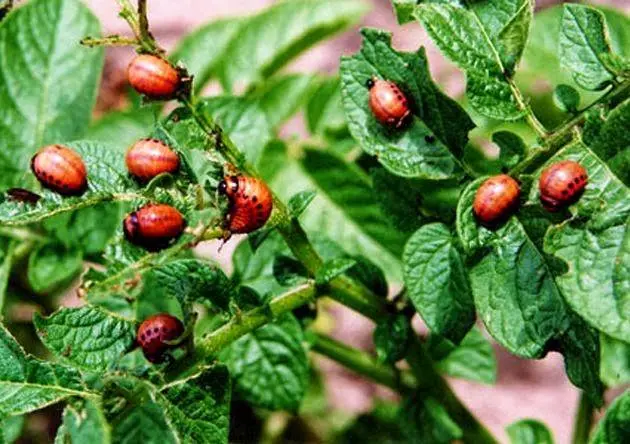
A representative of the American genus of leaf-cutting beetles, containing more than 40 species, the Colorado potato beetle, after penetrating the Eurasian continent, has become a real scourge of agriculture. The nightshade beetle that feeds on plants of the nightshade family harms not only potatoes, but also peppers, eggplants and tomatoes. Moreover, all these plants are his “native” food.
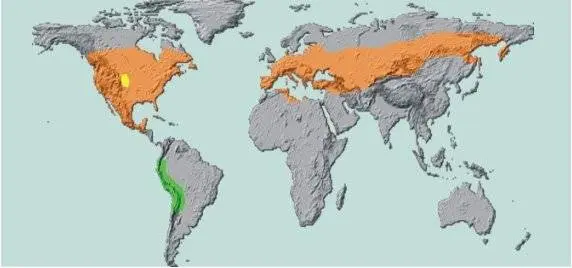
It’s good that, having made the decision to emigrate, the Colorado potato beetle did not take with it relatives who remained to vegetate in their homeland. A Colorado emigrant tried to enter Europe illegally several times, but he was caught and destroyed. Only in 1918, when during the war people had no time for insects, Colorado managed to take a foothold in Bordeaux and gain a foothold there. After that, the Colorado potato beetle began its victorious march across Europe.
The history of the penetration of Colorado into the territory of the USSR is worthy of spy novels. There are reasonable assumptions by contemporaries of this event that a biological sabotage took place. At least, the Colorado invader penetrated in the 50s into Poland and the Baltic States not randomly, but in pockets. In the same way, in foci along the roads, colorado was found in 1980 in the Komi Republic. Be that as it may, but today the Colorado potato beetle has occupied the entire territory of Eurasia, located at the same latitude as the United States.
Breeders are trying to develop all new varieties of nightshade plants resistant to viral and fungal diseases. They succeed. The only thing they fail to do is develop plant varieties that are resistant to pests and mollusks.
The effectiveness of chemical methods of dealing with the Colorado potato beetle
If poisons have already been developed for mollusks, then with the Colorado potato beetle it seems that chemistry does not take it. Actually it is not. The Colorado potato beetle also dies from insecticides, like any other insect. But the Colorado has ways of surviving such an aggressive extermination of its stock. The methods are so effective that the fight against colorado with chemicals is useless.
The fact is that chemicals act on any one stage of development of insects. Usually, in pests, development cycles are confined to certain months, during which it is possible to poison insects in the stage of either adults, or pupae, or adults, but not yet had time to lay eggs, individuals. The Colorado potato beetle does not. Adults, larvae of different ages and eggs can be on the same bush.
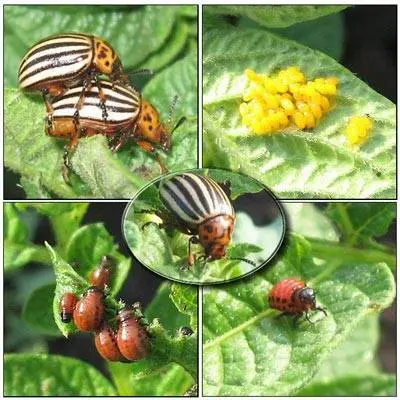

The American pest is perhaps the only one with whom folk remedies for the Colorado potato beetle are most effective.
Although, given the number of these methods and the principle “if there are many medicines for a disease, then it is incurable,” one can guess that folk remedies for dealing with colorado are also not much more effective than chemical ones. But they are at least harmless to humans.
Tactical and technical characteristics of the Colorado potato beetle and the fight against it with folk remedies
Before embarking on the fight against this brightly colored insect, it is necessary to find out the reasons for its vitality.
Why is it difficult to remove the Colorado potato beetle from the site:
primarily due to the fact that Colorado is a guest from America and has practically no natural enemies on the Eurasian continent;
- over the summer, the female Colorado is able to lay up to 1000 eggs;
- the beetle is capable of hibernating for up to three years under adverse conditions;
- the insect hibernates deep in the soil, being inaccessible to insecticides;
- Colorados are able to fly tens of kilometers;
- there is no way to carry out the destruction of the beetle simultaneously on the entire territory of Eurasia.
If the female Colorado mated in the fall, then in the spring, after emerging from hibernation, she lays eggs without additional fertilization. Just one female is enough to infect the garden.
Thanks to his abilities, an illegal Colorado migrant won recognition from people and even monuments.

How to deal with the Colorado potato beetle folk remedies
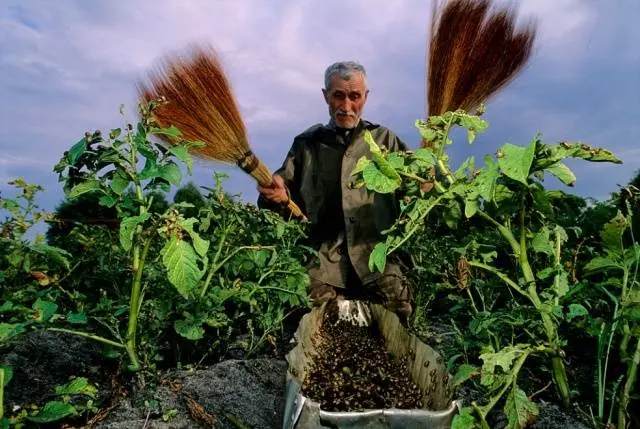
The best method is considered to be the manual assembly of Colorado pests and their larvae from plants. Having collected colorados from plants, they must be burned or drowned.
This leaves the pests a chance to survive and burns the leaves of the plants.
And if it is not possible to come to the dacha every day or the planting area is too large? The number of beetles can be reduced by their natural enemies, which, although few in Eurasia, do exist.
Natural enemies of the Colorado potato beetle
Ground beetles
Beetle larvae are eaten by ground beetles, of which there are quite a few species and they are all predators that prey on pests. One of them is a garden beetle.

Having found such a beetle in the beds, you should not immediately destroy it. It is the ally of man. There are many benefits, but no harm. The exception is the bread ground beetle, which is unlikely to harm peppers or other crops. She eats cereals.
Mantis
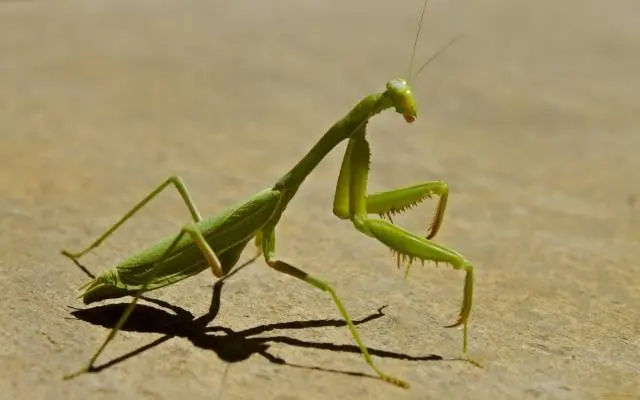

Many are afraid of this insect and try to kill it. No need. The praying mantis preys on adult Colorado potato beetles and other garden pests. Therefore, it is better to welcome the appearance of these predators on cultivated plants.
perillus
If suddenly near the laying of eggs of the Colorado potato beetle you found just such a picture

Do not rush to immediately destroy the insect. It’s not a pest. This is a natural enemy of the Colorado pest, specially imported from America: the predatory bug perillus. The bug larvae cope with the eggs and larvae of the beetle, and an adult may well dine on the colorado itself.
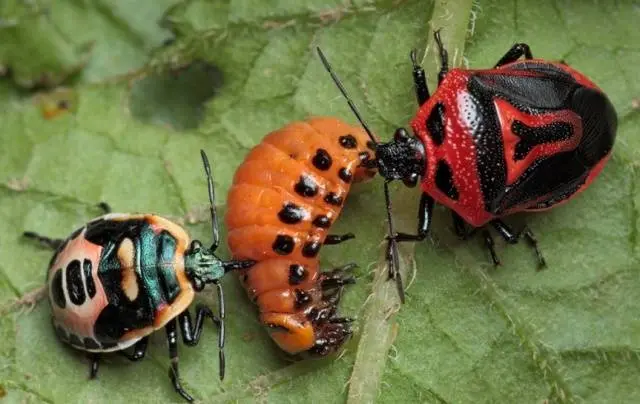

True, perillus can only be found in the Krasnodar Territory, where they tried to acclimatize it. Without much success.

In the photo, however, as a victim, a close relative of the Colorado potato beetle, differing from it only in the color of the elytra. But the perillus doesn’t care who it is.
Gold-eyed

Initially, this predatory insect fed on aphids, so in any case, its benefits in the garden are undeniable. But recently, the lacewing has tasted the taste of the Colorado potato beetle larvae.
Guinea fowl
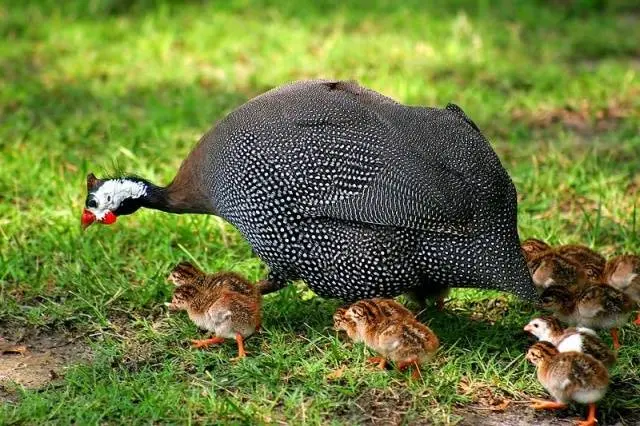

It is believed that guinea fowls can eat the beetle. According to the Nizhny Novgorod gardener, who decided to test this statement in practice, they forgot to tell the guinea fowls about their food preferences. Perhaps they need to be trained to eat Colorado pests, similar to turkeys. Guinea fowls, in general, are very cautious about unusual food and look at it for a long time. If they are familiar with striped snails as food, things can go faster.
[get_colorado]
But there is another nuance here. Even if chickens can effectively clear your garden of the Colorado pest, they will no less effectively clear it of your entire crop of peppers, tomatoes, berries and other things, along with plants. But the beetle will definitely not. Unfortunately, these birds do more harm than good.
Plants that repel beetles
The Colorado aggressor does not like the smell of some European plants very much and you can take advantage of this by planting flowers between pepper bushes such as:
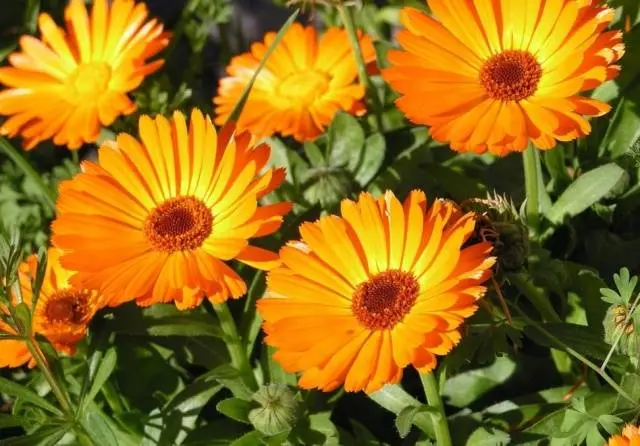
marigold

calendula

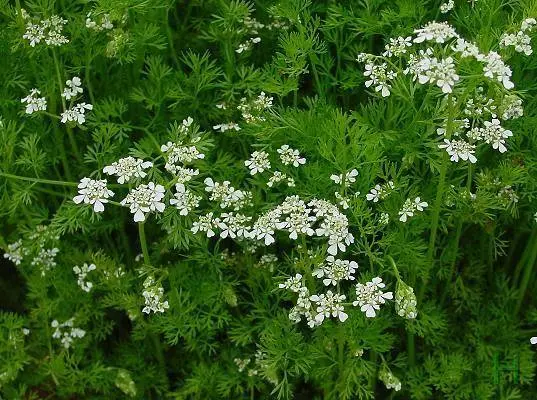
coriander

Not only will they expel the Colorado pest, but they will also provide the owner with spices or medicine such plants as:
nasturtium
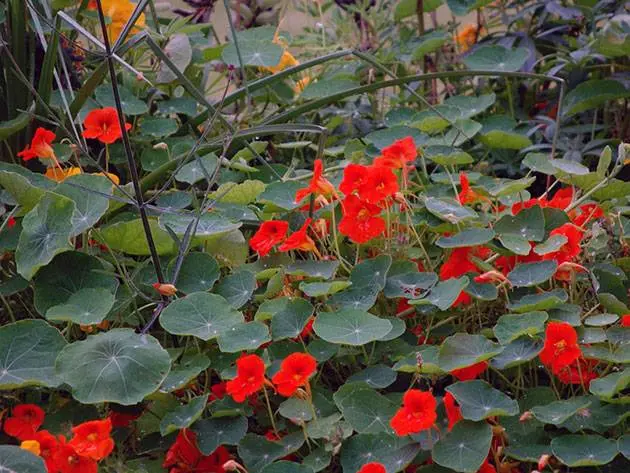

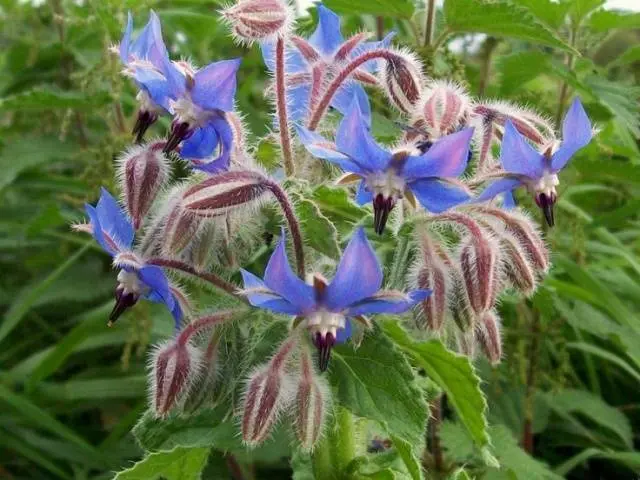
borage (borage)

night violet

The same double benefit can be obtained by planting onions, horseradish or legumes between the rows of nightshade plants.
On this, perhaps, the natural enemies of the Colorado potato beetle end.
It remains to figure out how to get rid of the Colorado potato beetle with folk remedies without attracting predatory insects to the garden (if they are present, it will be impossible to pickle any other pests besides the Colorado potato beetle) or planting scaring plants.
Ways to deal with the Colorado potato beetle with improvised means
Control methods against the Colorado pest are divided into:
- dry dusting;
- spraying;
- mechanical methods.
For dusting plants, various fine powders are used, up to gypsum and cement:
- sifted ash. Birch ash is considered the most effective. They say that a single dusting of a plant is enough at the rate of 10 kg of ash per hundred square meters. Colorados and larvae die after 2 days. But it is necessary to dust the plants every 2 weeks before the flowering of potatoes and once a month after flowering;
- corn flour. The expectation is that, having eaten particles of flour together with the leaves of plants, the Colorado pest will die as a result of swelling of the particles of flour in its stomach. It is unlikely that the method is effective, since the plants are powdered on wet foliage and the flour will swell even before it hits the beetle;
- cement or plaster. Summer residents practicing this method claim that the Colorados are dying. Is the cement blocking the intestines?

On this, the methods of destroying the beetle in a dry way end. The range of folk remedies for spraying is much wider.
Recipes for infusions to combat colorado on plants
There are so many recipes for infusions for spraying plants that the question inevitably arises of how effective they are. In addition, many infusions kill not only pests, but also helpers. Almost all infusion recipes require 10 liters of water, so the default is to use 10 liters of water unless otherwise specified.
For the manufacture of infusions use:
- tar solution. Dilute 100 g of tar with water, apply three times a week;
- sunflower. 500 g of flowers insist 3 days;
- elecampane. 100 g of herbs are poured with boiling water and infused for 2 hours. Sprayed 3 times during the growing season. The first time after the plants reach 15 cm in height;
- Walnut. Pour 300 g of shells and dry leaves or a kilogram of fresh leaves with boiling water. Insist a week. Strain before spraying;
- poplar leaves. Pour half a bucket of leaves with water and boil for a quarter of an hour. Add water to full volume and leave for another 3 days;
- white acacia bark. Leave a kilogram of crushed bark for 3 days, strain before spraying;
- celandine. Boil a bucket of plants filled with water for a quarter of an hour. The extract is diluted with water at the rate of half a liter of extract per 10 liters of water.
- onion peel. 300 g put under oppression, pour water with a temperature of 80 ° C, leave for a day;
- wormwood with wood ash. 300 g of bitter wormwood are mixed with a glass of ash, topped up with hot water, insisted for 3 hours;
- dandelion with horsetail. Boil 400 g of the mixture. Each plant is taken in 200 g. After cooling, it is diluted in a proportion of 0,5 liters of infusion per 10 liters of water;
- hot pepper. 200 g of dried raw materials are boiled for two hours. After cooling, 40 g of laundry soap is added to the broth;
- garlic. 0,2 kg of chopped garlic insist for a day. Before use, add 40 g of laundry soap;
- hemp. Boil 300 g of hemp flowers for 10 minutes in 5 liters of water. While the infusion is cooling, give tea to representatives of the State Drug Control Service and a platoon of OMON. After cooling, add 20 g of soap;
- tomato pod. Not a very reliable way, since the Colorado pest also eats tomato plants. But sits on them last, so they can be used to scare the Colorado from potato plants. Two options: a kilogram of finely chopped plants is infused for 5 hours in warm water, or 3 kg of finely chopped tomato plants are boiled for half an hour in 10 liters of water. Before use, 1 liters of water are added to 5 liter of solution. In both options, add 40 g of soap; bitter yellow. Boil 2 kg of dry plants. Before use, add 30 g of soap;
- tobacco. Half a kilogram of stems, dust or roots of the plant is infused for 2 days. Add 2 more parts of water to the infusion and add 40 g of laundry soap;
- nitrogen fertilizer. 100 g is diluted with water. Spray the plants with the solution;
- soda + yeast. Take 300 g of baking soda and yeast, stir in water. Spray the plants with the resulting suspension 2 times a week.

All infusions and decoctions are used only freshly prepared. Soap does not affect the well-being of the Colorado, but promotes the adhesion of solutions to the foliage of plants.
We fight the beetle in an old-fashioned way. The very recipe for the fight against colorado is spoken out only at the end of the video.
Mechanical ways to get rid of the beetle

Mulching with sawdust
A good way to scare away the Colorado potato beetle is to mulch the soil between plantings of nightshade plants with fresh pine or birch sawdust. In this way, you can also achieve several goals at once:
- when mulching with sawdust, weeds will not grow under the bushes of plants;
- the Colorado pest will fly around beds with nightshade plants sideways, as it does not like the smell of fresh wood;
- as it rots, fertilizer will form.
Onion peel can be used not only for decoctions, but also in dry form. If, in the process of planting nightshade plants, a handful of onion peel is put in the hole, then planting plants will get rid of the Colorado potato beetle. True, the method works in the Nizhny Novgorod region. An experiment conducted in the Donetsk region showed that either “thermonuclear colorados” or little husks were placed under the plants.
Trap in the form of a jar
For traps, a jar of any material is suitable, as long as it is deep enough. The edges of the future trap are smeared with potato juice, several pieces of potato tuber are placed on the bottom. The jar is buried so that the edges are at ground level. Can Density: 1 can per 5 m² of planted plants. Having climbed into the jar, the Colorado pest can no longer get out.

Young potato plants
When the potato plants planted for the harvest sprout and grow, several old potato tubers are buried between the rows. After the appearance of young plants, the Colorado pest will begin to move to tender young leaves, leaving the old coarsened plants alone. Collecting the Colorado potato beetle from a few young plants is easier than from an entire potato plantation.

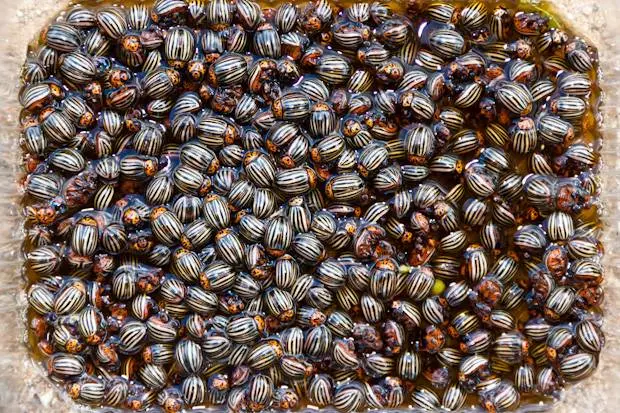
Natural chemical weapons against the Colorado potato beetle
You can poison the Colorado potato beetle by the Colorado pest itself. To do this, you will have to collect a full half-liter jar of Colorado beetles and pour the pests into a 10-liter container of water (it seems that there is something magical in this figure). Cover the water container with a lid. After the Colorado pests drown and sink to the bottom, the solution is ready. Normally, the process of preparing a poisonous solution takes from 4 to 6 days. The solution will be ready only after all the beetles have drowned. It is necessary that the toxins from the bugs dissolve in the water.
Add 2 parts of water to the solution.
Colorado beetle ash
Harvest 200 pests from plants. Make a fire and wait until the firewood burns to red coals. In an iron pan, fry the colorados to charcoal. Thoroughly grind the coals from pests into fine dust. The dust is loosened in a standard amount of water and sprayed with a suspension of potato plants.

Conclusion
Every gardener is trying to invent a new reliable remedy against the Colorado “biological weapons of mass destruction” nightshade plants, but so far no one has found a panacea for the Colorado emigrant.
Given the ability of the Colorado pest to fly and adapt to any chemical attack, gardeners will get rid of the Colorado occupier only when the governments of all countries agree on the simultaneous spraying of insecticides on all areas affected by the Colorado pest. But as a result, all other insects living in these areas will be destroyed. Therefore, gardeners can only slightly restrain and control the growth of the Colorado potato beetle population.









