Contents


Vitamin V9 is the basic medical definition of folate or folic acid. This is one of the 8 water-soluble B vitamins, necessary for the full functioning of the nervous system.
Folate is a natural form of vitamin B9 found in many foods. It is completely soluble in water.
Folic acid – an artificially obtained form of vitamin B9. Synthetic compound in active additives, in products for enrichment. Oddly enough, a synthetic vitamin is absorbed better than its natural counterpart – 85% versus 50%.
Vitamin B9 ensures the functioning of the brain, maintains the mental and emotional health of a person. It is necessary for the synthesis of DNA, RNA, the formation of genes. Folate appearance and growth of new cells. This property is indispensable during pregnancy, in childhood and adolescence. The combined action of folic acid and vitamin B12 is the creation of red blood cells, the normal absorption of iron.
Chemical formula — vitamin V9 — C19H19N7O6.
Products-record holders for the content of folic acid
The richest source of folic acid is liver (especially goose and duck), followed by various beans (chickpeas, lentils, various types of beans).
 Goose and duck: 738 mcg Turkey: 677 mcg Chicken: 578 mcg Beef 290 mcg
Goose and duck: 738 mcg Turkey: 677 mcg Chicken: 578 mcg Beef 290 mcg 727 mcg
727 mcg Dry: 557 mcg
Dry: 557 mcg Dry: 479 mcg
Dry: 479 mcg Dry: 444 mcg
Dry: 444 mcg Fresh: 399 mcg
Fresh: 399 mcg Dry: 394 mcg
Dry: 394 mcg Dry: 375 mcg
Dry: 375 mcg Dry: 364 mcg
Dry: 364 mcg Dry: 274 mcg
Dry: 274 mcg Fried: 237 mcg
Fried: 237 mcg 200 mcg
200 mcg 194 mcg
194 mcg 152 mcg
152 mcg Boiled: 149 mcg
Boiled: 149 mcg+ 15 more foods rich in vitamin B9 (mcg) | |||||
Dill | 150 | Broccoli | 108 | Bread white | 85 |
Bread crackers | 142 | Walnut | 98 | Avocado | 81 |
Rye bread | 110 | Roasted peanuts | 97 | Wheat bran | 79 |
Beetroot | 109 | Roasted hazelnuts | 88 | Cashew fried | 69 |
Buns (butter) | 108 | linseed | 87 | Cauliflower | 64 |
View the entire table of herbal products 300+ ➤
View the entire table of animal products 150+ ➤
How much folic acid do children, men and women need per day?

Given the better absorption of folic acid compared to natural folate, a dietary folate equivalent (PFE) has been adopted. It is taken as the basis for calculating the daily requirement of vitamin B9. The fact is that folic acid, which is produced
The calculation of the norm is carried out according to the following scheme:
1 microgram of dietary folate is equal to 1 microgram of PFU.
1 microgram of folic acid from fortified foods is equal to 1,7 micrograms of PFU.
1 microgram of folic acid in vitamin supplement form taken on an empty stomach is equal to 2 micrograms of PFU.
A simple example: if a person took 80 mcg of natural folate, then he received 80 mcg of PFU. When using an enriched product containing 80 micrograms of folic acid, the body receives 80 * 1,7 = 136 micrograms of PFE. A 200 mcg folic acid tablet will provide us with 400 mcg food equivalent.
Categories of people | Daily requirement, mcg PFE (Dietary Folate Equivalent) |
0-6 months | 50 |
7-12 months | 60 |
1-3 years | 100 |
3-11 years | 200 |
11-14 years | 300 |
From 15 years and older | 400 |
Pregnancy | 600 |
Lactation | 500 |
Norms of physiological requirements for vitamins in the Russian Federation (RF, MR 2.3.1.2432-08)
For comparison, consider the table of B9 norms in different countries:
Countries | Men (mcg) | Women (mcg) |
European Union (including Greece), Belgium, Italy, Spain, UK | 200 | 200 |
Holland, Ireland, Scandinavian countries | 300 | 300 |
France | 330 | 300 |
Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Portugal, USA | 400 | 400 |
* TRAIN, OON | 400 | 400 |
SCF/CS/NUT/GEN/18 Final 6 March 2003 «Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on the revision of reference values for nutrition labeling»
Factors that increase the need for vitamin B9
In a healthy body, vitamin B9 deficiency is practically not formed. This condition affects certain categories of people:
Pregnant women – the intake of the optimal amount of vitamin B9 activates the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Women of childbearing age – girls who want to conceive a child need a large amount of folic acid in order to prevent the development of defects in the neural tube of the embryo in the first trimester of pregnancy.
alcoholics – in their body, metabolism is disturbed, including folate. Ethanol accelerates the breakdown of vitamin compounds. Malnutrition of people suffering from alcoholism affects the insufficient supply of vitamin B9 with food.
Some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. People suffering from diseases associated with impaired intestinal absorption – inflammatory bowel syndrome, celiac disease, gastritis, tropical fever.
Individuals with identified MTHFR genetic polymorphism. In the case of C677T, insufficient enzymatic activity is observed. An acute shortage of MTHFR interferes with the synthesis of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. In this regard, such people are at high risk of folic acid deficiency. [1].
Why do we need folic acid?
Vitamin B9 is involved in the most important metabolic processes. Its insufficient intake in the body provokes the appearance of health-threatening conditions:
Megaloblastic anemia.
Cardiovascular pathologies.
Some types of cancer.
If a woman suffers a lack of folic acid during the period of bearing a child, this is fraught with the formation of birth defects in the fetus.
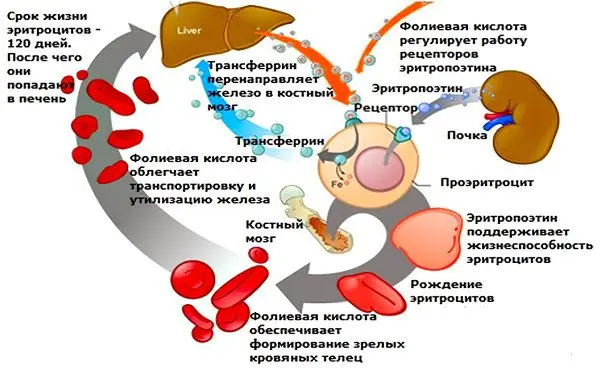
Without vitamin B9, DNA copying is impossible. Violation of DNA replication can lead to the development of a malignant neoplasm. The bone marrow is the first to suffer from folic acid deficiency. The precursors of erythrocytes, which are formed in it, increase without vitamin B9. Soon, megaloblasts form from hypertrophied cells, and megaloblastic anemia develops.
Application in medicine
Reduces the risk of stroke. A number of studies have found that the combined intake of folic acid and other B vitamins contributes to the prevention of stroke. An analysis of the results of 19 medical observations, in which more than 47 thousand people participated, showed that vitamin B9 reduces the risk of stroke by 12% [2]. Folic acid does not have a greater effect on the cardiovascular system.
During the survey, the subjects were offered 2500 micrograms of folic acid in combination with 50 mg of vitamin B6 and 1 mg of vitamin B12. The experiment lasted 5 years. In the group receiving vitamins, compared with the placebo group, there was a decrease in homocysteine levels. Vitamin supplements reduced the risk of cerebral hemorrhage by 25%, but had no effect on the development of heart attack and other cardiovascular pathologies [3].
Chinese doctors tracked the condition of 20 adults with hypertension who lived in regions with low folate content in foods. The subjects were offered 702 micrograms of folic acid and 800 mg of enalapril (a drug for lowering blood pressure). The risk of stroke decreased by 10%. The treatment effect lasted up to 21 years [4].
Cardiovascular diseases. An analysis of the results of 80 studies showed that while maintaining a moderate level of homocysteine in the blood, the risk of cardiovascular disease remains extremely high. The effect of homocysteine on bodily functions continues to this day.
There is an opinion that it negatively affects:
blood clotting;
thickening of the vascular wall;
arterial vasodilation.
The introduction of foods containing folate into the diet reduced the likelihood of coronary disease, other heart and vascular diseases, including stroke, myocardial infarction.
In Finland, 10 men were observed over a period of 1980 years. The use of an increased amount of natural folate reduces the likelihood of sudden heart disease by 55%. Folic acid has the greatest effect on the level of homocysteine, provided that there is a sufficient level of vitamin B12, B6.
Prophylaxis of cancer. Natural folate, which is ingested in food, reduces the likelihood of certain types of cancer. Synthetic folic acid can have both positive and negative effects. It all depends on the timing and dosage. If a person uses folic acid supplements before the onset of the disease, the risk of developing a tumor is reduced. However, if the drug is taken in high dosages with established colorectal cancer, then the pathology can progress. When taking an excessive amount of folic acid (more than 1000 mcg) should be administered with caution.
A study conducted by US scientists, involving more than 525 thousand subjects, was aimed at studying the antitumor properties of vitamin B9. Participants aged 50 to 71 received 900 micrograms of folic acid daily. They have a 30% lower risk of colorectal tumors than those who received 200 micrograms of the drug [5].
In Norway, food is not fortified with vitamin B9. For research purposes, 3411 subjects were offered folic acid at 800 micrograms per day in combination with 400 micrograms of vitamin B12. After 39 months, those with heart disease had a 21% increase in cancer incidence, as well as a 38% increase in cancer death rates. Data are presented in comparison with not taking folic acid supplements. [6].
All the information we have on the effects of folic acid in humans suggests that a rationed intake of supplements can reduce the chances of some malignant tumors. People with a family history of colorectal adenoma and other cancer feeds should use vitamins with caution.

Diabetes. Folic acid preparations have a positive effect on cardiovascular activity in patients with diabetes. They help control blood glucose levels and reduce insulin resistance. Regular use of vitamin B9 reduces the risk of diabetic complications, neuropathy [8], [9], [10].
Reduces inflammatory processes. Folic acid alleviates inflammatory symptoms in polycystic ovary syndrome in children with epilepsy. Vitamin B9 can lower inflammation markers, C-reactive protein [11], [12].
Helps in the treatment of depression. With an insufficient level of vitamin B9, the likelihood of developing depressive disorders increases. People taking antidepressants are prescribed folic acid for greater effectiveness. Preparations containing methylfolate enhance the effect of antidepressants.
Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. The most commonly reported type of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease. Medical observations have confirmed that the likelihood of developing dementia is reduced with sufficient consumption of vegetables and fruits rich in folate.
Vitamin B9 affects the functions of the body not only after birth or during pregnancy. Participation in the production of nucleic acids, methylation reactions are beneficial for the brain throughout life. In women suffering from Alzheimer’s disease, high levels of homocysteine and insignificant parameters of folic acid in the blood are always fixed. To prevent the development of dementia, it is important to ensure not a one-time intake of folate in the blood, but its regular intake into the body.
In one of the randomized trials, 168 elderly patients experiencing mild cognitive impairment were divided into two groups. One was offered 800 micrograms of folic acid each day along with 500 micrograms of vitamin B12 and 20 mg of vitamin B6. The second group received a placebo. All participants showed signs of atrophy in areas of the brain affected by the disease. However, in the first group, which received B vitamins, less destruction of gray matter was recorded. Compared with the placebo group, the rates were 0,5% versus 3,7%.
A pronounced positive result of vitamin exposure was observed in patients with higher levels of homocysteine. The data indicated that a decrease in circulating homocysteine lies in the prevention of dementia and cognitive damage. [13].
Benefits for women over 50

Adults over 50 are mostly deficient in vitamins B9 and B12. With age, this deficiency is felt more acutely and is observed in an increasing number of people. If the age of 50-60 years accounts for 14% of such cases, then among people over 80 years old it is already 23%. Insufficient levels of folic acid are typical for smokers, obese patients.
One of the latest studies, completed in 2019, proved that the administration of 400 micrograms of folic acid improves brain function, increases verbal IQ. The results of 180 participants showed that vitamin B9 inhibits the synthesis of proteins that affect the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease [14].
A study of 121 patients with newly diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease showed that taking 1250 micrograms of vitamin B9 together with donepezil for 6 months improved cognitive mechanisms, reduced markers of inflammation. The results were analyzed in comparison with the donepezil-only group. [15].
Benefits for men
The positive effect of folate on normal spermatogenesis has been proven by several authoritative studies. For experimental purposes, a group of men were offered folic acid and zinc preparations for 26 weeks. It turned out that in fertile and subfertile men, this caused an increase in healthy sperm by 74%.
A study of the sperm of men who received significant amounts of folic acid showed a decrease in the abnormal number of chromosomes from 18 to 30%. Scientists have reported that taking vitamin B9 at a dosage of 700 to 1100 mcg per day helps to reduce altered chromosomes in sperm.
In sports. Athletes involved in weightlifting or bodybuilding need more vitamin B9 than other people. This need is associated with a more active synthesis of the necessary proteins.
Used in cosmetics
Vitamin B9 is necessary for the skin to maintain youth. Folic acid contains antioxidants that inhibit oxidative processes, remove free radicals that penetrate from the external environment. Vitamin B9 retains precious moisture in the skin, reduces the feeling of dryness, so it is added to lotions and moisturizers. Topical use of folic acid products helps maintain the attractiveness and overall quality of the skin.
The Importance of Folic Acid in Planning and Early Pregnancy

Neural tube defects. Decades ago, it was proven that taking folic acid before conception helps prevent neural tube pathologies in the embryo. Neural tube anomalies are birth defects of the brain (anencephaly) or spina bifida. The formation of these defects occurs from 21 to 28 days of pregnancy – the neural tube does not close at the upper or lower end.
There are 10000 cases of spina bifida and 5,5 cases of anencephaly per 6,5 births. Since 1998, to combat the development of anomalies, the United States has introduced the indispensable enrichment of food products with folic acid. Development anomaly rates decreased by 28% [16].
Providing the body of a pregnant woman with folate helps to reduce the likelihood of congenital cleft palate. A study in Norway found that prescribing 400 micrograms of folic acid to pregnant women reduced the likelihood of cleft palate pathology by 64%.
Miscarriages. High levels of homocysteine can cause preeclampsia, placental abruption, and spontaneous miscarriage. Maintaining a high concentration of homocysteine can cause the baby to be too low at birth. The effect on homocysteine levels is possible only through folic acid.
congenital heart defects. The optimal intake of folic acid by the expectant mother reduces the likelihood of premature birth, the appearance of a child with congenital malformations, including heart defects.
In Canada, 1990% of all births were monitored between 2011 and 98. Women who took foods fortified with vitamin B9 were 11% less likely to have children with non-chromosomal heart defects [17].
In Atlanta, 3987 children were studied. Congenital anomalies in the development of the heart were 24% less detected in children who received folic acid in the perinatal period [18]. A similar observation made in California showed similar results in 866 infants. [19].
Disorder of nervous development in a child in the future. Disorders of nervous development include difficulties in socialization, limitation of interests, recurrent actions. This concept includes Asperger’s syndrome.
More and more observations are being made of pregnant women at different gestation periods. In Norway, 85 children from 176 to 3,3 years old and their mothers were examined. It was possible to determine that women who took 10,2 micrograms of folic acid per day in early pregnancy were 400% less likely to have a child with autism than those who did not take vitamin preparations [20].
An American population-based study showed that 837 children who were born to mothers who received at least 600 mcg of folic acid per day were 38% less likely to develop a neurodevelopmental disorder. [21].
Israeli scientists in 2018 examined a record number of children – 45300 people. If women received folic acid before conception and early in pregnancy, their children were at low risk of developing neurodevelopmental disorders. [22].
Low birth weight – is included in the list of causes of death of infants in the first year of life. Being underweight can negatively affect health in adulthood. Multiple studies have shown a correlation between folic acid intake and newborn weight.
Medical statistics in Britain say that every day two women are forced to terminate a pregnancy due to defects in the neural tube in the embryo. Based on these data, British doctors recommend the general fortification of food, primarily flour, with folic acid. Observations of US practice led to this decision. According to Professor J. Morris, by 2007 more than 3000 cases of the birth of children with congenital anomalies could have been avoided if a decision had been made in time to enrich foods with vitamin B9 [23].
[Video] Why do you need vitamin B9 during pregnancy? Difference between folic acid and folate.









