Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Folic acid is essential in the transformation of nucleic acids and proteins. It is used for the synthesis of purine and pyrimidine bases and amino acids. His examination is performed, among others, in the diagnosis of macrocytic anemia. The material needed for the test is serum.
Characteristics of folic acid
Folic acid is a vitamin from the B group (vitamin B9, B11, folate), which apart from being necessary for the human body, dissolves easily in water. The name of this vitamin comes from the Latin word leaf (leaf), which perfectly reflects the main sources of this substance. Folic acid is a light yellow substance that is destroyed by high temperature or incorrect pH.
In food, folic acid occurs in the form of folates, which can be found in green leafy parts of plants, e.g. lettuce, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, parsley, spinach and legumes such as avocado and cauliflower. In addition, a high content of folic acid is found in citrus fruits, egg yolks and chicken and beef livers. We very often destroy it ourselves, for example when preparing food (baking, cooking, frying), because folates are sensitive to high temperatures. Then, the losses of folic acid can be as high as 90%. Another way to enrich your diet with folic acid is supplementation. Check out 400 mcg Puritan’s Pride folic acid for a good price. At Medonet Market you can also buy M-Folin folic acid SOLHERBS, which can be taken even by vegans and vegetarians.
See also: What Happens at 34 Weeks of Pregnancy?
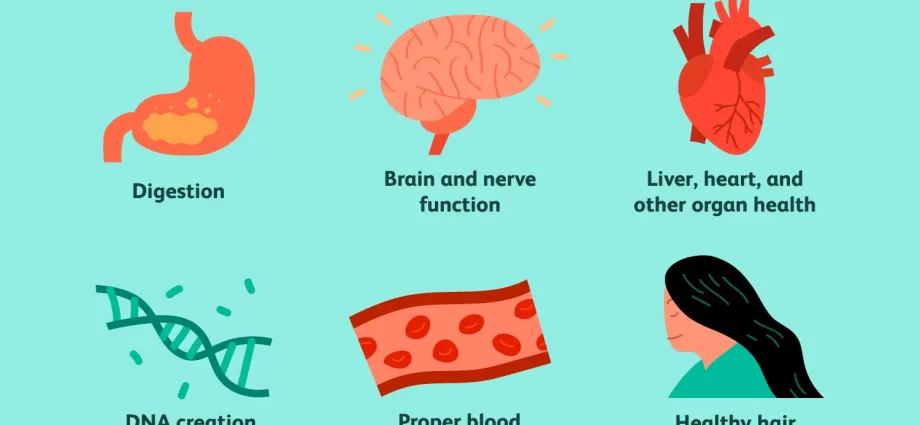
Basic functions of folic acid in the human body
Folic acid primarily:
- supports hematopoiesis, thus preventing anemia;
- is responsible for well-being and improves the thinking process;
- supports the nervous system by preventing the formation of neural tube pathologies (e.g. meningeal hernia or anencephaly). It converts amino acids, homocysteine into methionine, which in the process of transformation leads to the formation of the so-called neurostimulators, i.e. serotonin and norepinephrine necessary for the proper functioning of the nervous system;
- is involved in the production of digestive enzymes, supports the proper functioning of the liver, intestines and stomach;
- protects against atherosclerosis;
- influences the inheritance process supporting proper cell division; it is essential in the process of growth and reproduction;
- helps to cope with stress;
- regulates the development of nerve cells in the fetal period;
- has some effect on the prevention of female cancer, e.g. cancer of the uterus or stomach.
According to some studies, people who take small amounts of folic acid with food are more likely to develop depression. So let’s think about supplementing with folic acid. On Medonet Market you will find, among others preparation Folic acid 400ug + DHA Viridian available in packs of 90 capsules.
Folic acid is an exogenous substance that is ingested with food because the body is unable to produce it on its own (bacteria in the human digestive tract can produce it).
When do we do the folic acid test?
1. Diagnostics of macrocytic anemia.
2. Administration of drugs that are folic acid antagonists (eg antiepileptic drugs).
Material for folic acid testing: serum.
Preparation for the test: on an empty stomach (at least 8 hours).
The course of the folic acid test: one-time blood sampling from a vein in the arm.
Time to wait for the result: 1 Day.
Standard: 4,1-20,4 nmol/l (1,8-9,0 ng/ml).
Low levels of folic acid are seen in prolonged fever, vitamin B12 or C deficiency and severe inflammation. Physiologically, the level of folic acid may decrease in pregnant women and during menstrual bleeding.
Comments: The main sources of folic acid in the diet are vegetable leaves, liver and yeast. Folic acid is also involved in the synthesis of red blood cells and in the repair processes of cells and tissues; it determines the proper functioning of the cells of the nervous system. Folic acid deficiency can lead to anemia, and in pregnancy – cause damage to the fetal neural tube. Therefore, it is advisable to take folic acid by young women who are planning to have children. We recommend, for example, Fertility for women Viridian, which, apart from folic acid, also provides DHA acid and other essential vitamins and minerals.
Before performing the folic acid test, you should take into account that eating certain foods may affect the test result. These include cabbage, yeast, alcohol and lettuce.
Folic acid and pregnancy
Very often, the first thing that brings to mind folic acid is pregnancy. And rightly so, because every woman planning to have a baby or trying for a baby should take folic acid prophylactically, min. 3 months before planned pregnancy (0,4 micrograms / day 1x / day). The appropriate level of this substance is very important in a woman’s body.
You’re pregnant? Do the Pregnancy Testing – Blood Test Package to check if your folic acid levels are right. By the way, you will check many other parameters important for the proper course of pregnancy.
Gynecologists recommend taking folic acid by women planning a baby because it is important in the prevention of fetal neural tube defects (e.g. spina bifida, meningeal hernia, anencephaly). These types of defects may appear in the first weeks of a child’s fetal life, when the woman has no idea that fertilization has taken place. In addition, taking folic acid prevents anemia in pregnant women, especially since the need for folic acid during pregnancy increases up to four times. Preparations containing folic acid can be easily purchased at the pharmacy. In addition, it is worth including appropriate products in the diet.
Products containing large amounts of folic acid:
- egg yolks;
- rice;
- soy;
- wheat germ;
- spinach;
- asparagus;
- peanuts;
- cabbage;
- broccoli;
- sunflower;
- lentils;
- yeast;
- chicory;
- beans;
- citrus fruits (e.g. orange juice);
- veal liver.
When preparing meals with a high content of folic acid, it is important to remember that the vegetables should be raw or cooked for a short time, because long-term heat treatment destroys folic acid.
You can also find folic acid in the form of tablets. It is available on Medonet Market in a version suitable for allergy sufferers.
Neural tube defects – who is at risk?
The greatest risk of fetal neural tube defects is:
- in pregnant women with diabetes,
- in families where such diseases appeared up to the fourth generation back,
- in pregnant women taking anti-epileptic preparations,
- in women who have elevated fetal serum protein.
In Poland, the largest number of newborns with neural tube defects are born in the following regions: Podlasie, Łomża, Siedlce and Białystok. One in 1000 cases of this condition is fatal. The largest group of children with defects of the nervous system are those with a meningeal hernia of the lumbar spine. It should be noted that taking folic acid not only reduces the risk of nerve defects, but also reduces the incidence of congenital heart defects and cleft lips and palate.
Folic acid deficiency
Folic acid should be constantly supplemented. This applies especially to people most at risk of its deficiencies, including:
- people who consume alcohol,
- smokers,
- infants (especially low birth weight premature babies)
- pregnant women,
- women using hormonal contraception,
- women temporarily using the solarium,
- people suffering from chronic digestive ailments,
- elderly people,
- people using antiepileptic preparations,
- girls in adolescence,
- people with iron and vitamin C deficiencies
Vitamin B11 deficiency is manifested primarily by anemia. To restore the proper level of folic acid, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the deficiency, and then supplementation orally or intramuscularly. Supplementation is very important because the deficiency of folic acid in the body leads to unpleasant consequences:
- constant fatigue;
- irritability;
- greater susceptibility of cells to transforming into neoplasms;
- atherosclerosis;
- trouble with memory;
- threat to the life of the fetus;
- faster graying of hair;
- growth and development disorders;
- inflammation of the tongue, gums or lips;
- problems with the rebuilding of cells in the body;
- digestive problems (diarrhea);
- the risk of coronary heart disease;
- high levels of homocysteine in the urine.
Supplementation of folic acid is important not only in pregnant women, but also in people of all ages. It should be remembered that excess folic acid is not toxic and even daily oral doses as high as 5–15 mg are well tolerated. However, excess folate can mask vitamin B12 deficiency and developing pernicious anemia. In addition, large amounts of folic acid can reduce the sensitivity of tumors to chemotherapy. Additionally, too much supply of this substance may result in less effective treatment of epilepsy and inflammatory diseases.