Contents

What is focal pneumonia?
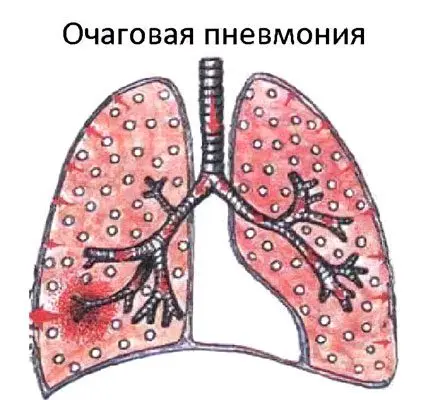
Focal pneumonia is an acute inflammation that is focused on a limited area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXblung tissue within the lobules of the lung. The disease is accompanied by fever, cough with a small amount of sputum, severe intoxication of the body and pain in the chest.
Focal pneumonia is widespread. It accounts for about 2/3 of all cases of pneumonia. First, the bronchi are involved in the pathological process, after which it spreads to one or more lobules of the lung. Therefore, focal pneumonia is also called bronchopneumonia and lobular pneumonia.
ICD-10 code: J18.0 – unspecified bronchopneumonia, J18.1 – unspecified lobar pneumonia.
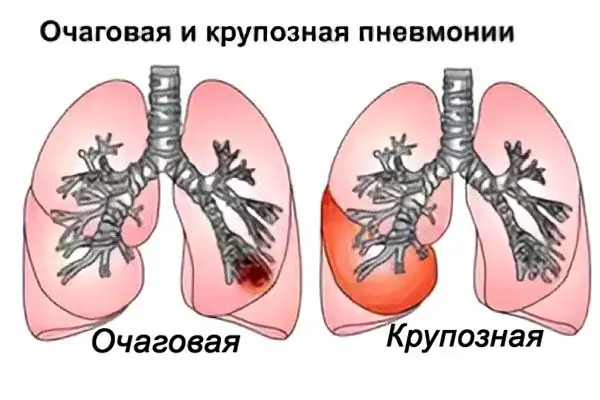
What is the difference between focal pneumonia and croupous pneumonia?
Croupous pneumonia also refers to acute inflammation of the lungs, but with it the clinical picture is more pronounced. With lobar inflammation, not a lung lobule is involved in the pathological process, but its entire lobe and pleura, that is, the lesion is larger.
Causes and risk factors
Focal pneumonia most often acts as a complication of the underlying disease. It can develop against the background of SARS, accompanied by inflammation of the trachea and bronchi. Massive outbreaks of focal pneumonia are observed against the backdrop of an increase in the seasonal incidence of influenza. This is due to the fact that viruses weaken the immune system, reduce the resistance of the respiratory organs to microbial attacks. Moreover, in this case, even conditionally pathogenic flora can become the causative agent of pneumonia.
Other diseases that can act as the root cause of focal pneumonia:
All kinds of infections: measles, whooping cough, typhus, meningitis, etc.
Viral flora: adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial viruses.
microbial flora. In 80% of cases, pneumonia is caused by pneumococci. Other bacteria that cause pneumonia include: E. coli, meningococcus, staphylococcus, streptococcus, etc.
Rare provocateurs of the disease are mycoplasmas and chlamydia.
If the disease is primary, that is, it was not preceded by another infection, the pathogenic flora enters the respiratory system by the bronchogenic route. In other cases, there is a hematogenous or lymphogenous mechanism.
Risk factors for the development of focal pneumonia in adults:
Decreased immunity, both general and local.
Smoking, alcohol abuse.
Subcooling.
Stress.
Diabetes mellitus, HIV.
Entry into the bronchi and lungs of toxins.
Respiratory diseases, for example, pneumosclerosis, COPD.
Vitamin deficiency, malnutrition.
Hospital pneumonia often develops in bedridden patients. In this case, forced immobilization becomes the main factor.
Symptoms
Focal pneumonia is a dangerous disease, as in people with reduced immunity, it gives a blurred clinical picture. Body temperature may remain within the normal range, or rise to subfebrile levels. The cough will be dry, with scanty sputum. Therefore, such people need to be especially vigilant. In case of discomfort that does not go away within 2-3 days, you should consult a doctor.
Classic symptoms of focal pneumonia:
Symptoms | Description |
Increased body temperature | Fever is observed in no more than 50% of patients. If the treatment was started on time, it recedes after 3-5 days. In the rest of the patients, the body temperature remains at subfebrile levels, or within the normal range. |
Cough | It may be dry or wet, with phlegm. Most often it is represented by mucus, but sometimes it contains purulent inclusions. |
Breath | It quickens to 25-30 breaths per minute, becomes hard. The doctor may auscultate loud, moist rales. If in parallel a person develops bronchitis, then the wheezing is dry, scattered. Pleural friction noises will be heard in patients with dry pleurisy. |
Dyspnea | In most cases, it is mild, but with the progression of inflammation with the capture of several lobules, shortness of breath becomes more pronounced. |
Chest pain | This is one of the common symptoms. The pain intensifies on a deep breath, when changing the position of the body, when touching the back. |
Tachycardia | The heart rate can reach 110 beats per minute. |
General symptoms | The patient’s weakness, lethargy and drowsiness increase, appetite disappears. With severe inflammation, a blue nasolabial triangle is observed. |
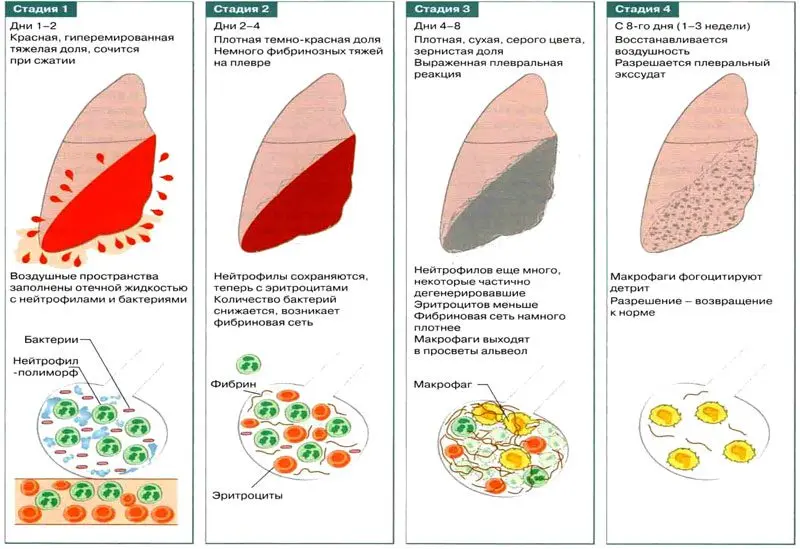
Stages of focal pneumonia
Focal pneumonia goes through 4 stages of development:
Stage tide. The affected tissues are hyperemic, blood microcirculation is disturbed, vascular permeability is increased. The walls of the alveoli in the focus of inflammation swell, the lung tissue becomes more elastic, the vessels that feed the focus of inflammation are sharply filled with blood. During this period, the patient has a dry cough, there are pains on inspiration. The duration of the stage is 1-3 days.
Red hepatization stage. Sweating plasma fills the alveoli, they lose their airiness, become red and dense. During this period, the affected area of u1bu3bthe lung resembles the liver in its structure. The pain in the chest increases, the body temperature rises, the phenomena of intoxication increase. This stage lasts from XNUMX to XNUMX days.
The stage of gray hepatization. Erythrocytes and hemoglobin leaked into the alveoli disintegrate. The affected area of the lung acquires a gray tint. The clinical picture is characterized by a wet cough, pus and a large amount of mucus may appear in the sputum. Body temperature begins to drop, may remain at subfebrile levels, chest pain is present, but it becomes less intense. In general, the patient’s health is normalized. This stage lasts from 2 to 8 days.
Resolution stage. During this period, the normal structure of the affected lung lobules is restored.
Types
Depending on the epidemiology, focal pneumonia can be hospital-acquired, community-acquired, immunodeficiency-induced, and atypical.
Depending on the causative agent of pneumonia, the following types of pneumonia are distinguished:
Bacterial.
Viral.
Fungal.
Mycoplasma.
Mixed.
According to the mechanism of development, focal pneumonia can be:
Primary (not caused by other diseases, develops as an independent disease).
Secondary (provoked by the primary focus of infection in the body).
Postoperative.
Aspiration (develops when a foreign body enters the bronchi).
Infarction-pneumonia (provoked by blockage of small blood vessels by blood clots).
Focal pneumonia can be unilateral or bilateral. Depending on the characteristics of the course of the disease, acute, acute protracted and chronic focal inflammation of the lungs are distinguished. Separately, uncomplicated and complicated focal pneumonia are distinguished.
According to the severity of focal pneumonia can be:
Easy. Intoxication is mild, body temperature does not exceed 38 degrees, shortness of breath appears only against the background of physical exertion.
Medium. Intoxication is expressed moderately, body temperature rises to 39 degrees, breathing is speeded up to 30 per minute.
heavy. Intoxication is intense, body temperature is high, clouding of consciousness can be observed, shortness of breath reaches 40 per minute.
Features of the course of the disease in children

In newborns, focal pneumonia is most often associated with intrauterine or nosocomial infection. In children of preschool and school age, the main culprit of pneumonia is pneumococcus. As for secondary infections, the danger is bronchitis and bronchotracheitis.
Symptoms of focal pneumonia in children most often manifest on the 5-7th day from the development of a cold. Body temperature remains within 38 degrees, severe fever is rare.
Parents may notice signs of intoxication, which manifest themselves in lethargy, drowsiness. The skin becomes pale, appetite decreases. Babies spit up profusely after eating, vomiting is not ruled out.
Cough can be dry and wet, shortness of breath joins. The nasolabial triangle is pale or blue. In children, retraction of the intercostal spaces from the side of the lesion is especially noticeable. Accessory muscles take part in breathing. Focal confluent pneumonia is especially difficult in children. It is complicated by respiratory failure, intense intoxication. Destruction of lung tissue is not ruled out.
If unusual symptoms appear, parents should be vigilant and consult a specialist.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pneumonia begins with the collection of anamnesis and examination of the patient. Full cycle of research:
Percussion of the chest. The doctor determines a dull percussion sound.
Auscultation. At the beginning of the development of the disease from the side of the lesion, breathing is hard (in a limited area of the lungs). As it progresses, sonorous moist small bubbling rales join, inflammatory crepitus is heard less frequently. Due to the foci of the process, the auscultatory picture is mosaic.
Donating blood for a general analysis. Neutrophilic leukocytosis will be detected with a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left, an increase in ESR up to 40 mm/h, an increase in the level of fibrinogen, sialic acids, a positive reaction to C-reactive protein.
General analysis of sputum. It is mucopurulent, the number of leukocytes and cells of the cylindrical epithelium is increased in it.
Bacterial culture of sputum It is aimed at identifying the type of pathogen and determining its sensitivity to antibiotics.
X-ray of the lungs. Focal darkened areas are revealed. Most often they are located in the lower parts of the respiratory system.
Differential diagnostics
Focal pneumonia must be differentiated from tuberculosis, alveolar lung cancer, abscess and pulmonary infarction. To make a correct diagnosis, data from a comprehensive examination, including X-ray and clinical and laboratory, will be required.
In doubtful cases, X-ray data are clarified with the help of CT or MRI of the lungs, bronchoscopy. To rule out septicemia, a blood culture test is performed.
Treatment

Treatment of focal pneumonia is possible on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is required for those patients who develop severe intoxication of the body, there are signs of respiratory failure.
Antibiotics. Most often, it is possible to get by with a single-component circuit. If it is necessary to use 2 antibiotics, the simultaneous use of bactericidal and bacteriostatic drugs, or drugs with the same toxic effect is undesirable.
Traditional antibacterial agents for the treatment of focal pneumonia:
Penicillins.
Cephalosporins.
Fluoroquinolones
The course lasts at least 10-14 days. The drugs are administered intramuscularly, and in severe cases intrapleurally or endobrochially.
Removal of symptoms. To relieve intoxication, detoxification solutions, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Body temperature is reduced with ibuprofen or paracetamol. Suprastin, Tavegil, Loratadin are used as desensitizing agents.
Mucus liquefaction. Mucolytics and bronchodilators are aimed at thinning sputum and removing it from the respiratory system. These can be drugs such as: Theophylline, Bromhexine, Ambroxol, ACC Long, Acetylcysteine.
Inhalations. People with severe shortness of breath need prolonged inhalations with humidified oxygen.
Recommendations. During the entire period of fever, the patient should adhere to bed rest. At least 1,5-2 liters of water should be consumed per day. The menu should be gentle, balanced, with limited salt. Choose foods rich in vitamin A and C. Make a choice in favor of easily digestible foods.
After the acute symptoms of the disease subside, and the body temperature returns to normal, the patient is prescribed physiotherapy procedures, including:
Electrophoresis with drugs.
UHF
DMV therapy.
Massage.
Exercise therapy.
With the right selection of drugs, recovery occurs after 2 weeks.
Interview with Bazarov Dmitry Vladimirovich, candidate of medical sciences, surgeon, oncologist, pulmonologist:









