Contents
In modern society, there is an interesting stereotype: if an animal foams at the mouth, it is rabid. In fact, clinical symptoms usually differ from the mass representation of this disease. There are other reasons as well. If a calf foams at the mouth, it is not rabid, it has serious problems with the digestive system.
A few reasons why a cow is foaming at the mouth
In fact, there is no reason why a calf may foam in the mouth. In some diseases, salivation occurs. But due to abundant salivation, restless behavior of the calf, constant chewing movements, saliva is churned into foam. Moreover, this usually happens when the disease is already running and the treatment is late.
Theoretically, foam in the mouth can occur for the following reasons:
- stomatitis;
- poisoning;
- tympanum;
- inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract;
- blockage of the esophagus.
But all these problems begin much earlier than the foam appears. If you closely monitor the calves and notice changes in their behavior, it is unlikely that it will come to foam.

There are enough plants in the meadows that can cause poisoning or burn the mouth of a calf
Ctomatitis
Inflammatory process on the oral mucosa. Occurs due to local exposure to irritants. It can be primary and secondary. Primary stomatitis are:
- biological;
- thermal;
- chemical;
- mechanical.
The type depends on the type of damaging factor. Secondary stomatitis occurs with diseases of the stomach or pharynx. May be a symptom of an infection.
Mechanical stomatitis occurs due to damage to the oral cavity by foreign hard objects or due to improper abrasion of teeth. The simplest and safest form of the disease. It is enough to file the teeth, exclude roughage and ensure the absence of debris in the pasture to remove the cause of the disease. Wounds in the mouth are treated by washing them with disinfectant solutions.
Chemical and thermal stomatitis often occurs due to improper administration of drugs or feeding too hot food (bran brewed with boiling water in winter). Causes of a chemical can be:
- too concentrated hydrochlorides, acetic acid or gallstones;
- poisonous burning plants;
- calf licking warming ointments from other parts of the body.
Here it is sometimes difficult to eliminate the cause, but this type of stomatitis also does not pose a particular danger.
Secondary, which is a symptom of another disease, is one of the most difficult. They cannot be eliminated until the true cause is eliminated.
In the list of signs of any of the stomatitis there is no foam in the mouth. Even profuse salivation is not the most characteristic symptom of the disease. But calves have foam. This is not a symptom – it is a consequence of pain. Animals tend to lick wounds that cause anxiety. Saliva foams up as the calf constantly “chews” and moves its tongue in an attempt to ease the pain.
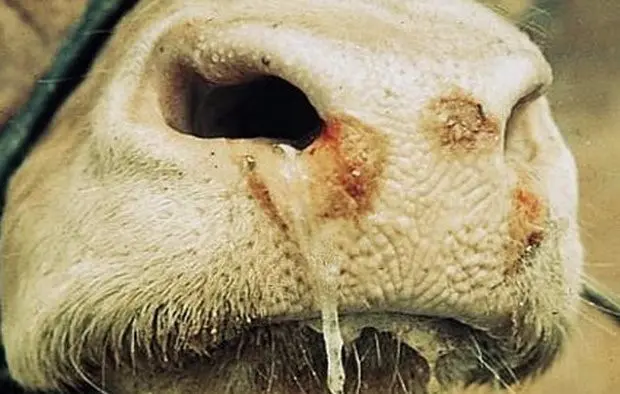
Since one of the signs of foot-and-mouth disease is stomatitis, foam in the mouth is also possible due to a “restless” tongue.
Poisoning
There are two reasons for the appearance of foam in case of poisoning:
- chemical stomatitis;
- foam from the nose, as a symptom of poisoning by certain plants and substances.
With severe intoxication, foam can go not only from the nose, but also from the mouth.
Symptoms of poisoning are different and depend on the action of the poison. Excitation and inhibition of the central nervous system, salivation and dryness of the mucous membranes are possible. The most characteristic symptom is diarrhea. But even diarrhea is not always the case.
Not foam, but drool appears when poisoned with compounds:
- copper;
- barium;
- arsenic;
- lead;
- chlorine;
- mercury;
- nitrophenol;
- calbamic acid;
- alkalis;
- urea.
Foam in case of poisoning with all these substances appears already in the preagonal state, when the calf does not control muscle movements.
Many poisonous plants cause profuse salivation. Foam in the symptoms is not indicated anywhere. But that doesn’t mean it definitely won’t. As with stomatitis, it can appear if the calf is actively working with its jaws and tongue. Salivation and, possibly, foam in the mouth can also appear when poisoning with “honest” feed. If the products exceed the norm of nitrates. This symptom is also characteristic of foods that form:
- mustard oil (rapeseed, field mustard, camelina and others);
- solanine (green or sprouted potatoes);
- hydrocyanic acid (wild clover, vetch, sorghum, flax, mannik and others);
- copper (soy and bean cakes).
Feed is more likely to become poisonous if stored improperly.

The development of diarrhea in a calf in case of poisoning is much more likely than the appearance of foam from the mouth
Salt poisoning
The only type of intoxication in which foam at the mouth is a “legitimate” symptom. The lethal dose of salt for cattle is 3-6g/kg of live weight. For this reason, it is undesirable to give calves salt in their feed. Much better to hang a lick. Animals themselves will lick salt as much as they need.
Leakage is always acute. Intoxication occurs within 30 minutes after consuming excess salt. Symptoms of sodium chloride poisoning:
- loss of appetite;
- dyspnea;
- possible vomiting;
- dilated pupils;
- excitation;
- aimless movement.
With the further development of intoxication, diarrhea develops, and general weakness increases. There are muscle tremors and cyanosis of the mucous membranes. Further, with salt poisoning, convulsions similar to epileptic ones can be observed. At the same time, foam appears in the mouth. But even in this case, this is only a consequence of the “churning” of saliva due to movements of the tongue and jaws uncontrolled by the calf. The animal dies a few hours after the first symptoms of asphyxia appear.
Survival depends on timely assistance:
- gastric lavage several times;
- intravenous infusions of calcium chloride at the maximum dose and glucose with caffeine.
Calcium chloride can be replaced by intramuscular administration of calcium gluconate.
Bloating
So in cows, tympania is usually called. Far from always, the release of gases in the rumen is combined with foaming of the contents of the proventriculus. More often, only gas formation occurs, which saves the lives of a large number of calves. Foamy timpania is more dangerous for animals.
Since there is no belching during tympania, the appearance of foam in the calf’s mouth means that the rumen is overflowing with fermenting contents. The appearance of this mass in the mouth of a cow means a weakening of the sphincter and a very poor condition of the animal.

The owner must have a special “talent” to bring the development of tympania to the appearance of foam in the mouth.
Qatar AIDS
Previously, the word “Qatar” was called almost any disease of the gastrointestinal tract, from gastritis to ulcers and viral enteritis. Today, the term is almost out of use. Instead, more specific types of diseases are usually named. There is only one thing that unites various diseases: an inflammatory process that affects the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Foam in the mouth is not on any list of catarrh symptoms. But often there is diarrhea in various variations: from watery to bloody.
Blockage of the esophagus
Foam is not included in the list of symptoms either. With an incomplete esophageal occlusion, the calf can swallow saliva and water but cannot eat. With full – animals do not eat, they are worried. Saliva cannot be swallowed, and it flows out. Belching stops and tympania develops. Cows make swallowing movements, trying to push through a foreign object.
Foam can form precisely when you try to push out the obstacle with the help of swallowing movements. Even with incomplete obstruction, the calf makes movements with the tongue and jaw to get rid of the obstruction of the esophagus.

The characteristic position of the head of a cow with blockage of the esophagus, due to the active work of the jaws and tongue, soon the animal will also foam
What to do if the calf is foaming at the mouth
Call a veterinarian immediately. You will be very lucky if the appearance of foam is associated with stomatitis. However, this problem can only be a symptom of a more serious disease. The appearance of foam in the mouth during poisoning means severe intoxication, when it is possible to pump out a calf only with the help of intensive care and droppers.
Worst of all, if it turns out to be a fermented mass from the scar. Although belching is normal for cows, it stops with health problems. The appearance of foamy vomiting in the calf’s mouth means that the sphincters have begun to weaken and the animal is most likely in a pre-agonistic state.
However, this may also be due to the fact that the owners prefer to seek free help on the forums. Until the owner gets the answers, analyzes the information, or runs the experiments on the calf, time will be wasted. The veterinarian will come when the disease is already running. So the first thing you need to do is call your veterinarian.
Preventive measures
All diseases in which a calf foams at the mouth are somehow related to the diet. The exception is infectious-viral diseases. But even here, the resistance of animals is higher if they receive good nutrition. Therefore, first of all, prevention is high-quality feed and the absence of poisonous plants on grazing. Next in importance are vaccinations against diseases, the list of symptoms, which include:
- stomatitis;
- gastritis;
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Good living conditions also help to strengthen immunity. Otherwise, the prevention of foam depends on the cause that caused this phenomenon. You may have to check pastures for inedible items, and clear the farm area of mineral poisons.
Conclusion
If a calf foams at the mouth, this is a very alarming sign, showing the last stage of the disease. It makes no sense to ask on forums and social networks “why does my calf have foam”, you need to look for other signs of the disease. Foam is not a symptom. This is a sign of the final stage of the disease.









