What is foot-and-mouth disease?

Foot-and-mouth disease is an acute zoonotic infection that is transmitted from a diseased artiodactyl animal to humans. The infection is accompanied by fever, as well as with the appearance of small blisters on the mucous membrane of the mouth and near the oral surface, and in addition, they form at the nail bed.
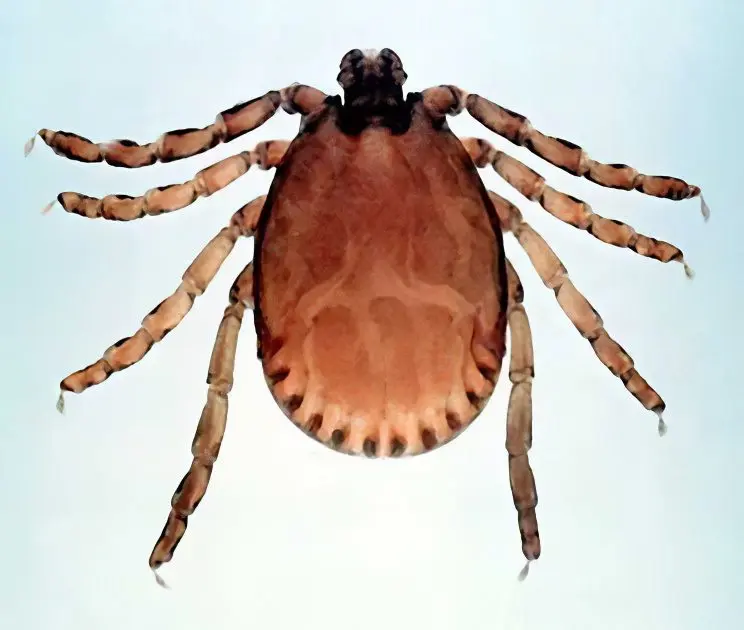
Due to the characteristic clinical picture, foot-and-mouth disease in humans and animals has been known since ancient times. However, the fact that the infection is able to pass from a sick artiodactyl animal to a person was established only at the end of the 18th century. Leffler in 1897 was able to prove that the FMD pathogen is able to penetrate through the pores of a bacterial filter.
FMD is caused by an RNA virus. It is characterized by high virulence, and it also resembles the epithelial structures of the mucous membranes and skin. FMD virus is persistent. It is resistant to various environmental factors, namely freezing and drying, retains its viability in animals on wool for up to about 4 weeks and up to 3,5 weeks on clothes. The death of this virus can be achieved by heating, UV radiation, and exposure to disinfectants. These include alkalis 2%, formalin 1% and ethylene oxide 1%.
As already mentioned, the source and reservoir of foot-and-mouth disease are ungulates, both domestic and wild. Some types of rodents can also be distributors, but it is worth noting that they do not have a significant impact on its distribution. As for birds, they cannot get sick with foot-and-mouth disease, but during migration they can carry it.
Foot-and-mouth disease can be attributed to an occupational disease. It mainly spreads in rural areas, and among those people who work in agricultural livestock enterprises, meat processing plants that slaughter livestock and process animal raw materials.
Foot and mouth disease can also occur in children. Children get the virus after eating contaminated dairy products.
Causes of FMD
The cause of foot-and-mouth disease in humans is poor personal hygiene. The main source of the disease, as already mentioned, are animals (cattle, pigs, sheep, goats, very rarely – dogs, cats, horses, poultry). Rodents, flies and ticks play a secondary role in the distribution. The mechanism of infection is fecal-oral (through food), contact and household contact, i.e. either through direct contact with aphthae of sick animals, or through contact with infected objects.
In addition, products such as milk and meat obtained from animals that suffer from foot and mouth disease can become a source of the disease. The infection cannot be transmitted from person to person.
Despite the above factors of infection, children can also be infected with FMD. In the case of children, infection occurs through the digestive tract. Foot and mouth disease can enter the body of a child with infected milk and dairy products.
FMD symptoms
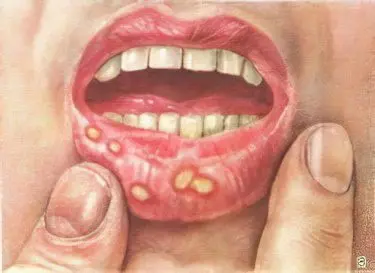
The incubation period of the disease is on average 3 to 4 days, but the disease can increase from 10 to 14 days or, conversely, be reduced to two days. The disease process begins with a strong chill, while the temperature rises to 40 ° C. To these symptoms are added a headache, decreased appetite, muscle pains are observed and especially severe in the lumbar region. On the first day of the course of the disease, the infected person feels a burning sensation and dryness in the mouth, as well as strong salivation. After some time, small bubbles begin to pour out on the mucous membrane of the mouth, from about 1 to 3 mm. Their largest accumulation is located at the tip and along the edges of the tongue, as well as on the gums, mucous membrane of the cheeks and lips. The liquid that fills the formed bubbles is transparent, it gradually becomes cloudy, the diameter of the bubbles increases, while forming erosion.
If foot and mouth disease has struck children, then they complain of difficulty swallowing, as well as pain when talking and chewing. Because of this, they become irritable and subsequently refuse to eat at all. Often salivation can be so strong that saliva can flow out in a stream. Eruptions of bubbles can also be on the mucous membranes of the nose, conjunctiva, stomach. In addition to the mucous membranes, rashes can also be on the skin of the face, forearms, hands, feet and legs, especially often they occur between the fingers. Provided that the disease proceeds without complications, the fever lasts from 3 to 6 days. After this, the recovery period begins, which is accompanied by the rapid healing of all ulcers. The total duration of the course of the disease is about 2 weeks.
There are cases when the duration of the disease is from 1 to 1,5 years, with periodic rashes.
If the virus penetrates through the gastrointestinal tract, then stomatitis may not appear. In this case, the whole disease proceeds according to the type of acute gastroenteritis. There are symptoms of intoxication, fever, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and loose stools. Usually this form of the course of the disease is observed in children who become infected through milk and dairy products.
In most cases, the disease ends with a complete recovery, while it does not leave any traces behind. But a completely different prognosis has a severely flowing foot and mouth disease, which affects young children. Some cases of the disease end in death.
Like many diseases, foot and mouth disease can cause complications. But this happens quite rarely. Complications can be expressed in the form of pneumonia, myocarditis, purulent skin diseases.
FMD treatment

Patients with foot and mouth disease need hospitalization. There are no specialized medicines for the treatment of this disease. Treatment is carried out in a hospital. The main treatment measures are aimed at caring for the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose, as well as local treatment and general relief of symptoms.
For a period of severe damage to the oral mucosa, the patient should eat semi-liquid food of moderate temperature, which is easily absorbed by the body. It should not include irritating components. These include horseradish, mustard, pepper, etc. If extensive lesions are observed, the nutrition process occurs parenterally or through a tube. For local treatment of foot and mouth disease, ointments are used, such as oxolinic, florenal and interferon ointments, as well as physiotherapeutic methods are used: laser and UV irradiation.
Antipyretics, analgesics, cardiovascular and desensitizing agents are usually prescribed according to indications. For general strengthening purposes, vitamins and adaptogens are often prescribed.
[Video] Infectious disease doctor Nailya Abdrakhmanova – Yashtur:









