Contents
The accumulation of fluid in the joints is a problem that requires the immediate intervention of a specialist. The absence of acute pain and other pronounced symptoms is not a reason to take the problem lightly. The importance of timely diagnosis and surgical treatment lies in the fact that the accumulation of fluid in the joints can be caused by many diseases, both direct, such as arthritis, and those that seem to have nothing to do with the joints, for example, viral diseases.
Moreover, most of the pathologies affecting the joints, with untimely treatment, can leave an indelible mark on the health and normal life of a person: cause chronic pain, discomfort in movements.
To prevent this, you need to monitor the health of the joints, not experience the body with excessive physical exertion, try to avoid injuries, do therapeutic exercises and preventive procedures. And in case of a problem, immediately seek help from specialists.
Symptoms of fluid accumulation in joints
Depending on the cause of the accumulation of fluid and in which joint it has accumulated, the symptoms may vary in each case.
Common symptoms include the following:
pain of a different nature: sharp, aching, dull;
swelling of the joint area: it can be very pronounced or almost imperceptible;
constrained movements: if a large amount of fluid has accumulated, movements become difficult, and sometimes completely impossible;
an increase in body temperature: it can be either local, in the area of the damaged joint, or general;
subcutaneous compaction in the joint area;
redness of the skin;
headaches or even chills can sometimes be accompanied if the accumulation of fluid is caused by an infection.
Causes of fluid accumulation in the joints
There are several different infectious diseases that can cause the accumulation of fluid in the joints. Do not underestimate the simple bruise, which can lead to serious complications.
The general list of causes of fluid accumulation in the joints is as follows:
Bursitis of the joint – a disease that can be caused by injury or infection. Bursitis provokes the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the synovial (periarticular) bag, which is accompanied by the accumulation of fluid. The disease is divided into several types depending on which joint is affected.
Thus there is:
elbow bursitis;
hip bursitis;
knee;
shoulder, etc.
Bursitis is a disease that can be classified as “professional”. They often suffer from people whose activities are associated with constant stress on individual joints. This primarily applies to athletes, miners, jewelers, watchmakers, some musicians, etc.
Arthritis – the general name of a group of diseases of the joints. A common feature of arthritic diseases is the inflammatory form.
Arthritis occurs for the following reasons:
allergic reaction;
infection;
mental trauma;
consequences of mechanical damage to the joint;
immune disorder;
constant load on one muscle group.
At risk are people who do not eat well, lead a sedentary lifestyle, are overweight and live in areas with poor ecology.
Arthrosis – a disease of the joints, which can occur for two reasons: natural aging of the body and wear of the joints, or an injury. Arthrosis occurs in two stages. At the first, painful sensations occur and the amount of fluid near the joint is significantly reduced. On the second, on the contrary, the fluid begins to accumulate and sometimes excessively, forming a swelling around the damaged joint.
Synovitis – an inflammatory disease that affects the synovial membrane of the joint and provokes the appearance of painful symptoms and fluid accumulation.
Synovitis may occur for the following reasons:
Aseptic inflammation occurs in most cases due to injury, hypothermia or due to an infectious disease. The fluid that accumulates in the joint, due to aseptic inflammation, does not contain any purulent or viral microorganisms.
Immune inflammation with the release of synovial fluid occurs mainly as a consequence of previous diseases or severe allergic reactions.
Purulent inflammation occurs after the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the joint. Depending on the type of harmful bacteria, chlamydial, tuberculous, dysentery, gonorrheal and staphylococcal purulent inflammation are distinguished.
Fracture of the bones of the joint. This severe damage also results in joint fluid and swelling.
Hemarthrosis – internal hemorrhage in the joint. In this case, it is not effusion that accumulates in the joint, but blood. This pathology may occur due to mechanical damage.
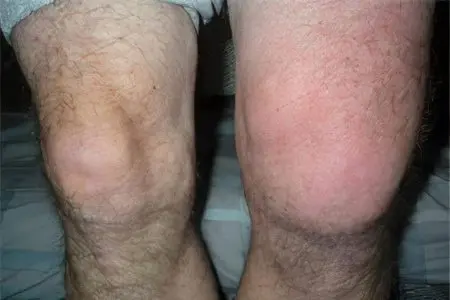
Causes of fluid in the knee joint
Fluid in the knee joint can appear for many reasons. Injuries are in the first place, since the knee is most often subjected to serious stress, and is also one of the most mobile joints.
Fluid in the knee joint can accumulate for the following reasons:
meniscus injury;
fracture;
arthrosis;
arthritis;
hemarthrosis;
synovitis;
bursitis.
As mentioned above, there are a lot of reasons for the development of each of these diseases. In the case of the knee, it most often comes with an injury or unbearable loads.
Having damaged the knee joint once, in most cases the patient will acquire one of the chronic diseases for life, since the joint can never be completely restored. But this does not mean that the patient will constantly experience discomfort, since in the chronic form of the disease they usually do not have painful and pronounced symptoms.
To prevent exacerbations of diseases, you need to follow the doctor’s recommendations and be attentive to the health of the joints in the future.
The most common disease of the knee joint, which is characterized by the accumulation of fluid, is damage to the meniscus. This problem is not only found in athletes, as many believe. Serious stress is only one of the reasons for the development of the disease. Much more often, a meniscus occurs due to injury, and no one is immune from this.
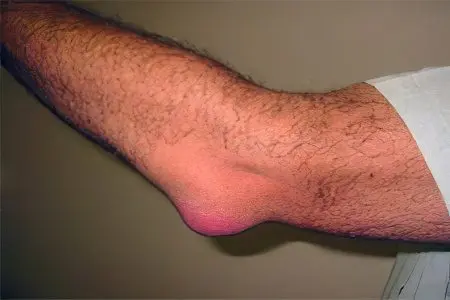
Causes of fluid in the elbow joint
Among the most common diseases that lead to the accumulation of fluid in the elbow joint, there are epicondylitis and bursitis. If bursitis is a disease that occurs due to the accumulation of fluid in the joint bag, then epicondylitis is caused by damage to the muscle tissue in those places where it connects to the epicondyles.
These pathologies can develop in the following cases:
prolonged mechanical pressure on the joint area;
injuries, sprains (most often occur during sports training, hard physical work);
excessive unbearable load on the joint, which lasts a long time or is repeatedly repeated;
an occupational disease that occurs due to the chronic position of the joint, for example, in musicians, drivers.
For successful treatment, a diagnosis is first made. With its help, the specialist determines the pathology, the cause of development, as well as the nature of the disease.
Diagnostics consists of the following activities:
inspection;
Ultrasound;
X-ray
general analyses;
if necessary, a puncture of the joint (if purulent or bloody contents of the fluid are detected during the diagnosis).
After the diagnosis, an individual treatment is prescribed, the methods of which are similar to the therapy of damaged ankle, knee and other joints.
Causes of Fluid in the Ankle
Swelling of the ankle joint can be caused by a lot more pathologies than in the case of accumulation of fluid in the elbow or knee. The fact is that damage to the ankle joint and, as a consequence, its swelling can occur due to various diseases of the veins. In addition, the aforementioned pathologies, a fracture, and internal hemorrhage can also become the cause of fluid accumulation.
Among the common diseases of the veins that lead to the accumulation of fluid in the ankle joint, the following are distinguished:
thrombophlebitis of acute and chronic nature;
phlebothrombosis;
phlebeurysm.
The force of gravity has led to the fact that the accumulation of fluid in the ankle joint is most noticeable in the transition area of the ankle to the foot.
Determining the presence of excess fluid in the ankle joint is very simple. To do this, just press your thumb on the swelling. If after you remove your finger, the dent remains for a while, then you should immediately consult a doctor.
If the cause of edema is vein diseases and fluid accumulation occurs regularly, then when a relapse occurs, it is recommended to lie on your back and put something under your feet so that your feet are higher than your head. This will help relieve swelling for a while. Then you should visit your doctor.
Therapies
Regardless of the cause of the accumulation of fluid in the joints, it is necessary to organize a comprehensive treatment to maximize the elimination of the disease and relieve painful symptoms.
Modern medicine is able to provide 2 treatment options.
Surgical intervention.
conservative methods of treatment.
Depending on the degree of neglect of the disease, an appropriate method of treatment is prescribed. However, in any case, it will be complex, since even after surgery, a long time is needed for rehabilitation with physiotherapy exercises, manual therapy, and vitamin therapy.
Operative therapy
Surgical treatment consists in the following procedure. The doctor inserts a special needle into the cavity of the affected joint, after which the liquid is pumped out with a syringe. In most cases, the procedure is performed without anesthesia. After the fluid is completely pumped out, the doctor injects an antibiotic into the affected area. Pharmacopuncture is mandatory, even if the nature of the inflammation is not infectious.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment involves the following activities:
Anti-inflammatory therapy: drug treatment (taking antibiotics), local treatment (pharmacopuncture, application of anti-inflammatory ointments, gels and other means).
Immunostimulating therapy: taking immunostimulating and restorative drugs, vitamins, calcium.
Physiotherapy and reflexology.
Manual therapy, especially acupressure and acupuncture.
Physiotherapy.
For some diseases, for example, with bursitis or a fracture, the first aid provided by doctors is immobilization, that is, immobilization of the damaged joint. Simply put, the traumatologist applies a cast.
In the case of open lesions, the affected area is treated with an antiseptic, and the patient takes an antibiotic to prevent the development of an infectious and purulent disease.
If we are talking about a chronic disease with regular relapses, then complex treatment should become an integral part of the patient’s life. In order to avoid exacerbations of the chronic form and prevent the accumulation of fluid in the joints again, the patient is prescribed a special diet, a set of exercise therapy exercises. The patient must regularly take health courses in medical and preventive sanatoriums.
It is important to understand that the accumulation of fluid in the joints is a problem that can be a symptom of very serious diseases. Therefore, self-treatment and folk methods in this case are not appropriate. Traditional medicine can only be used in combination with conservative methods of therapy and after consultation with the attending physician.









