Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Fluconazole is an ingredient in many drugs that are used to treat fungal, yeast and cryptococcal infections. The substance inhibits the growth of the fungus and, as a result, causes its death. This drug is available only with a prescription due to its numerous side effects. It is worth knowing the side effects of this substance.
Fluconazole is an active substance that can be found in many drugs used in the treatment of fungal infections, severe candidiasis, tinea versicolor, as well as in the prevention of these infections in people at high risk of recurrence. In Poland, drugs containing fluconazole are available only on prescription due to the long list of side effects.
Fluconazole – what is it?
Fluconazole is a substance with antifungal activity. It can be found in many drugs such as Flucofast, Mucocyst or Fluconazole Actavis. Fluconazole is a triazole derivative.
Fluconazole – action
Drugs containing fluconazole are very effective against various species of fungi, yeasts and cryptococci. The mechanism of action of fluconazole is based on the inhibition of enzymes that are responsible for the production of components necessary for the construction of the cell membrane of pathogenic fungi. As a result, the permeability of this membrane increases, the protective functions disappear, the fungus stops growing and dies.
Fluconazole can only be effective if its concentration allows it to inhibit growth and kill the fungus. At the same time, it must be safe for human cells.
Fluconazole – indications
Fluconazole is recommended for the treatment of:
- vaginal candidiasis of acute or recurrent nature,
- candidiasis of the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, esophagus and respiratory system,
- multifocal candidiasis,
- candidiasis of the peritoneum, respiratory tract, urinary tract, endocardium, meninges,
- genetically determined mucocutaneous candidiasis.
Fluconazole can also be successfully used in the treatment of more common infections, such as: athlete’s foot, smooth skin, groin, nails, tinea versicolor and cryptococcal meningitis or other organs.
Fluconazole – contraindications
Medicines with fluconazole should not be used:
- people who are hypersensitive to this substance or its derivatives,
- people taking astemizole, cisapride, pimozide or terfenadine in parallel,
- people with kidney problems,
- pregnant and lactating women.
In children between 6 and 13 years of age, treatment with fluconazole may be introduced only when absolutely necessary and on condition that the kidneys work properly. The safety of fluconazole has not been established in patients of this age.
The use of fluconazole may lead to liver dysfunction and toxic epidermal necrolysis (in HIV-positive people).
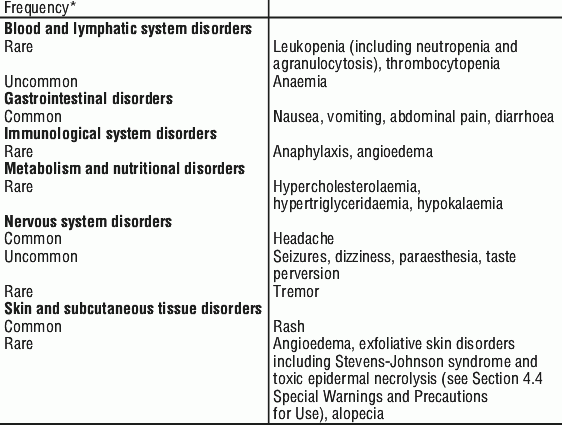
Fluconazole can cause many side effects. The most common are:
- headaches,
- nausea, diarrhea, vomiting
- increasing the concentration of AST and ALT,
- rash and increased alkaline phosphatase activity.
After treatment with fluconazole, the following symptoms appear less frequently: disorders of appetite and taste, sleep problems, convulsions, paresthesia, dizziness, anemia, fever, malaise, rash, urticaria, itching, increased sweating, muscle pain, symptoms such as constipation, indigestion, flatulence and asthenia.
Fluconazole – dosage
The decision on the dose of fluconazole is always made by the doctor. Usually, he chooses a daily dose of 50 mg fluconazole for the prophylaxis or treatment of mucosal candidiasis, up to a maximum of 400 mg for yeast sepsis. It should be remembered that, regardless of the type of disease, the daily dose of 400 mg fluconazole should not be exceeded.
Before use, read the leaflet, which contains indications, contraindications, data on side effects and dosage as well as information on the use of the medicinal product, or consult your doctor or pharmacist, as each drug used improperly is a threat to your life or health.