In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Influenza is an infectious disease that occurs mainly seasonally – this is when the highest number of cases is recorded. Every year, seasonal flu vaccines are available, and Polish pharmacies receive over 1,5 million doses of the vaccine. Despite this, many people will not get the flu vaccine. This is a big mistake because flu complications can be extremely serious.
Flu history
Influenza is a disease that, although we have known it for millennia, still in seasonal relapses can quickly cut us off our legs and exclude us from professional activities for a long time. It was first described by Hippocrates in the 1th century BC. Influenza was fought in the Middle Ages, and successive pandemics across Europe, Asia and America from the 1th to the XNUMXth centuries claimed the lives of millions of victims. The famous “Spanish” flu, or the HXNUMXNXNUMX mutation of the A virus brought by birds, in two years took a more numerous harvest than the entire First World War. Today, thanks to the increasingly popular vaccines, we are relatively safe from the outbreak of another pandemic, but this does not change the fact that in the individual sphere, influenza is still one of the most serious viral infectious diseases, mainly affecting the respiratory tract. Unfortunately, we can get flu many times because the virus keeps mutating. In addition, our age, previous diseases and the environment in which we live may increase risk factors and the occurrence of serious complications.
One of the challenges in managing periodic influenza epidemics is that it is highly contagious. By sneezing or coughing, we release viruses into the air, which travel even at a speed of 100 km / h, settling on all objects around the infected person. Although the flu virus hatch for up to four days, we must remember that it is able to transmit effectively up to 24 hours before the first symptoms appear. In Poland, the flu season lasts from September to April, and it culminates in the period between January and March. Hospitals across the country then register from several hundred thousand to several million cases of flu and flu-like diseases.
Flu symptoms
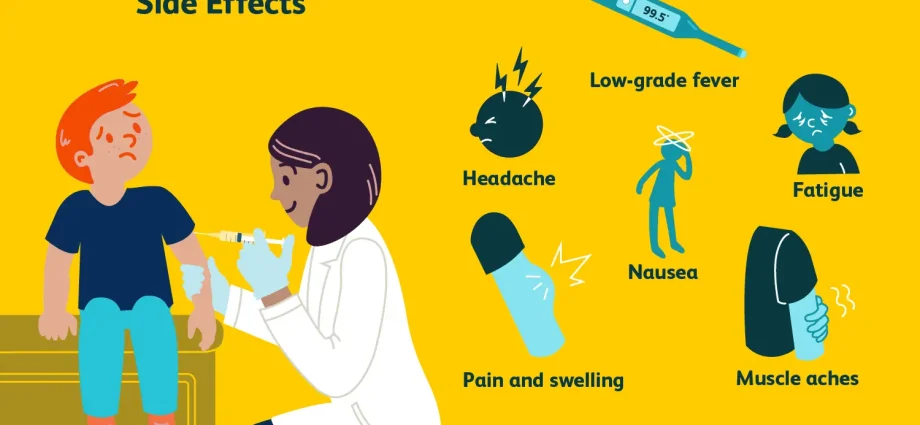
The thing about the flu is that it attacks very quickly – often without any transitional stages. These, in turn, are characteristic of a cold confused with the flu, which, although having similar symptoms, is a much milder ailment, often suffering from rhinitis, commonly known as a runny nose. However, it is not an indispensable element of the flu. On the other hand, almost always when undergoing a respiratory viral infection, we will be accompanied by a feeling of chronic fatigue, increased heart rate and shallow breathing. The worst flu symptoms should go away after about four days. If symptoms persist, consult a doctor. The most common symptoms of flu are:
– Pain in muscles and joints, which we colloquially call “breaking in the bones”.
– Fever, from 38 to 40 ° C, which usually drops naturally 3-5 days after the first symptoms appear. If the temperature rises again after an initial drop in temperature, this may indicate a bacterial superinfection. High temperature is often accompanied by chills and increased sweating.
– Dry and tiring cough associated with a scratchy throat. A sore throat may occur later in the disease, together with a slight rhinitis.
– Loss of appetite, which, contrary to appearances, is a useful activity of the body, which, at the expense of digestion, mobilizes the immune system to fight the disease more intensively.
– Headache and photophobia, generally decreased responsiveness to external stimuli.
Unfortunately, in children and elderly people suffering from cardiovascular diseases, the course of the flu can be much more violent and its symptoms are more severe. If you notice confusion, muscle weakness, a marked reduction in urination, low blood pressure, breathing problems and spitting blood – go to the nearest hospital immediately.
Flu – methods of infection
The influenza virus has returned cyclically since the dawn of mankind. Due to the ease of its transmission and constant mutations, despite the increase in hygiene and the use of vaccines, local seasonal epidemics continue to break out in the northern hemisphere every year during the fall and early spring. Every few decades, however, the threat increases; global pandemics appear, including swine flu A / H1N1v. Since the strain was new, the body’s natural resistance to the virus did not develop, therefore pandemic flu spreads many times faster than the seasonal flu.
The flu virus itself is divided into three types, A, B and C, of which humans are infected mainly with types A and B, while C causes only minor infections. The most common type A, depending on the presence of specific proteins on the virus surface, is divided into the subtypes neuraminidase (N) and haemagglutinin (H). Based on them, the most common mutations H3N2, H1N1 and H1N2 arise, which can be vaccinated in advance. Influenza B type is not as dangerous as A because it consists of only one strand of RNA and therefore has only two HA and NA subtypes, and is therefore not as susceptible to mutation.
Flu infection occurs through contact with a sick person or a person whose flu is asymptomatic. The virus itself spreads through droplets or through contact with the skin and objects that are “infected” by the person carrying the virus through their touch or sneezing. In this way, by touching the mouth, eyes or food – we introduce flu into the respiratory system, which is why washing hands is so important, especially after leaving public places. Flu can also be caught by contact with infected animals and by eating undercooked meat or raw bird eggs that carry the bird flu virus. The incubation period for the virus ranges from one day to a week, although most often it occurs two to three days after infection. The sick person infects the day before the onset of symptoms up to 10 days after their manifestation.
Flu treatment
The easiest way to start treating influenza is with prevention, i.e. with seasonal vaccinations. It is true that the influenza virus is constantly mutating and it is not possible to create a universal vaccine, the WHO, on the basis of statistical analysis, determines the predicted virus lines to which one can immunize in advance. It is estimated that vaccination reduces the number of cases in children by up to 36%. Once the first symptoms appear, there is no delay and treatment should be started immediately by staying at home in bed. An organism that devotes all its strength to fighting the virus, needs a lot of rest and hydration (it is best to drink water, fruit juices, herbal and fruit teas, such as raspberry or elderberry). It has been scientifically proven that elderberry extract, most likely due to the increase in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokinins in human monocytes, contributes to the inhibition of the development of viral strains and reduces the duration of the disease up to 3-4 days.
Early influenza is best treated with natural methods such as onion syrup, garlic, honey, raspberry juice, and chokeberry. These products have a warming and antibacterial role. During home treatment, we can only fight the symptoms of flu, so it is worth getting the agents that relieve the most serious ailments – runny nose drops, cough syrups and antipyretics. It should be remembered that children under 15 years of age should not be given drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid, as this may contribute to liver failure (the so-called Rey’s syndrome). Instead, in case of a headache, it is better to resort to paracetamol or ibuprofen medications. However, do not overdo them, and for joint pain than painkillers, it is better to use warm baths with essential oils, e.g. eucalyptus.
If traditional methods and “recovery” of the disease do not help, or we suspect that the flu may be very rapid, in the first 30 hours after the onset of symptoms, see a doctor for appropriate antiviral drugs. The most effective are prescription neuraminidase inhibitors, which inhibit the replication of type A and B viruses.
Flu – complications
While the flu itself is an extremely serious disease, the main cause of death is not the virus itself, but the complications after the disease. They occur in about 6 percent. people, most often in children up to two years of age and people over 65. Every year, 2 million people worldwide die as a result of complications, mainly due to the weakening of immunity by other parallel diseases.
The most common complications of influenza are:
– sinusitis,
– otitis media,
– pneumonia and bronchitis,
Muscle inflammation
– inflammation of the heart muscle,
– meningitis,
– Guillain-Barré syndrome (nerve damage),
– Rey’s syndrome (swelling of the brain and fatty liver).
Influenza virus entering the body damages the epithelium of the respiratory tract, in a way “wiping” the way for dangerous bacteria, which is why post-influenza complications are so often systemic diseases. Bacterial and fungal superinfections are particularly frequent and dangerous complications. If more than one organism is involved in the body, it can lead to toxic shock and, in extreme cases, to death in children and the elderly. Complications appear about two or three weeks after getting sick. Even after a serious illness, however, one should not panic because complications occur mainly in people with reduced immunity, suffering from cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, or after transplantation or chemotherapy.
However, it is best to get vaccinated against the flu. This is especially recommended for children and the elderly.
Also read: Flu attacks with new viruses