Contents
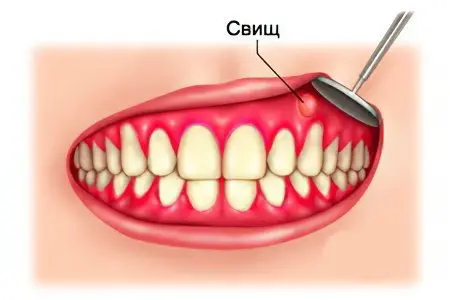
A fistula on the gum of a tooth is a pathological formation represented by a small passage through the gum to the lesion. Most often, the fistula comes from the root of the diseased tooth. Serous or purulent exudate is discharged through such a channel. You can see the fistula in the place of the projection of the tooth, in its upper part. It looks like a hot spot. The fistula does not form next to healthy teeth. Therefore, there is always caries near it, either a filling, crown, bridge or other restoration.
The fistula can be detected independently. Its appearance is preceded by swelling of the gums, pus accumulates in the tissues. When the purulent contents break through and begin to come out, the pain subsides somewhat. A non-healing hole is formed on the gum, from which exudate constantly oozes. This is the fistula.
A fistula on the gum can form in almost every person, regardless of age and gender. Children are no exception, as a fistula can develop even with milk teeth.
The presence of a fistula on the gum should not be ignored, since this pathology can lead to serious health problems. Pathogenic bacteria will freely penetrate into the open wound, which contributes to increased inflammation, intoxication of the body, and tooth loss. Therefore, if a formation is found on the gum, it is necessary to contact the dentist. However, it will be impossible to postpone a visit to the doctor for a long time, since the fistula will provoke pain, which will significantly worsen the quality of life of a person.
Symptoms of a fistula on the gum

The symptoms of a fistula on the gums are as follows:
Toothache, which can be quite intense. Her character varies from sharp and shooting, to aching and monotonous. Pain tends to increase with pressure on the affected tooth, for example, while chewing food.
The tooth acquires pathological mobility, loosens.
Inflammation forms around the gums, the skin becomes edematous and hyperemic.
Purulent contents are released from the fistula.
Possible increase in body temperature.
An unpleasant odor will come from the mouth, which characterizes the process of decay and is not eliminated by oral hygiene.
Pain will be as intense as possible at a time when purulent exudate only accumulates in the area of the inflamed tooth and in the tissues of the gums. After the pus breaks out and the fistulous canal is formed, the pain subsides.
When a fistula develops due to a violation of the technique of dental treatment, the fistula does not occur immediately. For some time, the process will have a latent asymptomatic course. The error of the dentist should be corrected as soon as possible.
Causes of a fistula on the gum

As an independent pathology, a fistula on the gums is not formed.
There must be appropriate reasons for this:
Untreated caries or its poor-quality treatment. Over time, caries can turn into pulpitis, and then into periodontitis. The infection spreads, affects the upper part of the root, a purulent abscess occurs, and then a fistula forms.
Violation of the technique of filling the dental canal. When the doctor fills the canal of the tooth, he then sends the patient to undergo a control x-ray examination. This allows you to make sure that the filling was of high quality. Otherwise, an abscess may develop, and then a fistula. Moreover, in 60% of cases, the fistula is formed due to poor-quality canal filling.
Damage to the root of the tooth. When a doctor works with a canal using traumatic instruments, he must be as careful as possible, as there is a risk of damage. If suddenly the dentist allowed the perforation of the canal and a rupture occurred, then the development of purulent inflammation is ensured in the future.
Eruption of wisdom teeth can lead to the formation of a fistula. Few have them erupt without pain and discomfort. In the most difficult cases, the process is delayed for a long time, the gum becomes inflamed and swollen. The tooth injures it from the inside as it grows. In this place, pus begins to accumulate, which finds its way out through the fistulous canal.
Prolonged eruption of milk teeth in children. In this case, the mechanism of formation of a fistula on the gum is similar to that which occurs when a wisdom tooth erupts.
Cystic formations in the gum cavity may be the cause of the fistula. Fistulas are formed against the background of inflammation of the cyst.
The presence of a granuloma of the tooth, in which pus accumulates in the soft tissues around. If this focus of infection is not sanitized in time, a fistula will form.
There are also risk factors that can give rise to diseases that contribute to the formation of fistulas, among them:
Strong overwork;
Sudden hypothermia of the body, or its overheating;
Violations in the work of immunity;
Diseases of an infectious nature, both of the organism as a whole and of the oral cavity in particular.
Dangers of gum fistula

If a fistula is found on the gum, it is necessary to seek help from a dentist as soon as possible. After all, the consequences of this pathology can be very serious.
If the existing inflammation is ignored for a long time, tooth loss is possible. This is due not only to its increased mobility, but also to the damage to healthy tissues located nearby. The more extensive the process, the higher the likelihood that the tooth will have to be removed surgically.
In addition, the periosteum may be involved in inflammation, in which there are vessels responsible for feeding other, healthy teeth. The infected periosteum undergoes degenerative processes, which in the future will lead to the loss of not one, but several teeth at once. In this case, a massive surgical intervention is required, which will be aimed at removing the entire diseased part of the periosteum.
If there is a lot of pus, then it can affect the soft tissues of the face. When this happens, they also have to be removed during the operation.
Such serious consequences must necessarily force a person to seek the advice of a dentist when a fistula is found on the gum.
Diagnosis of a fistula on the gum
A visual examination of the patient will be enough for the doctor to make a diagnosis. To clarify the condition of the diseased tooth, and to accurately identify the focus of inflammation, an X-ray examination may be required.
With its help, it will be possible to determine the depth of the fistula, the degree of growth of the granuloma or cyst, the extent of the damage to the periosteum, etc.
The doctor must make a differential diagnosis with diseases such as gum cyst, wen, purulent inflammation of the tissues. Self-diagnosis of a fistula is unacceptable.
Treatment of gum fistula
After the examination, the doctor will prescribe treatment for the patient. It can be of two types: medical and operational.
A combination scheme is usually used:
Opening the tooth to gain access to the root canals.
Pumping out purulent masses, removal of dead tissue.
Antiseptic treatment of inflammation.
The introduction of a therapeutic composition into the dental cavity for a certain time. After that, the patient is sent home, assigning him the date of the next appointment.
During a return visit to the doctor, he will remove a temporary filling from the tooth and assess the condition of the tooth cavity.
If necessary, the doctor will again treat the tooth with a medicinal composition. It is not excluded the appointment of physiotherapy procedures.
After the inflammation is qualitatively stopped, the dentist will install a permanent filling.
If the fistula has formed due to damage to the canals, then in some cases the doctor may not remove the filling from the tooth. Access to the focus of inflammation can be obtained through the gum.
In the presence of a crown or pin, the removal of a tooth filling is a very difficult process, so most often the doctor recommends surgical removal of the top of the tooth.
To complete the fistula treatment process, a rehabilitation course will be required. The affected area is irradiated with ultrasound or treated with a laser. It is possible to treat a fistula with a biometric current.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes oral antibiotics to the patient if local treatment is not enough. The imposition of professional dental gels and pastes on its surface will contribute to the speedy tightening of the fistula.
As for symptomatic treatment, it is possible to prescribe antihistamines to reduce swelling of the gums, and take painkillers.
At home, the doctor may recommend that the patient rinse his mouth with antiseptic solutions.
Operative therapy
As for surgical treatment, it is indicated in three cases:
Large areas of soft tissues are involved in the process of inflammation.
The tooth is crowned or has pins.
The periosteum of the tooth has undergone degenerative processes.
Affected tissues are removed mechanically, with the help of scraping. In the future, the canal of the tooth is treated with a laser. The surface of the tooth is filled. These are the main manipulations that the doctor performs in the patient’s oral cavity. Then he lets him go home, giving appropriate recommendations. It is mandatory to prescribe systemic antibiotics and antiseptic treatment of the affected area.
Conclusion
A fistula on the gums cannot go away on its own, so you should not waste time and postpone a visit to the dentist. Perhaps the extinction of pain, but not the relief of the inflammatory process. Therefore, the sooner professional treatment is started, the faster it will be possible to achieve a full recovery.









