A fistula, or fistula, is a hollow channel formed in the tissues of the human body. It appears due to purulent fusion of tissues as a result of the inflammatory process. From the inside, the fistula is lined with epithelial or granulation tissue; it may have one, two or more openings.
The formation of an abscess or phlegmon in the tissues of the body leads to the appearance of a fistula. Sooner or later, the pus formed in the abscess cavity or in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, as in the case of phlegmon, comes to the surface of the body. If a fistula appears on the leg, you should immediately contact a surgeon or traumatologist.
Causes of a fistula on the leg
The basis of this pathology in many cases is a leg injury as a result of a burn, hypothermia, bruise, bone fracture, exposure to aggressive chemical compounds. The injury can spread to the bones, periosteum, muscles, tendons, skin of the leg. In total, from a few millimeters to tens of centimeters of limb tissue can be affected.
As a result of a closed or open bruise, a fracture of the bones, hematomas occur, infection of the soft tissues and bones of the leg occurs. If staphylococcus, streptococcus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa gets into the wound, an inflammatory process begins, an abscess or phlegmon forms. An abscess is a cavity bounded by a capsule, inside of which there is pus. Phlegmon – spreading of pus over a large area of leg tissues with penetration between the muscles and muscle fascia. Sooner or later, pus from an abscess and phlegmon finds a way out.
If the patient suffers from endogenous or post-traumatic osteomyelitis, this condition will necessarily be accompanied by the formation of fistulas with the release of serous fluid or pus. Such fistulas are prone to temporary self-healing, but subsequently a relapse is sure to occur.
In moderate and severe forms of diabetes mellitus, the blood supply to the tissues of the lower extremities is disrupted, which affects the peripheral vessels. Violation of tissue microcirculation leads to the formation of phlegmon, abscesses and gangrene. The consequence of this is the formation of fistulas.
Another reason for the appearance of the fistulous canal is postoperative complications in the form of failure of surgical sutures, the introduction of an infection into the surgical wound, an atypical reaction of the body to the suture material (ligature), and its rejection.
A predisposing factor to the appearance of pathology is the low immune reactivity of the body due to advanced age, excessive physical or mental overwork, and a long course of the disease.
Symptoms of a fistula on the leg
The manifestations of this pathology are divided into general and local.
Common symptoms of a fistula on the leg:
Weakness, increased fatigue;
Weight loss;
An increase in temperature in the range from subfebrile to very high;
sleep disorders;
Frequent respiratory and intestinal infections of a long course due to weakened immunity;
With diabetes – pain in the muscles of the legs, increased sweating.
Local symptoms:
A hole in the skin of a limb;
Hyperemia and soreness of tissues near the fistula;
Discharge from the hole of pus and sanious fluid;
Additional symptoms depending on the cause of the fistula.
Diagnostics

Clarification of the diagnosis with the appearance of a fistula on the leg is not difficult. Usually the picture of the pathology becomes clear to the specialist already during a visual examination.
To determine the direction and size of the fistula on the leg, the following research methods are used:
Probing of the fistulous canal;
Ultrasound to determine the location and size of the abscess;
X-ray with the introduction of a contrast agent into the fistulous canal (fistulography).
To determine the reaction of the body, the doctor may prescribe a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test. If the fistulous canal has not yet found a way out, it may be difficult to visualize it, as it is filled with pus.
Treatment
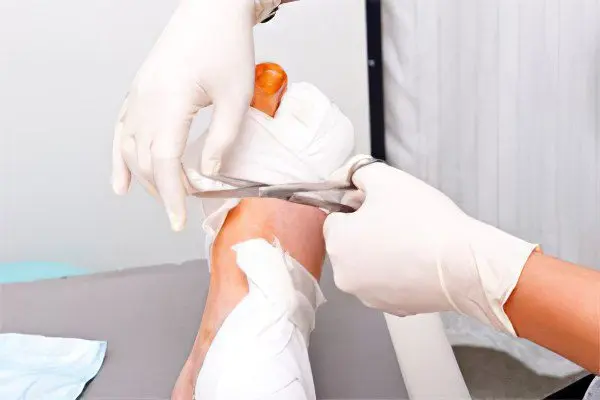
A radical method that allows you to completely get rid of the fistula on the leg is surgery. During the operation, the fistulous canal is excised, drainage is established, and the focus of infection is treated.
If the cause of the fistula was the rejection of the ligature, the surgical thread is removed from the wound. With osteomyelitis, devices for osteosynthesis are installed, after an injury, bone fragments and foreign bodies are removed.
Granulation fistulas can be cured without surgery. For this, a set of measures of conservative therapy is used, some of which are also used in the treatment of patients who have undergone surgery:
Treatment of the underlying disease, which has become a prerequisite for the appearance of a fistula;
Appointment of absorbable agents;
Laser exposure;
The use of antiseptics in the form of ointments and powders;
Antibiotic therapy.
Prerequisites for the use of antibiotics may be test results and symptoms such as redness of the skin, high fever for several days, severe pain. When prescribing antibiotics, contraindications and side effects of drugs must be taken into account.
Careful hygienic care of the fistula significantly reduces the risk of recurrence. Wound treatment, timely dressing with modern materials will contribute to rapid healing.
In order for the fistula on the leg to heal quickly, it is necessary to seek medical help at the first symptoms of the inflammatory process, to treat the underlying disease in a timely manner.









