Contents
Fibroadenoma of the breast – what is it?
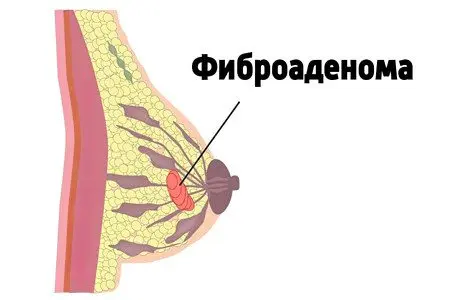
Fibroadenoma of the mammary glands is a tumor of benign origin. Consists of connective and glandular tissue, moves freely – the “float” symptom, is the main distinguishing feature of fibroadenoma.
Mammologists define fibroadenoma as one of the types of mastopathy that appears in the tissues of the mammary glands. The disease affects only women. The established fibroadenoma is subject to observation and therapy. Often, treatment involves surgery due to the active growth of the tumor. According to statistics, 5% of fibroadenomas degenerate into a malignant form.
The disease occurs in girls and women aged 15 to 35 years. The largest number of cases occurs at the age of 20 years. As a rule, nodules appear in one mammary gland, only in 10% the pathology is bilateral.
Usually the boundaries of the formations reach 2-3 cm, but sometimes large tumors are formed – more than 6 cm. In 80% of women, single nodes are found, in 20% – multiple. Benign fibroadenoma does not cause metastasis and does not pose a threat to a woman’s life.
How to identify fibroadenoma at home on your own? The tumor is usually detected by chance, since its appearance is not accompanied by any symptoms. A woman gropes for a slight seal in the glandular tissue, which is easily displaced. Unpleasant or painful sensations during palpation are not observed. In some cases, the tumor remains invisible until any symptoms appear.
If the disease progresses to later stages, the tumor increases in size. It is easy to palpate in the breast tissue. A woman experiences a feeling of fullness in a sore chest. If the pathology becomes malignant, the color and structure of the skin above it noticeably changes, and discharge from the nipple appears.
A hallmark of a benign fibroadenoma is smooth edges. A bumpy structure indicates a malignant process. Leaf-shaped fibroadenoma is considered dangerous.
Fibroadenoma Symptoms

At the very beginning of the formation of a fibroadenomatous nodule, a woman does not experience any specific symptoms. Only with a sufficient increase to 2-3 cm, the formation becomes easily palpable. In the supine position, it does not disappear. The detection of a tumor in the mammary gland is the reason for the obligatory visit to the doctor.
Usually the node is formed in the upper-outer or upper-inner quadrant of the breast. Multiple fibroadenomas are several formations of different sizes that are located in different parts of the chest.
With a benign tumor, the structure and color of the skin of the breast do not change. If the tumor is small, the size of the breast does not increase. A change in the shape and size of the mammary gland is observed with giant single formations. Breast asymmetry is visually determined.
For the purpose of early detection of transformations in the mammary glands, women are advised to systematically conduct self-examination. The best time to do this is after your period ends. To do this, you need to stand in front of a mirror, evaluate the symmetry of the mammary glands with your arms lowered and raised, and then gently palpate them. Feeling starts from the upper outer section and continues clockwise. A fibroadenoma is defined as a hard nodule that slides easily under the fingers.
The disease is accompanied by changes in the hormonal background, which is manifested by soreness and tension in the chest in the second half of the menstrual cycle. Often women notice increased sensitivity of the nipples. There is no pain during palpation of the tumor.
An increase in the boundaries of the tumor is observed in the second half of the cycle against the background of premenstrual syndrome. During this period, fluid is retained in the tissues of the mammary glands, edema appears, which can be mistaken for active tumor growth.
For fibroadenoma, discharge from the nipples is not typical, if they appear, then more often in the second half of the cycle. To check for discharge, gently squeeze the nipple with two fingers. The liquid is:
Serous.
Muddy white.
Brown
The appearance of an admixture of blood is an unfavorable diagnostic syndrome, which may indicate the development of a malignant process.
During the examination of the subclavian, supraclavicular, axillary groups of lymph nodes, their usual size and density are determined.
Large tumors, reaching from 7 to 15 cm, deform the mammary gland, compress soft tissues and nerve endings. In this case, the woman experiences a feeling of pain and burning.
Adenoma can be localized in the nipple area. In this case, the lymph nodes are not enlarged, the areola of the nipple is edematous, hyperemic. The discharge of serous fluid or ichor is characteristic. The tender skin of the nipple and around it is irritated, crusts and ulcerations appear. On palpation in the depth of the nipple, a movable node of a soft, elastic structure is determined. Areola – normal color, skin changes like orange peel and wrinkling are absent. These signs are characteristic of breast cancer.
Reasons for education
Hormonal disorders are the main reason for the development of benign neoplasms in the mammary glands and reproductive organs of the small pelvis. The female breast reacts with increased sensitivity or increase to physiological hormonal surges:
ovulation.
Pregnancy.
Menses.
Disorder of hormonal balance provokes the growth of tumors of various origins.
It has been established that fibroadenoma is a hormone-dependent formation, which is formed against the background of:
Puberty.
Spontaneous or induced abortions.
hormone therapy.
Incorrectly selected hormonal contraceptives.
Diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands.
The size of the tumor increases in the second half of the cycle, during pregnancy. Fibroadenoma can respond to hormonal surges by increasing by a factor of three.
Mammologists identify a number of factors that can affect the appearance of benign nodules in the mammary glands:
Mastopathy in the family history.
Obesity (visceral fat is an endocrine organ that synthesizes estrogen).
Tumors of the ovaries.
Long-term use of oral contraceptives.
Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system.
Refusal of breastfeeding.
Inhibition of lactation.
Miscarriages or abortions in a gynecological history.
The number of pregnancies, childbirth.
Problems in the family, frequent stress.
Bad habits.
Dissatisfaction in intimate life.
Irregular sexual relations or their absence.
Chest injuries.
Transferred operations.
Types of fibroadenomas
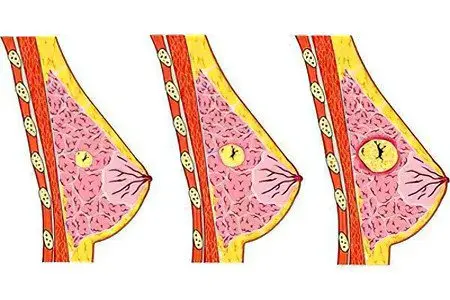
Fibroadenomas are classified into types:
Intracanalicular – the node is formed inside the duct, it has a heterogeneous structure.
Pericanalicular – the node grows around the milky streams, decreases independently with age.
Mixed.
Leaf-shaped (phylloidal) – a dangerous type, prone to malignancy. The tumor combines cells of different structures – normal, borderline, atypical.
There are mature and immature fibroadenomas. A mature tumor is enclosed in a dense shell, which implies only surgical treatment. Immature knots are common in teenage girls during puberty. This type of tumor may resolve on its own.
It should be remembered that fibroadenoma is a tumor, and fibroadenomatosis is a condition in which multiple cysts form in the breast. The etiological factors causing these pathologies are common, but the pathogenesis of therapy has significant differences.
Diagnostics
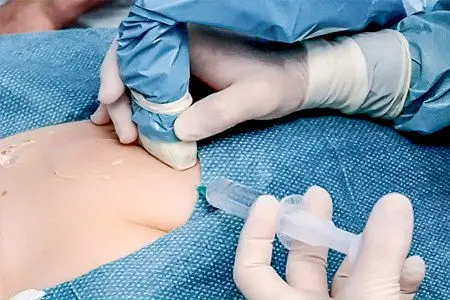
First of all, the mammologist performs examination and palpation of the breast. Ultrasound or mammography is indicated to confirm the diagnosis. In some cases, both studies are performed to clarify the parameters of the tumor and its origin. Histological examination shows the benign or malignant structure of the tumor, for which a biopsy is performed.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia by aspiration or excision. In the first case, a syringe is used, in the other, a special device. The most commonly used is a thick, long needle, which is used to take a tissue sample. The laboratory analyzes the biomaterial for atypical cells.
Complications
Small fibroadenomas are not prone to aggressive growth. Progression is recorded quite rarely, does not cause complications. Sharp hormonal surges can provoke active growth and further deformation of the mammary gland. A tumor of significant parameters is able to fill the entire mammary gland, which leads to its increase.
The most dangerous of the giant tumors is leaf-shaped fibroadenoma. Its pathological development leads to degeneration into sarcoma.
Fibroadenoma treatment
A tumor detected in adolescence needs systematic monitoring. The constancy of the size of the fibroadenoma gives hope that after the establishment of a stable cycle with ovulation, regression will occur. Expectant management without specific therapy is allowed with monitoring of the condition of the node every six months.
If a fibroadenoma is registered in a woman over 40 years old, waiting tactics are not practiced.
To date, there is no more effective way to treat fibroadenoma than removal.
4 modern methods of treatment
In modern mammology, ablative methods for removing tumors are used. These techniques are characterized by minimal trauma and high efficiency.
Fibroadenoma removal is performed in one of the following ways:
Cryoablation.
laser destruction.
FUZ-ablation (HIFU-therapy).
mammotomy biopsy.
Cryoablation – takes place on an outpatient basis with the use of local anesthesia. The patient does not need long-term rehabilitation. The method is used for women of any age, before a planned conception. After removal of the node, there is no connective tissue scar, which ensures normal patency of the milk ducts and does not interfere with breastfeeding.
After anesthesia, the doctor makes a small incision through which the probe is inserted. Under ultrasound control, it is directed to the neoplasm and then cooled down to -180°C. Cooling is carried out at the expense of a cryoagent (argon, liquid nitrogen). Minus temperature destroys the cell membranes of the tumor, thromboses the blood vessels and causes hypoxia of its tissues. Without the supply of blood flow, the node is destroyed. In the future, the body independently resolves its remnants through immune cells.
The method is used for tumors from 3 to 3,5 cm. As a result, it is possible to achieve a high therapeutic result with a maximum cosmetic effect.
Laser destruction – provides for a thermal effect on the tumor after the introduction of the probe into its structure. The mechanism of action is similar to cryoablation. The laser emits thermal energy and waves that act on the structure of the breast. Due to these features, not all doctors consider the laser to be a completely safe method. In 1999, during the observation of 27 women after laser removal of fibroadenoma, it was not possible to prove the complete safety of the method.
FUZ-ablation – impact on fibroadenoma by exposure to focused ultrasound radiation. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis. The woman does not need anesthesia. Ultrasonic waves pass through the skin to the node, necrotic and destroy it. After a few weeks, complete resorption of the tumor is noted.
mammotomy biopsy. It involves local anesthesia, an incision over the fibroadenoma, the insertion of a probe under ultrasound guidance, the use of a vacuum to remove the tumor. After such a manipulation, a quick recovery is noted, the scar is hardly noticeable.
[Video] Interview with Professor Avraham Rivkind, Head of the Department of Surgery at the Hadassah Hospital in Israel: how to treat fibroadenoma and should we be afraid of it?









