Contents
Wood in its pure form has recently been used less and less. Even for us, the material becomes too expensive, and processing is difficult. Increasingly, wood-based materials are being used in construction. One of them is fiberboard (hardboard). They are used in construction, in decoration, in the manufacture of furniture.
What is fiberboard, scope
Fiberboard is an abbreviation for the name “Wood Fibreboard”. It is a sheet building or finishing material. It has a relatively low price, it can be of different density – soft, hard and superhard. Sheet thickness – from 2-3 mm to 12-15 mm, some types can be up to 40 mm.
Sheet fiberboards are characterized by high density and strength, and have a relatively low price. Thin sheets bend perfectly, which allows them to be used for sheathing curved surfaces. Fiberboard is used in construction, as a sheathing in frame housing construction, for leveling floors and walls. Partitions in railway passenger cars are also made from this material.
Low density fiberboard is used as a soundproofing material. The chaotic arrangement of wood fibers contributes to the fact that the sounds “get stuck” in the material. This is the most inexpensive and easy-to-install type of soundproofing materials. There are more effective ones, but cheaper ones still need to be looked for.
Some types of fiberboards can be used as finishing materials – for finishing walls in rooms with normal humidity. For these purposes, fiberboard is used, one of the sides of the sheet of which is painted, covered with a decorative film, laminated.
Another area of application of fiberboard is the production of furniture. Usually this material is used as an auxiliary material – they make the back wall of cabinet furniture, hem the bottom in armchairs and chairs, bottoms in drawers, etc. In general, the scope is extensive. The disadvantage, in fact, is one – without hydrophobic additives, the material behaves poorly at high humidity. It swells, increasing in size. At the same time, the sheet material “goes in waves.” When dried, it remains deformed. So in unheated or damp rooms, only certain brands of fiberboard can be used.
Production technology
The feedstock for the production of fibreboard is waste from the woodworking industry: wood chips, sawdust, fire (lignified parts of the stems of spinning plants). The raw material is washed, foreign inclusions are removed from it, then it is dried. The dried material is crushed in special machines (defibrators and refiners) into the smallest particles – fibers. The degree of grinding can be from coarse to fine. Further, the process is different for different production methods.
Pressing is carried out under high pressure – 3-5 MPa and high temperature – above 300°C. Due to this, the material is bonded and compacted. Before pressing, additional components are added to the initial material that change the properties of the material – binders (synthetic resins), water repellents, flame retardants, etc.
Forming methods
There are two ways to produce fiberboard – wet and dry pressing. The “wet” method is more environmentally friendly. In wet pressing, fewer binders are used (sometimes without synthetic additives at all), but the material is more expensive, since the process is more energy-intensive. It takes up to 15 minutes to dry one sheet, which limits the productivity of the presses, and therefore increases the price of the material. With this method, the necessary additives, water, are introduced into the crushed material. The slurry enters the dispenser, which spreads it in an even layer on the tape. For faster removal of water, the tape has a mesh structure. After passing through the press, the back side of such fiberboard has an imprint of this fine mesh.
When wet pressed, some grades of fiberboard can be made without the addition of a foreign binder. Under pressure and at high temperature, lignin (a substance that characterizes the stiff walls of plant cells) is released from wood fibers. It is a natural binder. Lignin is found in significant amounts in coniferous wood. But not for all grades of fiberboard, a natural binder is enough. In this case, 4 to 7% synthetic binder is added.
In dry pressing, synthetic resins are usually added to the mass, which bind the fibers. It is this method that makes it possible to obtain fiberboard of great thickness – up to 12-15 mm, some factories can produce pits up to 40 mm thick. The compaction and pressing of the dry mass takes much less time – 3-5 minutes, depending on the class and thickness. The productivity of the press increases significantly. In addition, a smaller amount of additives is put into the dry mass – they are not washed out with water. All this leads to a reduction in the cost of the material. But cheap binders contain formaldehyde, and its content must be controlled, since in large quantities it is harmful to health.
For the production of furniture and interior decoration, material with formaldehyde emission class E0,5 or E1 must be used. This is usually wet pressed fiberboard. You can distinguish fiberboard made by the wet method by the print of the grid on the back of the sheet (see photo above).
Termination Processes
During high-temperature pressing, the particles stick together. The time spent under the press is not always enough, therefore, already formed sheets are transferred to a special chamber, where the material “ripens” at high temperature. The fiberboards are kept here for several hours. During this time, the fibers are sintered, glued together, the material becomes homogeneous and durable.
The slabs leave the chamber with almost zero humidity and begin to actively absorb moisture from the air. As a result of this process, the edges of the sheets swell. To avoid this disadvantage, the material is transferred to another chamber, where it is brought to normal humidity. And only after that, sheet fiberboard can go on sale or to other machines – for painting, laminating.
What is good is that the technology for the production of fibreboard is plastic. The press can have any shape, which allows you to make not only sheet material, but also figured products. For example, skirting boards or furniture facades.
Species and classes
The main classification of fiberboard is by purpose and density. By appointment, fiberboards are of general and special types. Special – this is with some special properties. Three main groups can be distinguished:
- Moisture resistant (bituminated). When preparing the mixture, bitumen is added to it, which improves resistance to moisture.
- Fire resistant. Flame retardants are added to the starting material, which reduce the flammability of the finished material.
Thin sheets bend well, thick sheets have high rigidity, so the material can be used for different purposes. - Finishing – with ennobled one side. The front side of fiberboard can be painted, glued with a polymer film that imitates various materials: wood, stone, brick, tile, etc.
It is customary to refer to special-purpose materials and finishing types of fiberboard – with an ennobled one side. There are a lot of subspecies and they can be called differently:
- Fibreboard with a coated or painted surface, smooth on the back (produced by dry pressing). In colloquial speech, such material is usually called “hardboard”. Usually it is a material of medium density.
- The same, but with a non-smooth back surface is called “masonite” (wet pressing).
Sheathe cottage fiberboard – a common solution - If the front side of the material is glued with a film – laminated – such material is called laminated fiberboard, sometimes the abbreviation LDVP is found.
General purpose fiberboard is also called construction. This class can include materials of both dry (with two smooth surfaces) and wet production methods.
Price or quality?
Usually, the main criterion when choosing a general-purpose fiberboard is a low price. If you use it for sheathing the frame, you need a lot of material, so you want to save money. But do not chase cheapness.
Cheaper fiberboard sheets are made with more formaldehyde. This substance in large quantities contributes to the development of cancer. To make the house safe, do not use material with an emission class higher than E1 for interior cladding. Materials with class E1 are absolutely safe. They emit formaldehyde as much as natural wood.
Density, weight, sheet thickness
The technology for the production of wood-fiber boards allows you to make them of different densities. Depending on the density, they have different technical characteristics and scope. There are such types of fiberboard:
- low density. They are also called soft, they can be designated with the help of the attached letter “M” – DVP-M. Pretty loose material with a density of 200-350 kg/m³. Sheet thickness can be 8, 12, 16, 25 mm. If desired, you can find up to 40 mm. They are usually used for soundproofing or as finishing / cladding in places that are not subject to stress.
Low-density fiberboard has a loose structure, is used as insulation and sound insulation - Medium density – up to 850 kg / m³, sheet thickness can be 8, 12, 16, 25 mm. According to the classification, they also pass as soft.
- Semi-solid – from 860 to 900 kg / m³, sheet thickness 6, 8, 12 mm.
- Solid (DVP T) – 950 kg / m³, sheet thickness 2.5, 3.2, 4.5 and 6 mm.
- Superhard (DVP-ST) – 960-1000 kg / m³, can be 2.5, 3.2, 4.5 and 6 mm thick.
Hard and superhard grades are used where resistance to mechanical stress is important. In household construction and decoration of houses / apartments, fiberboard-T is placed on the floor, walls can be sheathed with them.
Types of solid boards
For all that, general-purpose solid fibreboards come in several types – with different front and back sides. According to GOST, solid fiberboards have the following marking:
- T – solid slabs with an unfinished front surface. Often referred to as “technical” fiberboard. It is used for works in which appearance is not important.
- T-P – solid slabs with a tinted front layer. This is the so-called hardboard. It is used in the furniture industry for back walls in cabinets, tables, etc.
The choice of colors is wide - T-S – solid boards with a front layer of finely dispersed wood pulp. One side of the sheet has the same color, but is smooth, like varnished. It can be used for sheathing frame buildings from the inside. Requires minimal finishing work. Wallpaper can be glued to such a surface of a rhinestone, but it will be very inconvenient to remove them. But the putty does not fit well on the smoothed surface – it rolls off.
- T-SP – solid boards with a tinted front layer of finely ground wood pulp. It can be used as a finishing finishing material.
Solid fiberboard grades can be in two classes – A and B. They are distinguished by quality. As you can see, even in the same class there are different materials. With the same (or almost the same) technical characteristics, they have different applications.
Subspecies of superhard fiber boards
Superhard fiberboards are rarely used in domestic construction and repair – the price is too high, and high density and rigidity may not be in demand. Sometimes excessive rigidity can be uncomfortable.
According to the standard, there are two types of such material:
- ST – “construction” brand, not very attractive in appearance;
- ST-S – with a smooth face layer – finely ground wood pulp is compacted to a very smooth state.
Dense and smooth boards
There are practically no laminated or decorative types – material that is too heavy and hard for finishing is also not needed.
Names depending on the density
Also, fiberboards have different names depending on the density. Usually this is a calque (transliteration) of English / international names. Although, under the same name, in other countries, a different material is often meant.
- LDF – from English low density fiberboard – LDF. Translated – low-density fiberboard. In fact, this is the name of the material of medium density, simply having characteristics at the lower boundary of the zone. It has nothing to do with softwood boards.

Characteristics of MDF - MDF – from English medium density fiberboard – MDF. In translation – medium-density fibreboard. If we talk about standards, then this material corresponds to the GOST definitions of medium density fiberboard.
- HDF — hight density fiberboard – HDF. According to the characteristics, the DVP-T brand (solid) can be put in line.

HDF boards are usually thin and are used for milling patterns.
As you can see, there is no clear distinction. Another confusion is added by the incorrect use of names. In general, each time it is necessary to clarify what exactly the speaker means by this or that term.
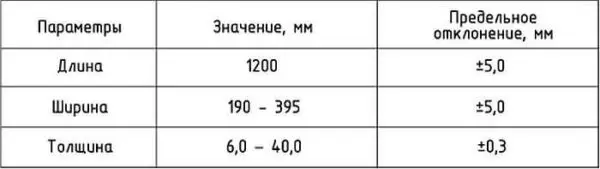
dimensions
It makes sense to talk about dimensions only in relation to standard sheets or plates. As mentioned earlier, the thickness of fiberboard sheets can be from 2 to 40 mm. The rest of the dimensions are defined by the standards:
- width 1220 mm and 1700 mm;
- height 2140 mm, 2440 mm, 2745 mm.

Please note that in any production you can find unformatted sheets. After forming in the press, they are trimmed, and sometimes, due to malfunctions in the equipment (which forms the carpet on the tape), more edges have to be trimmed. Because of this, narrower or shorter sheets are obtained. If you do not care about the standard size, you can always buy these. In terms of quality, they hardly differ in anything, but at a price they will be much lower.
Modern use of some species
If we are not talking about construction, but about finishing work, then more and more often in this area the name “MDF” began to emerge – a medium-density fibrous material. Interior doors are made from laminated sheet MDF. The frame of wooden planks is sheathed with this material, getting budget products that look very good. Soundproofing characteristics depend on the type of filling of the frame, and the durability of the product itself depends on the quality of lamination and the rigidity of the film.

The production technology allows you to create not only sheet wood-fiber products. The shape of the press, theoretically, can be any. Therefore, they began to make various kinds of moldings from MDF – platbands for finishing the same door frame, skirting boards and other similar products. They can be matched to the color of the doors and similar in shape.
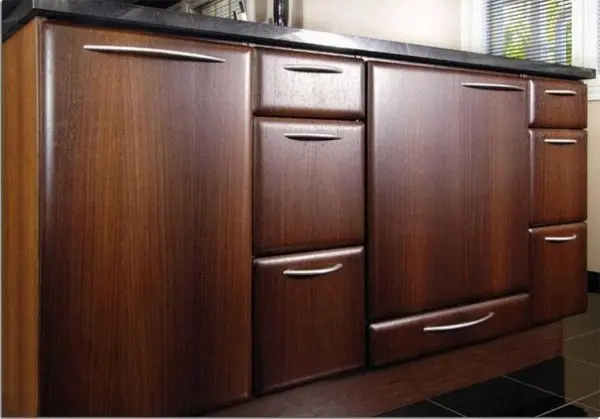

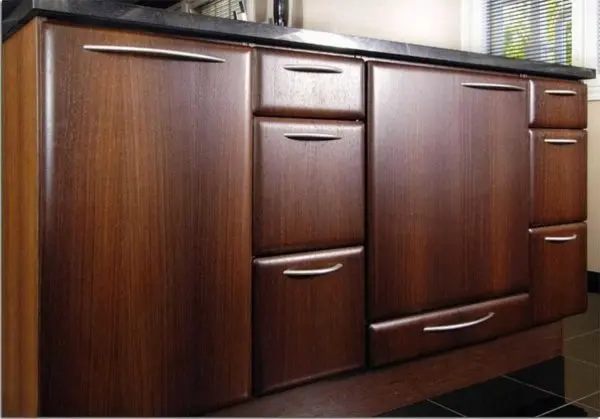
They began to make facades of cabinet furniture from MDF. For example, kitchen. Moreover, if furniture made of chipboard has a linear structure, curved, smooth, rounded shapes are formed from ground wood fibers. All this allows you to create greater species diversity. Using the same technology, MDF wall panels are made. These are not only even smooth sheets, but also with a pattern of various types / types.
Rigid fibrous materials
HDF, a high-density material, is used in some areas. In particular, due to its rigidity, it is convenient to work with it when forming an openwork. Using laser cutters, a slotted openwork is formed on thin laminated or painted HDF boards. Various decorative elements are made from openwork plates, in particular, screens for radiators.

Some types of finishing materials are formed from HDF. The plate is covered with a layer of film or painted. The surface can be plain painted, imitate wood, stone surface, etc. If the material is molded in the form of planks with locks, the same laminate is obtained. If the material is made in the form of sheets, they can be sheathed on walls, ceilings, used to finish the working area in the kitchen – a kitchen apron.
Surely there are other areas of application for fiberboard of different densities. And, most likely, there will be other uses. The technology is flexible, it allows to obtain materials with different properties.