Contents
The late variety of felt cherry Leto attracts gardeners with its self-fertility and unpretentiousness. The rules for planting and caring for felt cherries Leto are quite simple. By adhering to them, you can easily get a healthy, beautiful bush that pleases the eye and gives a not very plentiful, but regular harvest.
History of breeding
The felt cherry variety Leto was obtained at the Far Research Institute of Agriculture in the middle of the 10th century. The author of the variety was G. T. Kazmin, who painstakingly worked for this with more than 000 seedlings in four generations. Felt variety Leto was grown from the seeds of another crop – sandy (bush) cherry through free pollination. And so it combines the features of both felt and sand varieties.
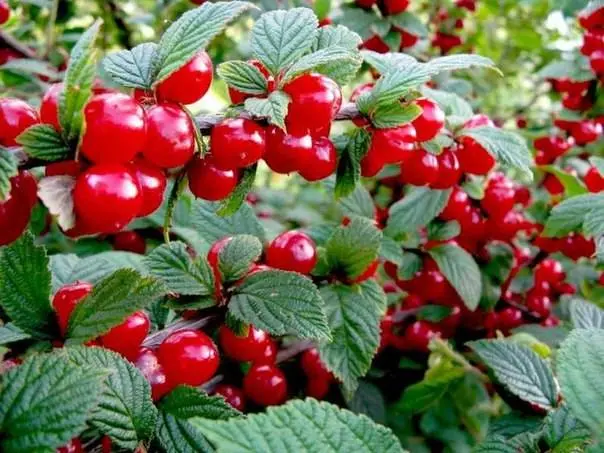

Felt cherry Leto is included in the list of the State Register. The variety was introduced into the elite in 1955.
Description of the culture
Felt cherry bush Summer is compact, skeletal branches are straight, branching is characteristically medium or rare. The bark of perennial branches is rough. Young shoots are thick, even, brownish-green in color, strongly pubescent.
The leaves of the plant of this variety are hard, ovoid, pubescence is pronounced.
Fruit buds are small, red-brown. They adhere relatively tightly to the shoot (only the upper part is raised). They are formed, in addition to annual shoots, on bouquet branches, but the latter are noticeably shortened (3–10 cm). The flowers of Summer are large, pale pink, medium open, with oval petals.
The berries of the felt cherry Leto are large (weighing 3–4 g). Their shape is characteristically irregular (one side is beveled towards the base), resembling a rounded cylinder. The color is light red, unevenly distributed. The pubescence of the skin is very pronounced. The peduncle is short (0,5 cm), green, thin. Bone weight (on average) – 0,2 g.
The pulp of Summer berries is pale pink, juicy, thick. The taste is sweet, with a clear hint of acid, but at the same time fresh. Light pink juice.

Initially, this variety of felt cherry was zoned in the Khabarovsk and Primorsky Territories. However, later, due to the excellent characteristics of Leta, the territory of its distribution went beyond the boundaries of the Far East region. Felt cherry Summer is very popular today in the Moscow region and other areas of the central strip.
Features
Drought resistance, winter resistance
The winter hardiness of the Leto variety is considered average – it is somewhat lower than that of most other varieties of felt cherries. At the same time, spring frosts are well tolerated by the fruit buds of the plant. And also the bushes of this variety are relatively resistant to the lack of moisture.
Pollination, flowering period and ripening period
Unlike most varieties of felt cherries, Leto is self-fertile, that is, it is able to be pollinated by its own pollen. At the same time, the presence of other related plants in the area can increase its yield. Pollinator for felt cherries Summer may well be another bush of the same variety.
Summer blooms relatively late – from May 25 to June 6. In terms of ripening, Leto also belongs to the late varieties of felt cherries. The bushes can be harvested by July 25, however, ripe berries can hang on the branches without falling off until the end of August.
yield, fruiting
An important characteristic of felt cherries of the Leto variety is a stable, but average yield. The bush of this variety begins to bear fruit in the second year. The berries ripen at the same time.
In the case of a bush growing on a strong rootstock, from a biennial plant, from 100 to 300 g of fruits can be collected. An adult plant, which has entered into full force, is able to produce 7–8,4 kg of berries per season.
In the pulp of Leto cherries, 9% is sugar, 8,5% is tannins, 0,7% is various acids and 0,6% is pectin. Tasters rate their taste at 3,5–4 points out of a possible 5.
Due to the semi-dry separation of berries from the stalk, the Leta crop has an average transportability. At room temperature, the berries are able to keep their presentation for up to 4 days.
Scope of berries
Summer refers to table varieties of felt cherries. Berries of this variety are quite suitable both for fresh consumption and for use in recipes for various preparations (jam, marmalade, marmalade), desserts (marmalade, marshmallows), drinks (including alcoholic ones).
Disease and pest resistance
It greatly facilitates the work of gardeners in growing felt cherries of the Leto variety, its high resistance to moniliosis (monilial burns). To the “pocket disease” of cherries, another misfortune of felt varieties, it is relatively stable.

The weak point of this variety is the codling moth, which causes significant damage to the plant.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Self-fertility | Yield is moderate |
Fruit buds are frost resistant | Frost and drought resistance is average |
The compactness of the bush | Slow bush growth in the first two years |
resistance to moniliosis | Significantly damaged by codling moth |
large berries | Taste qualities are average |
Features of landing
Recommended dates
The preferred time for planting felt cherries Summer in the ground – early spring, before the buds open. However, autumn planting is also possible, in September. Seedlings that were purchased later should be dug into the ground until next spring.
Choosing the right place
Site for planting felt cherries Summer, it is desirable to choose a sunny and dry, if possible, located on a slope or hill. Ideally, if the soil is:
- fertile;
- light in composition (sandy or sandy loam);
- well drained.
What crops can and cannot be planted next to cherries
Recommended | Not recommended |
Shrubs and trees | |
Felt cherries of other varieties | Apple tree |
Cherry plum columnar | Pear |
Cherry | the norm |
Plum | gooseberries |
Black elderberry | lenses |
Flowers | |
Marigold | Primrose |
Cleansing | dark geranium |
Periwinkle | Irises |
Violets | Hosta |
vegetable crops | |
Bow | Peppers (any kind) |
Garlic | Tomatoes |
Greens | |
Nettle | Parsnip |
Dill |
|
Parsley |
|

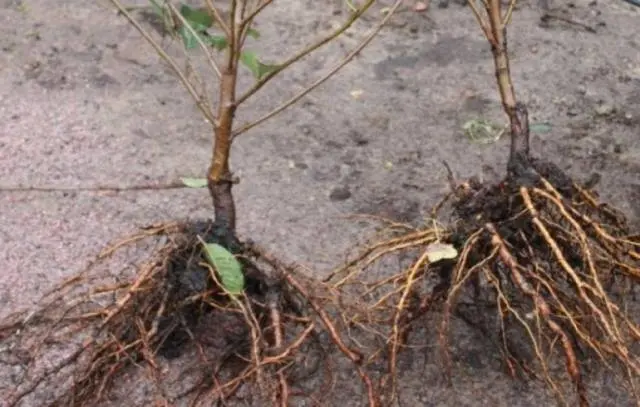
Selection and preparation of planting material
Most often, seedlings of 1–2 years old act as planting material for felt cherries of this variety.
Characteristics of a quality seedling:
- height about 1 m;
- there are several branches;
- the root system is branched;
- leaves and bark show no signs of disease or damage.

Reproduction of felt cherries Leto is made:
- scions (for cherry plum, Vladimirskaya cherries or thorns);
- layering;
- cuttings.
Landing algorithm
In short, the procedure for planting felt cherries Summer is as follows:
- first, a landing pit is prepared with a diameter and depth of about 0,5 m;
- the pit should be filled with a mixture of soil with rotted manure, lime, potash and phosphate fertilizers;
- the roots of the seedling are cut off a little and dipped in clay loosened in water;
- the seedling must be lowered into the pit strictly vertically, observing the same planting depth that it had in the nursery;
- the root circle is covered with soil mixture, compacted, then watered;
- the ground around the plant is recommended to be mulched with peat to control the level of humidity.

Culture aftercare
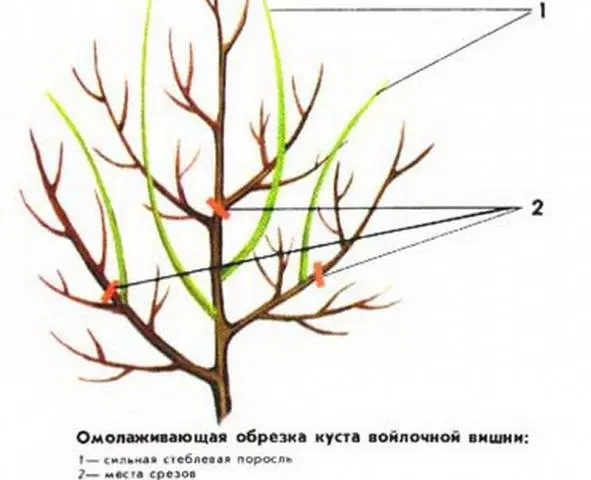
Pruning of felt cherries of the Leto variety is carried out in several stages:
- unbranched annual seedlings, planted in spring, are cut to a height of 30–40 cm;
- in the first few years they form a bush, removing weak shoots and leaving 4–6 powerful branches at the base of the trunk;
- by 10 years and later, rejuvenating pruning is regularly performed, maintaining the ability of the felt cherry bush to grow and bear fruit.
Felt cherry bushes should be watered. Summer should be moderate – excess moisture harms it. As a rule, watering is carried out in case of a long absence of precipitation.
Felt cherries are fed annually, carefully applying fertilizers to the near-stem circle to a depth of about 5 cm. Spring fertilizing with nitrogen-containing substances stimulates the growth of shoots. In autumn, on the contrary, in order to avoid growth, the bushes are fertilized with organic matter (humus, manure).
In regions with severe winters, and also if the Leto cherry is planted in a lowland, before the onset of frost, bend down its branches and cover the bush (tops, straw, special artificial material).
The subtleties of caring for felt cherries will be demonstrated by the video https://youtu.be/38roGOKzaKA
Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
Disease / wrecker | Symptoms | Warning and ways to fight |
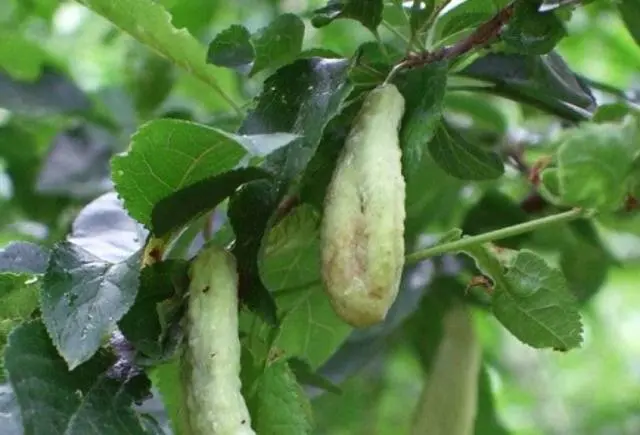
“Pocket Disease” | Fungus spores germinating on branches and in ovaries. The latter, instead of fruits, form soft pods with spores inside. | Destroy the diseased parts of the plant. Spraying the plant with a fungicide (Fitosporin-M, Skor, Horus) |
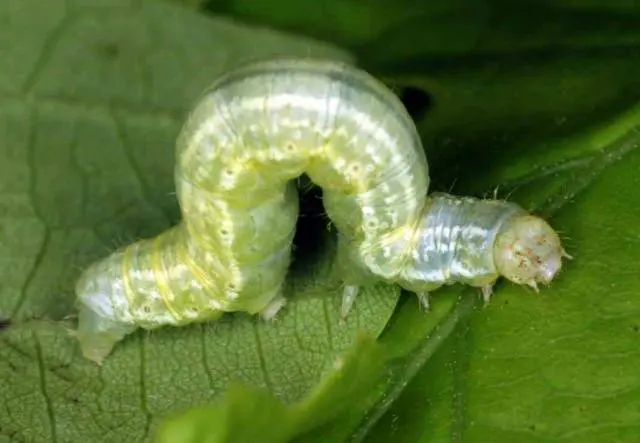
Codling moth plum | The larvae feed on the pulp of the berries. Affected berries stop growing, dry | Place butterfly traps in the garden (containers with sweet compote mixed with glue). Processing bushes with Decis, Alatar, Karbofos or Kinmiks |
Rodents | In the lower part of the plant, the bark is peeled, gnawed | Wrap the barrel with a metal fine mesh. Spread bait with mouse poison around the bush |

Conclusion
Felt cherry Leto is a variety that combines the features of sand and felt cultures. An unpretentious compact bush with large berries was originally intended for northern latitudes. And although Leto does not produce large yields, its self-fertility, good frost tolerance and high resistance to moniliosis allowed the variety to quickly win the recognition of gardeners throughout the country.









