Contents
Fattening pigs is one of the main tasks of a pig breeder. Only the best individuals are left for breeding, the rest must be grown and sold as quickly as possible. The longer the piglet grows, the less profit its owner will receive after selling the meat. Diets for pigs have been developed that allow getting meat or lard at the output.
What do pigs eat
Pigs are omnivorous mammals. In the wild, they eat anything they can find:
- roots;
- mushrooms;
- grass;
- acorns;
- insects and their larvae;
- bird eggs and chicks;
- away
Boars will not refuse to come to the potato field and conscientiously plow it, having eaten the entire crop. Domestic pigs are no different from wild relatives in this respect. At home, no one will feed pigs with “forest delicacies.” The exception is acorns. But even here, pigs leading a semi-wild lifestyle are more often fed with acorns. This method of pig breeding is practiced in Hungary.
Usually, feeding pigs at home is carried out with grain concentrates, root crops and kitchen waste. Pigs rarely get meat. Regulated feeding of pigs allows you to get products of different quality:
- lean pork with hard fat;
- fatty meat and soft, smearing fat;
- lard with layers of meat.
The diet of pigs in this case is strictly standardized and regulated. Such animals cannot be sent to free grazing in the forests.
What not to feed pigs
Contrary to the saying “the pig will eat everything”, you can not feed piglets with all kinds of products. The principles for determining feed that is not suitable for pigs are the same as for the rest of livestock. When giving fresh grass, you need to make sure that poisonous plants do not get there. There are quite a lot of such plants and it makes no sense to list them, since the “herbaria” differ depending on the region. Each owner will have to independently study the flora near his farm.
Other feeds for pigs are “standard”: cereals, root vegetables and feed of animal origin. Do not give to pigs:
- compound feed with the smell of mold;
- “burning” grain;
- rotten roots;
- sprouted potatoes.
Such feed will lead to poisoning of animals.
Types of fattening pigs
Pigs are fed, wanting to get 3 types of products:
- meat;
- fat;
- bacon/bacon with meat streaks.
It is impossible to get everything from the same pig, so it is necessary to choose how to feed the piglet to obtain one or another product.
No matter how ridiculous it sounds, but the types of feed in any direction of cultivation are the same. Their ratio and feeding time vary. There is no miracle food that is better to feed pigs so that they quickly gain weight. There is the right balance between protein, fats, carbohydrates, amino acids and minerals. Without lysine, it will be very difficult to fatten a pig for meat, and without vitamins, not a single piglet can be raised. At the same time, feeds differ in efficiency and the result obtained. Therefore, when feeding, it is also necessary to take into account the properties of each type of feed.
How to properly feed pigs
The protein ratio in the diet affects the build-up of muscle or sebaceous mass. The protein ratio is calculated by the formula:
PO – protein ratio;
BEV – nitrogen-free extractive substances.
A pig receives digestible protein from feeds containing nitrogen. A narrow protein ratio is called a ratio of 1:6, that is, on the right side of the formula, the result should be equal to 6 or less. With this protein ratio, the pig builds muscle mass. The yield of fat is small, the product is solid.
With a wide protein ratio: 1:8-1:10, the pig is salted, gaining a small amount of meat. The fat is soft, smearing. The quality of such fat is considered low.
The quality of pork is also affected by the feed itself. They are all divided into 3 groups:
- improving;
- worsening fat;
- deteriorating meat.
When feeding the second group, the fat turns out to be watery, soft, smearing and tasteless. When feeding the third group, the meat acquires an unpleasant aftertaste and a watery texture.
Improved foods include:
- peas;
- wheat;
- rye;
- barley;
- carrot;
- beets;
- buttermilk;
- return;
- meat flour.
Table squash as feed for pigs is not very suitable. Therefore, young animals raised for meat are usually not fed with it. The production of fodder gourd is underdeveloped. But studies have shown that feed squash is one of the best feeds for pigs not only during fattening. She was fed to the breeding stock in an amount of up to 19 kg per head per day. Feeding fodder pumpkin in the amount of 30% of the diet led to an increase in daily weight gain up to 900 g in six-month-old gilts.
But fodder pumpkin is more suitable for fattening pigs for lard and bacon. When feeding raw and boiled pumpkin in the amount of 15-20 kg per day, gains from 500 to 800 g were obtained.
Group of feeds that worsen fat:
- soybeans;
- corn;
- bran;
- oats;
- cake;
- potatoes;
- fish flour.
Salo turns out to be worse in taste, soft and smearing. These products are best fed at the first stage of fattening.
Feeds that degrade the quality of meat include waste from the production of wine, alcohol and sugar:
- mezga;
- loss
- at the bar.
The meat acquires an unpleasant smell and taste.

Compliance with the regime
All animals are conservatives who do not like change and violation of the established regime. Animals very quickly get used to the established daily routine. Violation of the regime causes anxiety and stress. It is even better to clean the pens at the same time, and unsystematic feeding impairs the digestibility of the feed and can lead to gastrointestinal diseases.
Therefore, it is better to feed the pigs at the same time. “Knowing” the schedule, the pig will wait for food, and gastric juice will begin to be produced in the stomach in advance. The frequency of feeding is set by the owner. The minimum amount is 2 times a day. If there is someone to look after, then they are fed three times a day. At the enterprises of meat-fed pigs, in general, they often do not restrict access to feed. But in this case, they usually give dry feed.
It is convenient for a private owner with a large livestock to use bunker feeders, where dry concentrates or compound feed are poured. The feeder prevents pigs from throwing feed on the floor and does not restrict access to feed throughout the day.
Although the pig is omnivorous, it does not digest whole grains very well. Her teeth are not really meant for long chewing. The animal swallows food in large pieces. Because of this, whole grains pass through the intestines intact. Grain pigs are best given in crushed form. For better digestion of food, porridge is cooked for animals. In winter, warm porridge also helps piglets keep warm.
Separate feeding of piglets
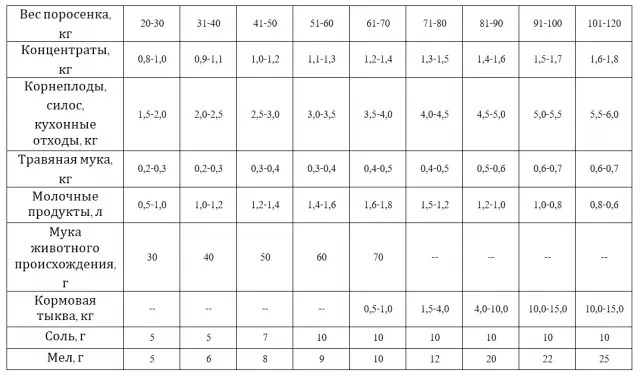
Up to a month, the main food of a piglet is mother’s milk, although they begin to try “adult” feeds after 10 days. Piglets are accustomed to vitamin and mineral supplements from the 5th day of life. After 7 days, a little fried cereal grain is given. 10 days after birth, piglets are fed with fresh cow’s milk or milk replacer. From the same time, they begin to feed concentrates.
From a month to two, piglets can eat with the sow, and she will not strongly drive them away from the feed. But at the time of feeding milk to piglets, it is better to separate the sow. Also, the pig still allows the piglets to suckle itself, although already from a month it is desirable to feed the brood with reverse and milk porridge separately from the mother.
From the age of 2 months, the sow believes that the cubs are able to get food on their own, and begins to aggressively drive them away from the feed, not letting them near the nipples. From this point on, the piglets are separated from the sow and fed separately. Dairy products must be included in the diet of a piglet up to 3 months.
The division of the diet by type of feeding is done from 3-4 months of life of piglets. At this time, pigs are fed. The diet is calculated based on the type of desired product.
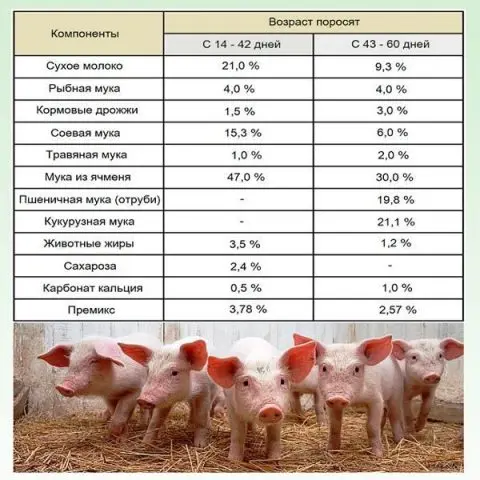
Fattening pigs at home for meat
In theoretical pig breeding, to obtain lean pork, you need to take elite meat breeds: Landrace, Duroc, Pietrain. In practice, everything is more difficult. The listed breeds really give high-quality meat with a minimum of fat. But because of the thin layer of fat, these pigs are very demanding on the temperature regime. It is difficult for a private trader to maintain a year-round narrow temperature range, therefore, in practice, they use a large white breed of pigs. This breed is officially considered meat-greasy, but it has lines of the meat direction. When crossing Large White with meat breeds, hybrids inherit good climate resistance. The quality and yield of meat from the carcass of hybrid pigs also increase.
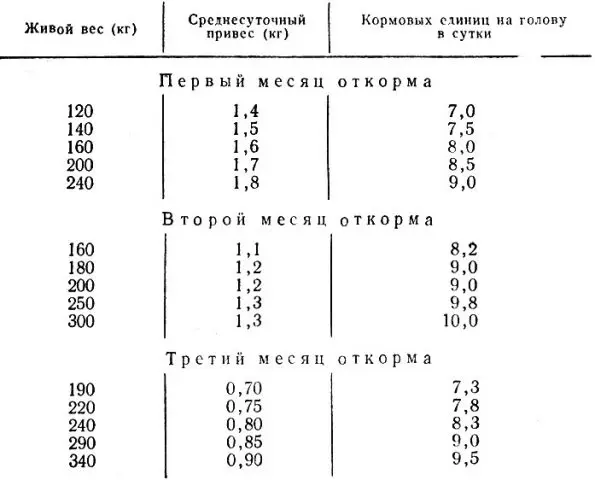
Piglets are put on meat fattening from 3-4 months. Finish fattening when the piglet reaches 100-120 kg. At the beginning of fattening at 3 months and a daily weight gain of 550 g for 6 months, a pig can be grown up to 120 kg. With the meat version of feeding, it will not be possible to fatten the pigs as quickly as with the greasy one, since the meat grows more slowly, although it is heavier than fat.
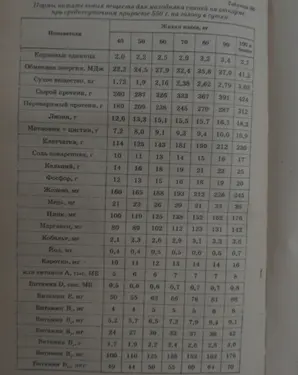
When feeding for meat per 100 kg of piglets, 4,2-4,8 feed is required. units in the first fattening period and 3,5-4,2 feed. units in the second. Digestible protein in the first period needs 90-100 g per 1 feed. units, in the second – 85-90 g.
The average daily weight gain can be increased or decreased. For rapid growth, pigs need to be properly fed, that is, given foods that will have as much energy as possible in the dry matter and as little fiber as possible. With meat fattening, the optimal content of fiber in dry matter is not more than 6%.
Pig diets
The basic principle when feeding pigs for meat: in the first period they give more protein feed, in the second – carbohydrate. For winter fattening, there are 3 types of diets. They differ in the presence or absence of potatoes and root crops in the feed.
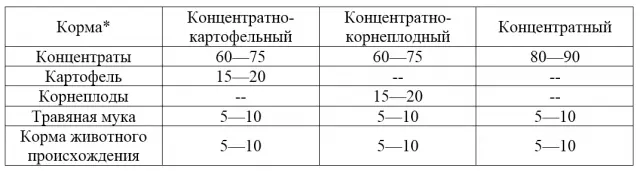
Feeds are indicated as a percentage of the need in feed units.
In this case, concentrates mean:
- corn;
- peas;
- barley;
- wheat;
- wheat bran;
- compound feed (2-3 kg per day);
- meal: soybean, linseed, sunflower.
In the first half, you can feed any concentrates, but a month before slaughter, you need to exclude those that worsen the quality of pork.
The category of succulent feed includes:
- silage;
- beet;
- potatoes;
- fodder gourd;
- kale;
- fodder beet;
- carrot.
Cabbage has the ability to stimulate the secretion of gastric juice. When feeding a large amount of cabbage, the stomachs of animals inflate. Root crops and vegetables are fed in the amount of 3-5 kg per day. Silage give 1-1,5 kg. Since silage is a product of fermentation, you should not get carried away with its quantity either.
From products of animal origin, pigs are fed:
- reverse (1-3 l);
- pahtoi (1-3 l);
- meat and meat and bone meal;
- blood meal;
- low-fat minced fish and fish meal (20-40 g).
Herbal flour made from leguminous plants is given 200-300 g per day. Flour before feeding should be soaked in cold water. Often it is sold in tightly compressed granules. Swollen in the stomach, flour can clog the intestines.
In summer, instead of grass flour, legumes 2-4 kg per day are included in the diet. At any time of the year, mineral additives must be mixed.
Vitamin-mineral premixes are placed at 10 g per 1 kg of dry matter of the feed. If necessary, balance the ratio of protein and carbohydrates with the help of protein-vitamin and protein-vitamin-mineral supplements. The lack of lysine in the diet is replenished with lysine feed concentrate. The need for pigs in this amino acid is 5-10 g per day.
Pigs are fed on meat for about 6 months with a daily weight gain of 550 g. A larger weight gain usually means that the pig has begun to lean.
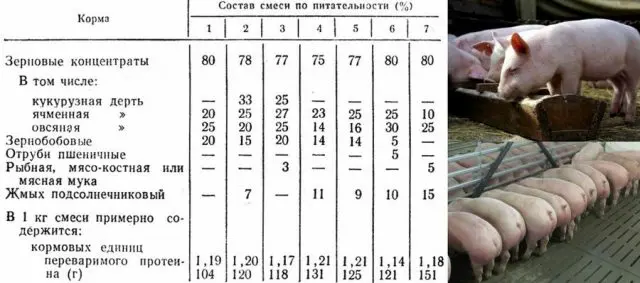
Final fattening period
Before slaughter, the pig must gain at least 100 kg of live weight. At the second stage, it is undesirable to feed products from those groups that degrade the quality of pork. It is better to refuse fish products immediately after the start of the second fattening period, replacing them with meat meal or dairy products. Also at this stage it is better not to give food that degrades the quality of fat. A month before slaughter, you need to stop giving food that worsens the quality of meat.
How to feed pigs for bacon
Bacon fattening is considered a variety of meat pigs, meat pigs in the West are also often called bacon pigs. In Our Country there was a certain division of concepts. Bacon began to be called lard with meat streaks. For bacon, meat breeds and their hybrids are also chosen. Meat-greasy piglets can sometimes be used if the breed is not very prone to obesity. In Our Country, most often, and for these purposes, they prefer to choose a large white breed.
Weight gain when feeding for bacon can be even higher than for meat. No wonder it is considered intense. But gains increase with a set of fat, not meat. Fattening for bacon is considered the most profitable with a daily weight gain of 600-700 g.
Piglets are selected more strictly for bacon than for meat. The piglet should be long-bodied and have a level bottom line. No drooping belly. For bacon fattening, gilts are preferred, as they produce less greasy bacon than hogs. Piglets are put on fattening from 3 months of life, after reaching a weight of 30 kg.
Animals not suitable for obtaining bacon:
- older age;
- pregnant or farrowing sows;
- uncastrated boars;
- boletus castrated after 4 months of age;
- late maturing breeds;
- pigs with traces of injuries;
- animals with signs of disease.

Features of feeding and maintenance
Fat in pigs is recruited with a calm lifestyle and feeding carbohydrates with a high energy value. Meat grows with a lot of movement and protein-containing feed. It is not enough to feed the pig so that the fat is with layers of meat. She must also be forced to move during the period of time when she must increase the meat. That is, they combine 2 factors: food and lifestyle.
But for this, in the “greasy” period, it is necessary to provide the pig with a quiet life in the barn, and in the “meat” period, force it to walk. The ideal option at this moment would be to “walk” the animal to a distant pasture.
In other words, the “convenient” keeping of a pig in a barn with the issuance of feed to it is not suitable here. If we are talking about bacon in the foreign sense of the word, that is, pork cut from the ribs, then everything is simpler. Most often, for these purposes, they take the same meat breed and put it on a more intensive fattening than when obtaining meat.
3-month-old piglets are first fed in the same way as for meat, receiving 500 g of daily weight gain. In the second half, they are transferred to fat fattening with daily gains of 600-700 g.
Feeding rations
At the first stage, you can use the feeding rations developed for meat products. From the second, protein feeds are halved against the meat feeding option. The share of grain concentrates, on the contrary, should be greater than when feeding for meat. From the second half of fattening, pigs can be given fodder pumpkin, which contributes to fat gain.
In the first two months, pigs can be fed cheap, high protein feed:
- oats;
- bran;
- cake.
These feeds have a negative impact on the final product, but at the first stage it does not matter. From the second period, cheap feed is removed and pigs are transferred to barley, peas and rye. You can also give millet, but it will be more expensive.
Another option for a more detailed feeding ration for bacon, in which animal feed is completely removed at the last stage.
The final stage
As with meat fattening, in the last month before slaughter, all feeds that impair product quality are excluded from the diet. In general, pigs for bacon are fed the same way as for meat. All pigs are prone to brining. When fed for meat on the ribs, the same bacon is obtained, but with a thinner layer of fat. Moreover, the thickness of the fat often also depends on the individual characteristics of the pig.
Bacon piglets are fed for about 6 months. At the end of fattening, the piglet should weigh 80-100 kg.
Technology of fattening pigs to fat conditions
For fattening pigs are selected not so much by breed as by unsuitability for anything else. Usually, lard is fed to mature sows and boars culled by age from the main livestock. Also included in this group are young, but unproductive sows. For this reason, feed for lard starts at the weight at which meat and bacon fattening ends. That is, up to fatty conditions, pigs begin to be fed from 120 kg of live weight.
If initially the goal was to get fat from the piglet, then for fattening to fat conditions it is better to take the same large white from the lines prone to salting. Also, a good return is received from the Hungarian mangalica.
The task of such feeding is to get the maximum amount of high-quality fat and internal fat in the shortest possible time. Fattening lasts 3 months. During this time, the pig should gain another 50-60% of its original weight. The thickness of the bacon in the region of the ridge in the region of the 6th-7th ribs should reach 7 cm.
Pigs are examined before fattening. The emaciated in the first month are fed like meat, bringing them back to normal condition. Then apply the technology of fattening to fatty conditions.
This meat is used to make sausages. It is too tough for use in the form of steaks and chops.
What to feed pigs
Pigs are fed 2 times a day with wet nutrient mixtures. In the first half of fattening give up to 60% concentrates. The rest is supplemented with voluminous feed:
- root crops;
- potatoes;
- silo;
- hay;
- other vegetables.
Oats, bran and cake are given in very small quantities. The need for feed units is calculated taking into account the live weight of the pig and the planned weight gain. On average, there should be almost 2 times more feed units in the diet than when feeding for meat.
In the second half – the last third of the period, the share of concentrates during feeding is 80-90% of the total diet. Juicy feed is reduced to 10-20%. Cakes and bran are completely removed and concentrates from the “improving” group are introduced: wheat, rye, barley, peas.
Practice shows that good results are obtained when feeding pigs:
- silage from corn cobs in milky-wax ripeness;
- turd from corn;
- potatoes.
But these products are suitable only for the first stage of fattening. Corn mash is best fed mixed with fresh grass or legume hay.
When fattening a large group of pigs for fat, not only feed is important, but also the conditions of detention. “Greasy” pigs contain 25-30 individuals in one paddock. For a private owner with a small livestock, this issue is not relevant. But even a small farmer will be forced to comply with the conditions of detention.
What to feed pigs for rapid growth
It is beneficial for the owner that the pig grows as quickly as possible. It cannot be said that the addition of vitamin and mineral premixes accelerates the growth of pigs. But without vitamins and minerals, the development of piglets stops. Therefore, premixes are added necessarily for the normal growth of the pig.
“Accelerators” of growth are antibiotics that fight pathogenic microflora. Without gastrointestinal infections, a pig grows slightly faster than one that expends energy fighting microorganisms. When growing for sale, it is beneficial to use such bactericidal preparations. On sale, they can usually be found under the name “growth accelerators.” One of these drugs is Etonium.
The advantages of any antibacterial drugs are that fattening pigs get sick less and gain weight better. Cons from the point of view of the consumer are drugs.
With accelerated growth, bones and joints do not have time to form. The animal grows up disabled. But for the future of meat it does not matter.
Conclusion
Fattening pigs for meat in these days of promoted healthy eating is more profitable. But lard provides a significant amount of energy and in some cases it is better to fatten pigs for lard than for meat.










Acha nione kama ushauri wenu una reason