Contents

Farsightedness, or scientifically hypermetropia, this is a visual impairment in which nearby objects are visualized indistinctly, and distant ones are much better, although in a severe form of this disease, the child does not see well at any distance. According to ophthalmic systematization, hypermetropia refers to ametropia, that is, to anomalies of refraction (the process of refraction of light rays passing through the optical medium of the eye). Normally, the rays should focus exactly on the surface of the retina, in the region of the macula (macula). So, if the focus shifts forward, myopia (nearsightedness) occurs, and if it moves back – hypermetropia (farsightedness).
A slight degree of this pathology in early childhood should not cause concern to parents, moreover, almost all babies under 3 years old have physiological hypermetropia, and this is completely normal. The child grows and develops, his eyes undergo changes – the correct relationships are established between their individual structures, due to which vision gradually becomes sharp both near and far. However, unfortunately, this does not always happen. It is very important to notice the violation in time in order to be able to successfully correct it.
Hypermetropia is a very insidious disease, which in childhood is characterized by the secrecy of symptoms, unpredictability of the course and a high risk of developing serious complications. Children with this pathology experience learning difficulties, cannot focus on small nearby objects for a long time, suffer from headaches, sleep poorly, get tired quickly and act up. Today we will tell you how to identify the problem as early as possible, and what to do if your child is diagnosed with farsightedness.
Causes of farsightedness in children

To understand the mechanism of development of this disease, let us consider in more detail the process of refraction. So it depends:
From the shape of the cornea – a transparent organic lens that first encounters light rays penetrating the eye. If the convexity of the cornea is weak, the rays are not refracted enough, and this contributes to a shift in focus to a plane conditionally located behind the retina, and not on it;
From the distance between the cornea and the lens, and then between the lens and the retina – if it is too small, the problem is aggravated;
From the shape of the lens and its ability to accommodate – with the help of the efforts of the ciliary muscle, the curvature of our second, biconvex organic lens can change. If the focus of light rays “left” behind the retina, it can be forced into place, expanding the lens and thereby increasing its refractive power. Accommodation compensates for refractive errors within five diopters, but this requires strain on the visual apparatus and leads to its accelerated wear;
From the length of the PZO of the eyeball – the anteroposterior axis is a segment between the cornea and the macula, and if it is shorter than the physiological norm, hypermetropia inevitably occurs.
Thus, it is possible to combine the causes of farsightedness in children into two groups: defects in the refractive function of the cornea and / or lens and insufficient length of the eyeball in the anteroposterior direction. It is noteworthy that these factors can be combined with each other in an arbitrary order. The least potential danger is children’s hypermetropia against the background of shortening of the ASO, since there is a chance that the eyeball will grow to the desired parameters. If the disease arose due to violations of the cornea or lens, the prognosis is less favorable.
Heredity can lead to the occurrence of farsightedness: if one or even both parents of a baby have such a problem, he needs regular examinations by an ophthalmologist, starting from the age of 6 months. Pathologies of the course of pregnancy, bad habits of the expectant mother, and tense environmental conditions can aggravate the genetic factor. In very rare cases, hypermetropia in a child is the result of a congenital absence of the cornea and / or lens (aphakia). Such deviations in the development of the fetus are usually combined with each other and lead to serious consequences, up to complete blindness.
Farsightedness in children: the norm and deviations

There are two forms of childhood hypermetropia:
Physiological;
Congenital.
In babies 1, 2, 3 years old, farsightedness is natural, physiological in nature, if it is within +3 diopters. This is the case for 90% of kids. It is, in fact, incorrect to talk about congenital, pathological hypermetropia before the age of 5, 6, 7, because before this age the eyes actively grow and develop, the situation can still correct itself. Only in the case when a preschool child has a deviation from normal vision of +5 +6 diopters or more, it can be unequivocally stated that there is a congenital pathology that requires treatment.
Farsightedness in the chest

In an infant, the eyeballs are not at all the same as in an adult: they are shorter (16-17 mm versus 24-25 mm) and rounded, and the curvature of the cornea and lens, on the contrary, is less pronounced. There is even a special medical term – “physiological farsightedness of newborns”, which describes the normal state of the visual apparatus of babies who have just been born. The norm is within +2 +4 diopters.
If the indicator is exceeded, this may indicate microphthalmos (pathological reduction of the eyeball) and its accompanying defects:
Cataract (clouding of the lens);
Aphakia (lack of the lens);
Coloboma (absence of part of the eye membrane);
Aniridia (absence of the iris);
Lenticonus (spherical or cone-shaped lens).
The listed pathologies of the eyes are often combined with other congenital malformations, for example, with a “cleft lip” or “cleft palate”. If the baby has a burdened history and unfavorable heredity, he needs to consult an ophthalmologist no later than six months of age.
In children under 1 year of age, farsightedness, as a rule, is not diagnosed, since it is very difficult to notice visual impairment in the absence of any other abnormalities in the state of health. However, if hypermetropia up to +3 diopters is detected at this age, you should not worry, this indicator is a variant of the norm.
Farsightedness in a child 1-3 years old

At one and a half to two years, parents usually already know about the presence of a similar feature in their child, thanks to a preventive examination. A pediatric ophthalmologist can accurately determine the degree of hypermetropia and give the necessary recommendations, if necessary.
It is noteworthy that too large, or vice versa, too small stock of farsightedness in this period is an alarm signal. If a child of 1-3 years old is diagnosed with hypermetropia above the physiological norm, this can lead to the development of strabismus and amblyopia, and if lower, to myopia.
Farsightedness in children 4-7 years old

By the age of four, most kids are already attending a kindergarten, where they are offered a lot of interesting activities related to increased use of near vision: modeling from plasticine, collecting pyramids and cubes, drawing and coloring, cutting applications from colored paper, and so on. Games are being replaced by the development of more serious skills – counting, reading, writing. If at the same time a child of 4, 5, 6 years old suffers from moderate or high hyperopia, the problem will certainly manifest itself as learning difficulties, headaches, watery eyes, fatigue and irritability.
There are other sure signs of hypermetropia in preschoolers:
In the process of drawing, coloring, modeling, the baby does not bend over the work;
Looking at the pictures, the child holds the book on outstretched arms;
If you place an interesting object in front of the baby’s face, he will take a step back.
The age of seven is a kind of milestone: if by this time there is congenital, pathological farsightedness, it will most likely be diagnosed as part of a pre-school medical examination. Such a first grader will most likely need glasses in which he can study without overstraining the visual apparatus.
Farsightedness in a child 8-12 years old

At this age, it is no longer necessary to talk about physiological hypermetropia, which passes on its own – the length of the PZO of the child’s eyeballs should reach the norm of 23-24 mm, and vision should become emmetropic, that is, one hundred percent. Any deviation from these indicators is a pathology and needs to be corrected.
It is not difficult to detect farsightedness in a student of primary and secondary school, because in addition to the obvious signs of a problem (difficulties with the educational process, eye fatigue, low reading speed), complaints and subjective feelings of a sick child, who is now old enough to to describe them clearly.
A son or daughter will point out to you the fuzziness of the contours of objects, lacrimation and photophobia, headache, burning, discomfort and a feeling of fullness in the eyeballs that occurs after several hours or even minutes of active use of near vision. All this indicates the presence of a moderate or high degree of hypermetropia.
Farsightedness in adolescents 13-16 years old
By this age, the human visual apparatus completes its growth and development, the length of the posterior eyeball reaches 24-25 mm. If this does not happen, the boy or girl probably has some kind of ametropia.
Teenagers with hyperopia do not have to wear glasses – they can switch to more comfortable and discreet contact lenses. And upon reaching the age of sixteen, young people have new opportunities in the treatment of farsightedness – laser correction. But in some clinics, such operations are performed exclusively from the age of 18.
Spectacle correction of vision
Successful selection of optics for hypermetropia in a child depends on compliance with the following rules:
Each eye has its own lens. With this visual impairment, a situation is very often encountered when one eye sees better, and the other worse. Moreover, the difference in refraction can reach impressive values. The larger it is, the higher the risk of developing such a formidable complication as amblyopia;
The lens should “unload” the sore eye as much as possible. It’s about accommodation. If you choose the first lens for glasses, in which the child clearly sees the letters in the tenth row of the visometric table, this will be wrong, because he sees them, tensing the ciliary muscle as much as possible and stretching the lens. Therefore, the ophthalmologist uses this technique: increases the refractive power of the lenses until the tenth rad starts to look blurry. The lens that preceded this will be the required one;
Binocular vision needs to be checked. Sometimes it happens that the lenses for each eye are perfectly matched, but when they are combined, the effect of diplopia (doubling of the picture) occurs. Therefore, before writing a prescription for ready-made glasses, you need to make sure that the child sees correctly and clearly with the selected lenses;
Lens tolerance and comfort level should be assessed. Let the young patient sit in them for some time, try to read something or look at it from a close distance. If at the same time there are no negative symptoms (burning, cramps, tearing, tension, pain in the eyes), we can conclude that the glasses are suitable for the baby;
It is necessary to accurately measure the distance between the pupils. This is a segment connecting the outer edge of the cornea of one eye with the inner edge of the cornea of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe other. The fact is that the frame can have different parameters, therefore, the lenses in the finished glasses can move apart or closer. If they are installed incorrectly, the child will not be able to see well in such a product.
Gymnastics for the eyes
With hypermetropia in babies, it is useful to perform the following simple exercises:
Gently massage the eyeballs with the eyelids closed, performed with the fingertips of the parent, in gentle circular motions clockwise and then counterclockwise, for five seconds with several repetitions;
“Snake”. Lay the child horizontally on his back, take a bright toy, lift it to a height of about a meter above the baby’s face, get his attention, make sure he fixes his eyes on the object. Then slowly bring the toy closer to the eyes, making winding movements so that the child follows it. Repeat 2-5 times;
“Ball rolling”. Sit with the baby on the floor opposite each other at a distance of about one meter, legs apart. Take a small bright ball, and roll it towards the child, asking you not to take your eyes off the toy, otherwise, according to the rules of the game, it will be “lost”. Let the kid catch the ball and send it back to you, and so on several times;
“Zhmurki”. This simple relaxing eye exercise is great for little kids. Make a funny grimace, and when the baby pays attention to you, alternately close your eyes and open your eyes wide – your son or daughter will certainly repeat after you, simultaneously improving eye circulation and training visual muscles;
“Reading”. Such an exercise can be offered to a child mastering the first books. It should be in large print. First, determine the maximum distance from which the baby can see the letters well. Ask him to read a few lines. Then turn the page and bring the book closer to 10 cm. Have the child read a couple of lines again. Repeat these steps until the book is 15-20 cm away from the baby’s face.
Older children may well perform “adult” gymnastics for the eyes:
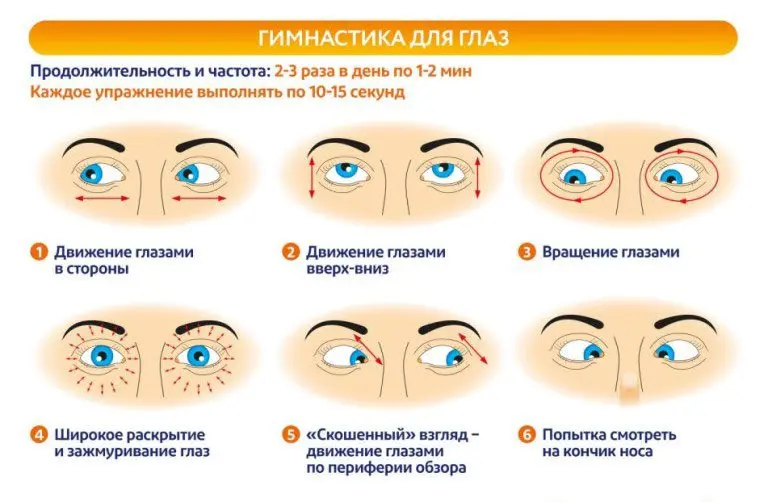
Sports and outdoor games
Children with a weak degree of farsightedness are very useful for active activities associated with frequent changes in the focus of their eyes on moving objects located at different distances. These are games such as football, volleyball, basketball, hockey. Any sports that involve a projectile that you need to follow with your eyes will train the accommodation mechanism and help fight hypermetropia.
With an average degree of farsightedness, too dynamic games, such as football or hockey, can be dangerous for the child, since his visual apparatus will get tired faster than that of his peers. And this is fraught with tearing and headaches, not to mention blurred vision and the risk of injury. Swimming, table tennis, badminton are recommended for such children.
A high degree of farsightedness makes mobile sports impossible for a child. But this does not mean that physical education should be banned altogether, because the health of the visual apparatus depends, among other things, on good health, proper blood circulation and strong muscle tone. A child with severe hypermetropia should do morning exercises, and at the same time with it, gymnastics exercises for the eyes.
Vitamin therapy
On the table of a child with hyperopia, there should be foods rich in vitamins and microelements useful for vision:
Dried fruits (figs, dried apricots, prunes, raisins);
Nuts (walnuts, almonds, hazel, cashews);
Fresh fruits and berries (bananas, apricots, peaches, oranges, blueberries);
Vegetables and greens (carrots, cabbage, tomatoes, celery, parsley).
The decision on the additional intake of vitamin-mineral complexes or biologically active food supplements should be made by a doctor. Such products may be of dubious quality or simply not suitable for your child. You should not buy a widely advertised drug to improve vision for reasons of “it definitely won’t hurt”, because hypervitaminosis and an excess of some micro and macro elements are no less dangerous to health than their deficiency.
Prevention of farsightedness in children

If a baby is diagnosed with a mild degree of hypermetropia, this is already an occasion to think about prevention. When a child is making something, drawing or reading, his workplace should be lit by an overhead chandelier or table lamp with a power of 60-100 watts. Every 30-60 minutes of such activities, you need to distract the baby and take a break, it is best if it is an outdoor game, exercises for the eyes, a small home task or a walk in the fresh air. At least do an eyeball massage or a blind man’s buff exercise.
Of course, the main “root of evil” lies in the gifts of modern civilization – TV, computer, tablet. It is about these devices that children “kill” their eyes, even if there were no rudiments of visual impairment. What can we say about the existing farsightedness? The most harmful thing a sick baby can do is sit in front of a TV or monitor for a long time, play games on a tablet or smartphone. The second is even worse because the image is usually too close to the face. Of course, this does not mean that all electronic devices should be thrown out of the house as soon as a son or daughter has been diagnosed with farsightedness. You just need to limit the time of their operation to reasonable limits or take breaks more often. Take care of the children and be healthy!
Author of the article: Degtyareva Marina Vitalievna, ophthalmologist, ophthalmologist









