Contents
The whole world is currently fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. While everyone is focused on defeating SARS-CoV-2 as soon as possible, experts warn that we are facing another global threat from infectious diseases. What are they talking about?
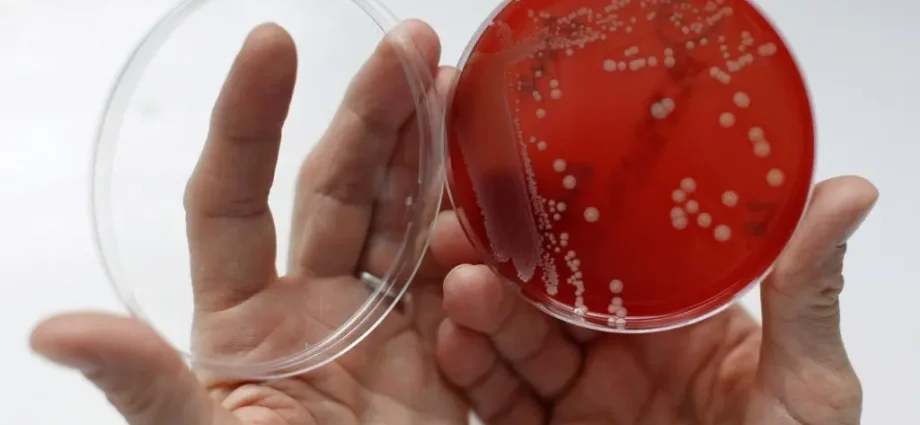
- Antibiotic-resistant bacteria may become a comparable threat to the coronavirus
- Around 700 people die worldwide from antibiotic-resistant infections. people.
- According to estimates by the World Health Organization, the number of victims may reach 30 million in the next 10 years
- Experts: This is already a global crisis that is worsening under the influence of the current coronavirus epidemic
- You can find more such stories on the TvoiLokony home page
The problem is not new – doctors raised the alarm long ago. If their fears materialize, there will be nothing to heal the sick, and the infections and injuries we have dealt with for decades will again become the cause of death. Organ transplantation or chemotherapy, for example, will also become impossible. What is it about? I am talking about resistance to antibiotics.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are not getting as much attention as COVID-19. The diseases they cause do not attack as violently as SARS-CoV-2, on the contrary, they spread slowly and evenly. Nevertheless, according to scientists, these pathogens may become a threat comparable to the coronavirus.
- The post-antibiotic era has begun. Even mild infections can kill
According to estimates by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, an agency of the US federal government that is part of the Department of Health and Human Services), nearly 3 million Americans develop an antibiotic-resistant bacterial infection each year. Of these, about 35 thousand. dies.
Around 700 people die worldwide from antibiotic-resistant infections. people. According to estimates by the World Health Organization, the number of victims may reach 30 million in the next 10 years.
Where does drug resistance come from?
Where does the problem of antibiotic insensitive superbugs come from? Experts remind that the spread of microorganisms with drug resistance mechanisms was caused, among others, by abuse of these agents in both human and veterinary medicine. Meanwhile, not every infectious disease should be treated with an antibiotic, we give these measures as a last resort, specialists note.
- Antibiotics and bacteria, or the arms race
Taking the wrong dose or taking it irregularly also contributes to the development of drug resistance. That is why it is so important to take the antibiotic only in justified cases, in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations and without randomness (because, for example, we have drugs from the previous treatment).
New research also suggests that contamination of the environment with heavy metals may contribute to the resistance of bacteria to antibiotics.
As a result, infections with some pathogens have become extremely difficult to treat. This is because a small fraction of the bacteria that an antibiotic fails to kill in its defense against it evolve and multiply by developing resistance. Such a problem concerns, for example, the treatment of antibiotic-resistant tuberculosis. It is estimated that around the world it costs 230 lives. patients per year.
- Mycobacteria strike back. Tuberculosis more dangerous than ever?
Tom Frieden, former director of the CDC and CEO of Resolve to Save Lives, notes that there is a need to focus specifically on how infectious diseases spread in hospitals. “ I have absolutely no doubt that in 20 or 40 years we will look back at healthcare implemented in 2020 and shake our heads wondering how we allowed so many infections to spread in healthcare settings.
- The antibiotics stop working. There will be no drugs for superbugs soon?
Experts emphasize that too little is said about the problem of drug resistance. – Unlike COVID-19, which emerged suddenly with tremendous force, the superbug crisis is in full swing. This is already a global problem that is worsening under the influence of the current coronavirus epidemic, says Steffanie Strathdee, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego (USA). Most of the attention and resources that could be spent on fighting bacterial threats goes to trying to defeat COVID-19. In this sense, the coronavirus pandemic may aggravate the problem of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, the expert notes.
- Do antibiotics fight the coronavirus?
In July, the WHO called for more cautious use of antibiotics among COVID-19 patients to help reduce the risk of bacterial resistance. Analyzes from May showed that out of about 2 COVID-19 patients hospitalized around the world, 72 percent received antibiotics, although only 8 percent. documented bacterial or fungal infections.
Lance Price, founder of the Antibiotic Resistance Action Center at George Washington University, points out that the COVID-19 pandemic has revealed how a “dysfunctional” public health system “exposed us to slowly spreading antibiotic-resistant bacteria.”
It is also worth emphasizing that antibiotics can cause allergic reactions. In the case of non-specific symptoms, it is worth performing an antibiotic allergy diagnosis available on Medonet Market at an attractive price.
You may be interested in:
- Why are bacteria becoming resistant to antibiotics? Discovery of Swedish scientists
- Coronavirus infection can be asymptomatic. How to recognize it? [WE EXPLAIN]
- Vitamin D Deficiency Increases COVID-19 Risk? A disturbing study
- Until recently, it was victorious against the epidemic, today it records infection records. What happened in Iceland?
The content of the medTvoiLokony website is intended to improve, not replace, the contact between the Website User and their doctor. The website is intended for informational and educational purposes only. Before following the specialist knowledge, in particular medical advice, contained on our Website, you must consult a doctor. The Administrator does not bear any consequences resulting from the use of information contained on the Website. Do you need a medical consultation or an e-prescription? Go to halodoctor.pl, where you will get online help – quickly, safely and without leaving your home.