Contents
With euthyroidism, the functioning of the thyroid gland is disrupted. This state can be called borderline. If treatment is not started in time, the disease threatens to turn into such severe forms as diffuse or nodular goiter. Therefore, when a person is diagnosed with euthyroidism, he should be regularly observed by a doctor.
Euthyroidism negatively affects the functioning of the body as a whole. It is difficult to identify the disease, since it is not always possible to determine the pathological process by the level of hormones T3, T4 and TSH. Therefore, it is so important to know the main symptoms of euthyroidism. This will allow you to contact the doctor in time and start treatment.
What is euthyroidism?
Euthyroidism – These are pathological changes in the thyroid gland, which, with properly selected therapy, are reversible. With this disease, the functionality of the organ remains unimpaired.
Symptoms of euthyroidism are important to distinguish from symptoms of other thyroid pathologies, including:
Hypothyroidism. At the same time, the patient develops persistent insufficiency of the thyroid hormones T4 (thyroxine) and T3 (triiodothyronine). They are produced in the body little, or they are quickly destroyed. While the level of pituitary hormone (TSH) remains elevated.
Hyperthyroidism. In this disease, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland is observed. The patient will have elevated levels of hormones such as T3 and T4.
As a rule, euthyroidism does not last long. Serious disorders occur in the patient’s body, primarily related to the performance of the thyroid gland. Therefore, it is so important to recognize the disease at an early stage of development.
The fact is that thyroid hormones are responsible for such important processes as:
Growth and development of the organism as a whole.
Control of the work of the digestive tract, nervous system, heart and blood vessels, musculoskeletal system, reproductive function.
Regulation of metabolic processes. Hormones are involved in the metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates. Without them, it is impossible to maintain a normal water-salt balance in the body.
Formation of the immune system.
Stress resistance.
Euthyroidism – causes
There are several reasons that can lead to the development of euthyroidism, including:
Iodine deficiency in the body. When there is little iodine, the thyroid gland begins to increase in size, which becomes the basis for the development of various serious diseases.
hereditary predisposition. If close relatives of a person suffer from thyroid pathologies, then it is likely that he will also face a similar problem. In order to recognize the disease in time, you need to undergo a thorough examination.
Prolonged stress.
Infectious diseases. Diseases such as tonsillitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis can provoke euthyroidism.
Frequent and uncontrolled use of antibiotics or hormonal drugs.
Inflammatory processes localized in the thyroid gland itself.
Living in adverse environmental conditions.
In pregnancy
Euthyroidism can be found in pregnant women who previously suffered from hyperthyroidism. The level of hormones returns to normal, as the body badly needs them during this period.
When there is no decrease in thyroid hormones, the doctor will recommend drugs to correct the hormonal background. Medical recommendations should not be ignored, since the course of pregnancy and the health of the child depend on this. Therefore, all women with hyperthyroidism need to achieve euthyroidism at least for the period of gestation.
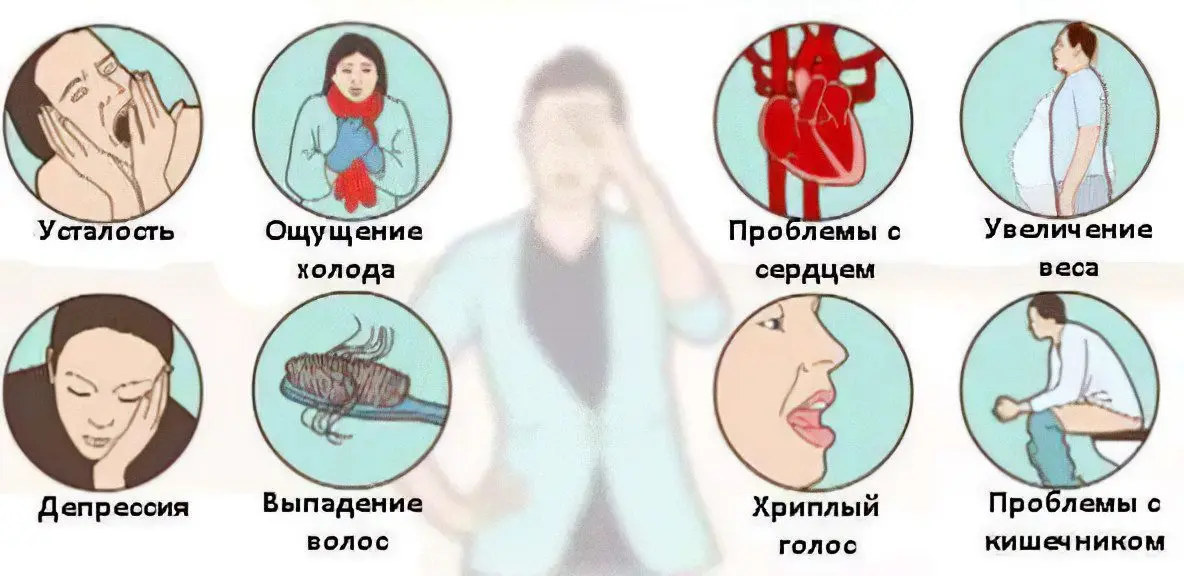
Symptoms of euthyroidism

Since the thyroid gland continues to produce the same amount of hormones during euthyroidism as before, the symptoms of the disease will be mild. People turn to the doctor after they find themselves with an increase in the size of the neck. Moreover, they consider this a problem of an exclusively cosmetic plan. The first symptoms of euthyroidism are manifested by the nervous system.
Nervous system. The person becomes lethargic and may become depressed. Moreover, the obvious reason for this condition will not be identified. Memory begins to deteriorate, cognitive processes in general suffer. If hypothyroidism is congenital, then the child develops cretinism.
Women notice a hearing impairment, their eyesight begins to deteriorate. Often there is numbness of the limbs. Changes in the work of the nervous system lead to the appearance of symptoms from other organs.
Neck. A lump appears in the throat. This leads to difficulty in swallowing food. From time to time, or on an ongoing basis, a person experiences a pressing feeling in the neck. People compare this symptom to the sensation of a noose around the neck.
Heart. There is a violation of his rhythm. Moreover, failures can be both barely noticeable and pronounced. They proceed either according to the type of extrasystoles (extraordinary heartbeats), or according to the type of tachycardia (rapid heartbeat).
The weight. In people with euthyroidism, body weight decreases. At the same time, the person continues to eat as before, that is, he does not follow a special diet. He does not have any serious pathologies.
Forms and degrees of the disease
Depending on the severity of pathological symptoms, there are 3 degrees of euthyroidism:
First degree. The thyroid gland increases in size, but not much. It will not be possible to detect the growth of its tissues with the help of palpation. There are no external signs of a change in its size.
Second degree. The thyroid gland increases in size, but it also cannot be determined by palpation.
Third degree. The thyroid gland increases significantly, this is noticeable during examination and palpation.
In non-toxic goiter, the thyroid tissue increases in size, resulting in the formation of one or more nodes.
Varieties of nodular goiter with damage to the gland:
Endemic. It is formed due to iodine deficiency in the body.
Nodular goiter in euthyroidism. The gland increases in size, but there are no nodes in it.
Nodular goiter 1 degree. In such a goiter, 1 node is formed.
Nodular goiter 2 degrees. In this case, several nodes are formed in the thyroid gland at once.
Nodular goiter with multiple nodes intertwined with each other.
Depending on the stage of development of the disease, the patient will have different symptoms of euthyroidism.
During palpation and examination of the thyroid gland, the doctor can detect both its diffuse structure and several nodes. There may be several or one. Sometimes they merge into a single entity. With euthyroidism, the formation of a mixed goiter is also possible. At the same time, both diffuse and nodular tissues will be present in it. This type of disease is most often diagnosed in older women.
Can there be nodular euthyroid goiter?
A nodular euthyroid goiter may be detected in a patient, but it will not persist for a long time. With a diagnosed nodular euthyroid goiter, experts talk about the functional autonomy of the thyroid gland. After a short time, such a goiter is transformed into thyrotoxic.
Diffuse and hypertrophic changes in thyrocytes occur only at an early stage of the disease. Thyrocytes have a different ability to proliferate, therefore, in some parts of the gland, cells divide faster, and in others, more slowly. For this reason, the patient develops a multinodular euthyroid goiter. When these pathological changes are completed, the transformed gland will begin to produce triiodothyronine, regardless of the commands given by the pituitary and hypothalamus.
What is the danger of euthyroidism?

Euthyroidism can be considered a safe state, but only as long as a person has a normal level of hormones in the blood. If the disorder develops rapidly, then the patient will form a nodular goiter. This pathology requires emergency treatment.
If you ignore the disease, then after some time severe complications may occur. The likelihood of the formation of a malignant tumor, or clamping of the trachea, increases. In such a situation, the thyroid gland has to be removed.
Other complications of euthyroidism include:
Impairment or loss of memory.
Panic attacks.
Disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
primary infertility.
Depression.
High blood cholesterol.
Video: surgeon, doctor of medical sciences Kosovan Viktor Nikolaevich will talk about the methods of treating nodular goiter with euthyroidism:









