Contents
Erythema is a limited area with reddening of the skin, which is caused by increased blood flow. When you press your fingers on the affected area, the redness disappears. External factors, inflammatory and pathological changes can cause such a reaction. Areas of redness may have delineated or blurred borders, accompanied by itching and peeling.
Types of erythema
By the nature of the formation of erythema are:
activearising from an increase in the lumen of the arterial vascular tissue. They are characterized by an inflammatory course, which acquires a bright color, an increased level of temperature, painful sensations and swelling of the tissues.
Passive, which are formed as a result of stagnant processes in the venous vessels. Such erythema acquires a cyanotic or burgundy color, is characterized by a chronic inflammatory course.
Depending on the cause of the formation of erythema, there are:
Non-infectious nature, что приводит к ответному действию организма на окружающие факторы и внутренние раздражители. Такими раздражителями могут быть: действие низкой температуры, ультрафиолетовое излучение, аллергены).
infectious naturearising from the penetration of infectious agents into the vascular system. The infection can enter the vascular tissue through the epidermis of the skin, mucous membranes or systemic circulation.
Infectious erythema does not need specialized treatment and disappears after the cessation of exposure to etiological factors. Infectious erythema is characterized by inflammation, swelling of tissues, and an increase in body temperature. Such erythema needs symptomatic treatment.
Etiology of non-infectious erythema
На появление эритемы, которая не связана с инфекцией, могут повлиять следующие факторы:
The action of X-rays or high-frequency electromagnetic radiation;
The action of infrared rays;
Symptomatic factor that occurs after contact with the allergen. On the skin, it manifests itself in the form of hyperemic redness protruding above the surface of the epithelium;
Холодовой фактор при воздействии низкой температуры. В этом случае на коже появляются пятна синюшного цвета с отёчностью и зудом;
Toxic erythema of newborns – is a variant of the child’s adaptation to the environment or as an allergic reaction to breast milk;
Idiopathic, associated with a hereditary increase in the lumen of the capillaries. This factor includes Lane’s disease, in which a significant part of the vessels of the palms and feet are dilated;
Emotive erythema occurs in response to stressful and emotional stress. Such erythema most often affects the skin of the face and neck. The bright red shade of the spots is associated with vasodilation;
Ultraviolet effect on the skin.
Types of infectious erythema
Erythema of an infectious nature is accompanied by the ingress of an infectious agent into the vascular bed. Such an infection can be viruses, bacteria, helminths, protozoa. Infectious erythema includes:
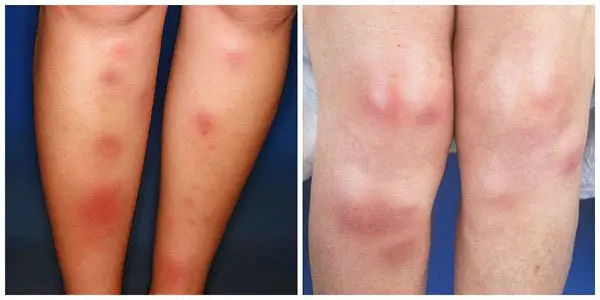
erythema nodosum
It is characterized by the appearance of subcutaneous nodules of red color. Localization of lesions – the front surface of the legs, thighs and forearms. On palpation, the formations are dense and rise above the epithelium. The appearance of such erythematous nodules can be observed with scarlet fever, tuberculosis or tonsillitis. The etiology of erythema nodosum is the use of drugs and oral contraceptives.
Erythema annulare Darier
The causes of occurrence are not well understood. The occurrence of the disease is associated with fungal infections and an allergic reaction to medication. The disease is characterized by a chronic course and affects a young age. The lesion is associated with the appearance of small pink nodules, which gradually progress and increase in size. Their central part sinks over time, the formation has an arched appearance. The formation of nodules is multiple, itching and slight peeling appear.
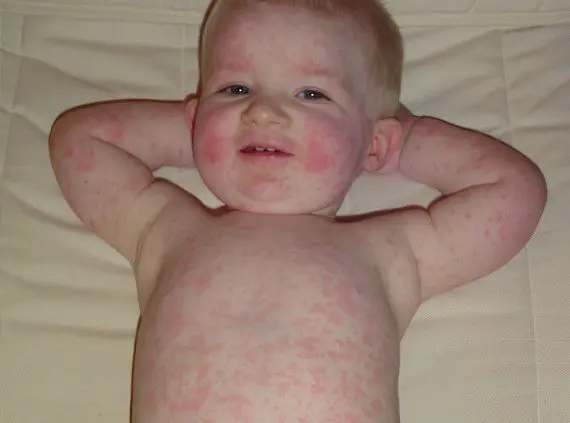
Erythema Chamera
The disease affects children. The etiological factor is parvovirus B19. The disease manifests itself in the form of a small rash on the face, which, when merged, forms erythematous spots. Then the rash spreads over the entire body and arms.
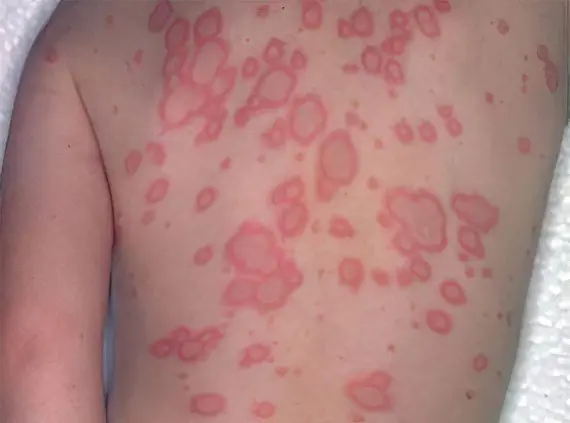
Exudative erythema multiforme
Acute disease is characterized by the appearance of red spots on the surface of the skin, mucous membranes. The spots have clear boundaries and papular formation inside. Such papules may contain purulent or serous exudate, and then they are replaced by ulcers.
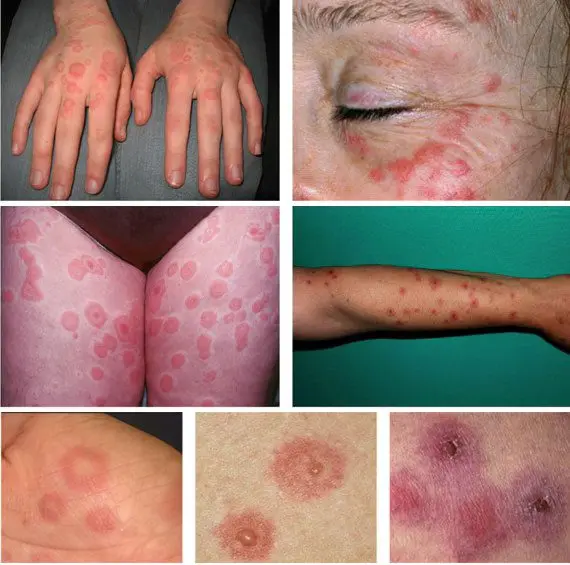
The etiology of the disease can be toxic-allergic or infectious-allergic in nature.
Infectious-allergic is characterized by an acute onset, headache and muscle pain, fever. On the second day, a rash appears, more often on the mucous membranes. After the rash passes, the general condition improves and all accompanying symptoms disappear. Localization of the rash-hands, palms, soles, lower leg and forearm. Rash in the form of flat bright red outlined spots that increase in size. After the center of the papule sinks, it becomes blue. In place of the spots formed, blisters with serous or purulent contents may appear. The rash persists for several weeks and completely disappears in a month. Erythema multiforme exudative can recur, especially in spring and autumn.
Toxic-allergic erythema is associated with intolerance to certain drugs. Such drugs can be sulfonamides, barbiturates, tetracyclines. With this form of erythema, the general condition is not disturbed, sometimes a slight rise in temperature may appear. The nature of the rash does not differ from the infectious-allergic form.
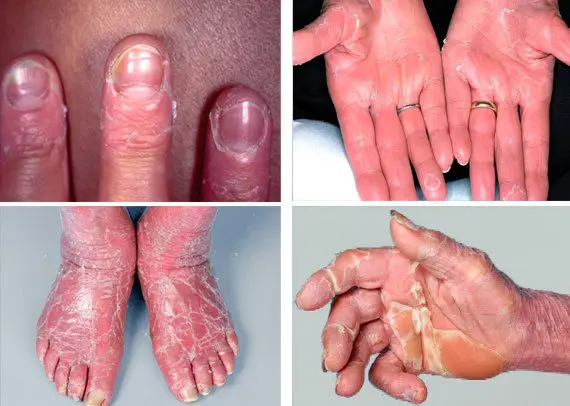
Erythema Ferreol-Besnier
The disease is manifested by the acute nature of the course and frequent relapses. It has an allergic genesis and a favorable outcome. Factors that lead to the appearance of the disease can be drugs, stress factors, hypothermia, intoxication and other infectious pathologies. It is characterized by the appearance of a bright red rash with foci of confluence. When the rash disappears, itching and peeling appear on the surface of the skin. The keratinized layer of the epidermis leaves in the form of “stockings” or “gloves”.
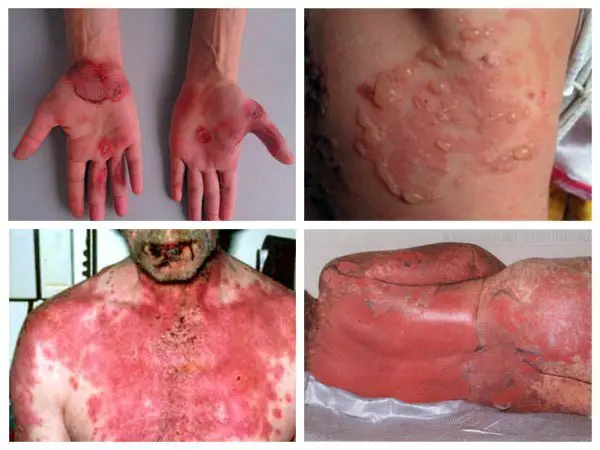
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
An allergic disease with an acute course. The syndrome is associated with the appearance of blisters in the oral cavity, on the mucous membrane of the throat and in the eyes. The disease often recurs and leads to the appearance of a new rash.
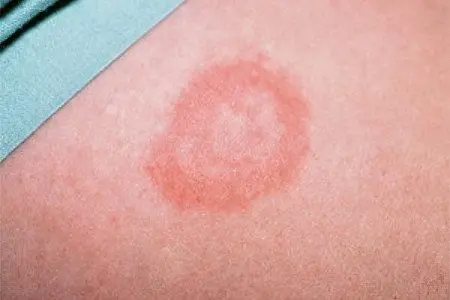
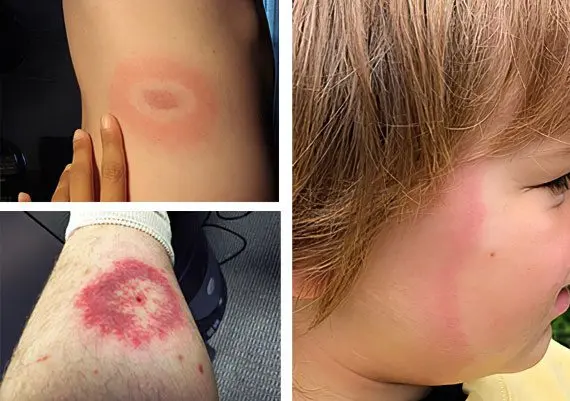
Lipschutz’s erythema migrans
The etiology of the disease is Borrelia bacteria, which ticks carry. Manifested by a centrally located erythema with a pale ring around. Outside, erythema is surrounded by a red inflammatory ring.
Rosenberg’s infective erythema
A pathology that affects the younger generation and manifests itself in the form of symmetrically located spots on the surface of the body and mucous membranes. The disease is accompanied by a sharp rise in body temperature, joint pain and sleep disturbance. After a few days, the skin may become covered with an asymmetrical patchy red rash. Erythema also affects the oral mucosa. The rash resolves 5-6 days after its onset and leaves behind lamellar peeling of the skin. The illness lasts for 7-13 days.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of erythema is carried out by a dermatologist based on the study of complaints, the clinical picture and laboratory diagnostics. A blood test may show an elevated ESR and leukocytosis. In order to exclude other pathologies, the doctor may prescribe a cytological diagnosis of a smear-imprint and study the cellular composition of tissues under magnification. For differential diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe PCR diagnostics for infectious diseases that are sexually transmitted. Serological diagnosis and evaluation of the immune system are also carried out.
It is necessary to differentiate erythema between its various types and with other diseases with similar manifestations. These diseases include: secondary syphilis, toxicoderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, Kawasaki syndrome, herpetic stomatitis, erosive form of lichen planus.
Erythema treatment
The objectives of therapeutic therapy are:
Reduction of symptomatic manifestations and the number of rashes;
Symptomatic help at the stages of exacerbation;
Reducing the period of recurrence;
Prevent possible complications of erythema;
Reduce the number of relapses and increase the patient’s immune response.
In some cases, treatment is not required and it is enough just to remove the factor that provokes the occurrence of erythema. If erythema and its complications cause discomfort to the patient, symptomatic therapy is carried out, aimed at improving the general condition of the patient. Immunocorrection of the patient’s body is often carried out to further exclude relapses or as a relief therapy.
In the case of severe diseases, hospitalization and inpatient treatment may be required. Usually, drug treatment of erythema consists of taking antibiotics, corticosteroids and angioprotectors. They also prescribe drugs that help strengthen the walls of blood vessels and antiplatelet agents.
[Video] Professor, MD, dermatovenereologist, allergist-immunologist of the highest category Lomonosov K. M. – Erythema nodosum:









