Contents
At the first signs of an enlarged liver, it is necessary, first of all, to identify the cause or disease.
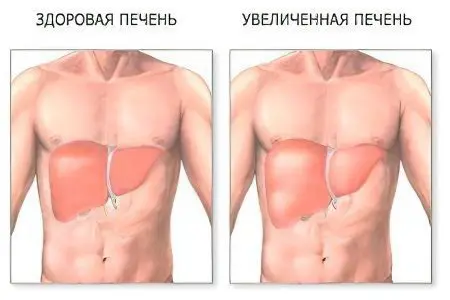
What does an enlarged liver mean?
An enlarged liver is not a disease, but a symptom of a liver problem. In medicine, this phenomenon is called hepatomegaly and means that the liver ceases to perform its functions. Hepatomegaly, if left untreated, can lead to the development of a fatal disease – liver failure. To detect an enlarged liver, a simple medical examination is sufficient.
To identify the causes, more thorough research and analysis will be required:
Ultrasound or tomography to accurately determine the size of the liver and assess the general condition.
MRI – will accurately show the condition of the bile ducts.
Blood tests. Necessary for the examination of liver enzymes, the presence of viral infections and other disorders.
Biopsy. This study is prescribed for suspected cancer or fatty disease.
Reasons for an enlarged liver
Liver diseases:
Fatty liver disease (a large number of fat cells in the liver).
Cholestatic hepatosis (impaired flow of bile)
Hepatitis
Viral or bacterial infections
Cirrhosis
Hereditary diseases associated with metabolic disorders
Diseases associated with circulatory disorders:
Heart failure
Blockage of the hepatic veins
Exchange disorders:
Hemochromatosis
Fat Metabolism Disorders
The appearance of neoplasms:
cysts
Benign tumors
Cancer tumors
Exposure to toxins:
Alcohol defeat
drug lesion
Cholelithiasis
Defeat by helminths
Symptoms of an enlarged liver

An enlarged liver can be determined independently when the following symptoms appear:
Feeling of discomfort in the right hypochondrium, a feeling of heaviness
Dyspeptic disorders – nausea, heartburn, stool changes, belching, accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
Change in the color of the skin – jaundice, characteristic of hepatomegaly.
Changes in behavior – nervousness, irritability, drowsiness or insomnia.
Since the above signs may indicate other disorders in the body, for an accurate diagnosis, you need to contact a specialist. There is no need to delay the visit to the doctor – timely measures taken will help to avoid serious consequences.
Enlarged liver in a child
In infants, liver enlargement may be associated with neonatal jaundice. She does not need treatment, as it passes within a month. The causes of this condition can be birth trauma, diabetes and other disorders in the endocrine system in the mother.
In a child under the age of 7 years, hepatomegaly is a completely normal physiological phenomenon. It is considered normal if the baby’s liver slightly protrudes beyond the edges of the ribs (by 1–2 cm). As the child grows, the liver becomes normal in size. In any case, the doctor will most accurately determine whether the child needs treatment.
In children, an enlarged liver may indicate the following diseases:
Inflammatory processes in the body.
Congenital TORCH infections
Damage to the liver by toxins or drugs.
Pathology of metabolism
Disorders of the biliary tract, blockage of the bile ducts
Metastases or tumors
A cause for concern is an enlarged liver in children in combination with other “danger signals”: fever, venous network on the abdomen, vomiting, skin rashes, weight loss, loss of appetite, yellowness of the mucous membranes. When these signs appear, the pediatrician prescribes a consultation with a hepatologist, infectious disease specialist, gastroenterologist. To identify the exact cause of an enlarged liver, a number of tests and ultrasound are needed.
Diet with an enlarged liver
A properly organized diet will help the liver cope with hepatomegaly. A diet with an enlarged liver excludes spicy, salty, fatty foods. The diet must contain proteins, vitamins, minerals and fiber. You need to eat more fish, vegetables, fruits, taking into account their calorie content.
The most useful products: apples, avocados, dried apricots, turkey, turmeric, green tea, herbs.
Food should be ingested in small portions so as not to overload the diseased liver. Fractional meals (6-7 times a day) are recommended for better digestion. Read more about what you can eat and what you can not with liver diseases.

Monday.
1 reception – Milk rice porridge without the addition of butter and sugar, green tea with honey or rosehip broth.
2 reception – Boiled river fish
3 reception – Boiled carrots, grated
4 reception – Steamed vegetable dish (without salt and spices)
5 reception – Fresh fruit
Tuesday
1 reception – Omelette from one egg (without yolk), rosehip broth or green tea
2 reception – Dried fruits (dried apricots, prunes, raisins), previously filled with boiling water.
3rd reception – Veal or chicken broth, bran bread
4 reception – Low-fat cottage cheese
5 reception – Salad of greens and cucumbers
Wednesday
1 reception – Low-fat kefir or cottage cheese
2 reception – Rosehip broth with honey
3 reception – Steam meatballs
4 reception – Pumpkin puree, herbal tea
5 reception – Baked cheesecakes with the addition of dried fruits
Thursday
1 meal – Oatmeal with milk, green tea with honey and lemon
2 reception – Compote with dried fruits
3 reception – Steamed river fish, bran bread
4 reception – Vegetable casserole, bran bread
5 reception – Herbal tea
Friday
1 reception – Boiled pasta in a small amount
2 reception – Dietary buckwheat soup, bran bread
3 reception – Dried fruits soaked in boiling water
4 reception – Milk porridge
5 reception – Green tea with honey
Saturday
1 meal – Buckwheat porridge boiled in water without salt and sugar, herbal tea
2 reception – Fruit platter
3rd reception – Veal or chicken broth, bran bread
4 reception – Salad of sauerkraut
5 reception – Marshmallow or fruit marmalade
Sunday
1 meal – Cheesecakes with dried fruits cooked in the oven, green tea with honey and lemon
2 reception – Veal or turkey, boiled and mashed with the addition of boiled carrots or pumpkin
3 reception – Rosehip broth, bran bread
4 reception – Kefir or cottage cheese
5 reception – Salad of fruits or vegetables
It is also necessary to observe equal intervals of time between meals. Any diet should be discussed with a doctor who will give all the necessary recommendations. With an enlarged liver, nutrition should be optimally balanced. Therefore, it is periodically necessary to adjust and diversify the diet. Alcohol, coffee, chocolate, confectionery, salt, pepper, vinegar are the main enemies of the liver. For any liver disease, legumes in any form, nuts, carbonated drinks are contraindicated.
[Video] Dr. Berg – 7 Ingredients That Destroy Your Liver:









