Contents
Eggplant diseases in the greenhouse have different causes, most often they are associated with a violation of the rules of care. For example, gardeners water plants abundantly, which creates a moist environment that is favorable for fungi and bacteria. There may be objective reasons related to the weather.
Why do eggplants get sick
Eggplant diseases in the greenhouse appear for various reasons, they are mainly associated with improper care:
- insufficient lighting – plants do not tolerate shade;
- lack or excess of water – the soil should always remain moderately moist;
- watering with cold water;
- nutritional deficiencies, including trace elements (for example, due to a lack of calcium, such an eggplant disease develops in a greenhouse, such as blossom end rot);
- lack of ventilation of the greenhouse, stagnation of moist air;
- sharp temperature changes (eggplant seedlings are transferred to the greenhouse no earlier than the second half of May).
Eggplant diseases in the greenhouse: description with photos
When grown in a greenhouse, plants can suffer from various diseases. Of particular danger are infectious pathologies of a fungal, viral or bacterial nature. The most common diseases with photos and how to treat them are described below.
Blackleg
The main sign of pathology is the blackening of the root neck, the formation of a gray tint on it. Gradually weakened plant dries up, and then the fungus moves to the roots. This is dangerous for eggplants in the greenhouse, as well as at the stage of growing seedlings.
If signs of pathology are found, it is necessary to treat with Trichodermin. But if this does not help, the affected bushes must be removed immediately, since they will no longer recover and at the same time infect healthy plantings. The soil is dried and loosened, then sprinkled with wood ash.
Since it is quite difficult to cure this disease in a greenhouse, plant seeds must be dressed before sowing. To do this, they can be held in a weak solution of potassium permanganate or Fundazol.
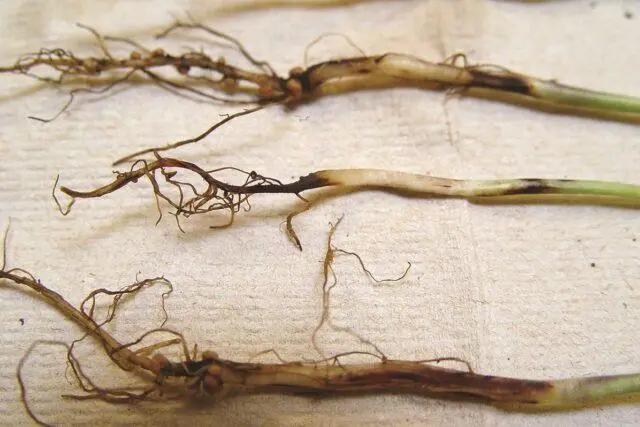

Signs of a black leg – blackening of the root collar
The main provoking factors are sudden temperature changes, high humidity and dense plantings.
Leaf curl
Leaf curl can be due to a variety of reasons, mainly due to insufficient care:
- deficiency of potassium compounds;
- stagnant water due to excessive watering;
- invasion of aphids, spider mites;
- lack of lighting.
To accurately determine the root cause, you need to carefully examine the eggplant in the greenhouse. If their leaves are covered with cobwebs, this is due to the spider mite. Aphid invasion is also quite simple to detect – insect clusters are visible to the naked eye. To treat the disease, eggplant is treated with insecticides:
- “Karate”;
- “Biotlin”;
- “Match”;
- “Agravertin” and others.
It is also worth adding potassium sulfate (30 g per 10 l) to the soil, eliminate the cause of the shadow and normalize watering.
Mučnistaâ rosa
The signs of this eggplant disease in the greenhouse are:
- white bloom on the lower foliage;
- infection of the upper leaves;
- the fruits are covered with powdery coating and crack;
- balls form on the upper parts of the leaves.

Eggplant leaf affected by powdery mildew
For processing, it is recommended to use “Gaupsin” or “Trichodermin”. These are the most effective biological preparations that can be used even at the fruiting stage, including shortly before harvest.
Black spot
This disease also often affects eggplants in the greenhouse. First, black spots with a yellow border form on the leaves. Gradually they increase in size. Dots of a dark shade appear on the fruits, they have a blurry, “watery” border.
The disease often develops in a greenhouse due to lack of ventilation and high humidity. Hot weather also contributes – the bacteria that cause the infection develop well in the range of 27-30 degrees. There is no adequate treatment – the affected bushes are removed, and the rest are treated with Zaslon or Fitoflavin-300 preparations.

Leaf affected by black spot
Leaf yellowness
Another common eggplant disease in the greenhouse is yellowing of the leaves. It is associated with various reasons:
- nitrogen or potassium deficiency;
- too bright sun, scorching rays;
- when watering, water gets on the leaves, which leads to burns;
- Fusarium wilt is a dangerous fungal disease.
To eliminate the cause, it is necessary to improve the conditions of care. Young seedlings are shaded with a white shield so that they do not suffer from excess solar energy. Eggplants need to be watered only at the root, and it is advisable to do this in the evening. Fertilizers are applied several times during the season – first with nitrogen, and during the formation of buds – with potassium and phosphorus. If the cause of yellowing is associated with Fusarium, Falcon is treated.
Phytoplasmosis (stolbur)
This is a dangerous disease that affects eggplant most often in the open field, less often in greenhouses. It is caused by special pathogenic microorganisms – mycoplasmas. The main signs are:
- leaves turn pale, acquire a yellowish color;
- then curl up, become wrinkled;
- begin to fade;
- flower clusters grow up, not down.
There is no adequate treatment – you just have to remove the plant from the site, then plow the ground deeply and water it with a solution of any fungicide. For prevention, it is recommended to constantly remove weeds and destroy insects that carry the pathogen.
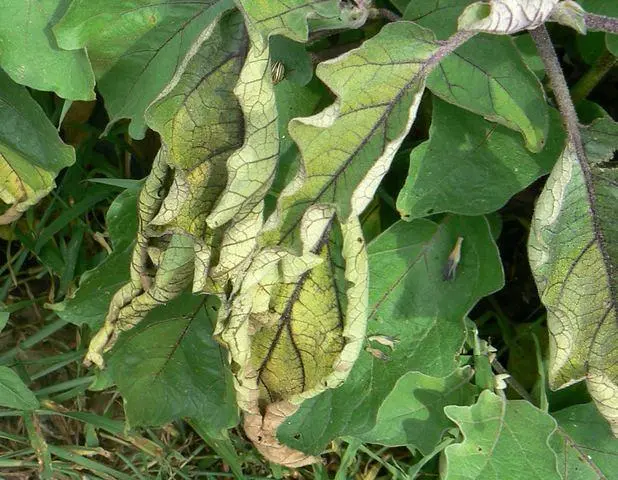

Symptoms of stolbur can be detected by examining plants
Phomopsis
Signs of this disease appear on different parts – leaves, petioles, shoots and fruits. The main symptoms are:
- spots of a dark brown, gray shade with chlorotic edges form on the foliage;
- they grow, go to the cuttings;
- tissues die, the tops dry out;
- grayish spots appear on the stems;
- dark brown dots form on the fruits, they partially soften.
Pathology is infectious in nature, it is caused by fungi. For prevention, it is recommended to treat the seeds, as well as treat them with fungicides, for example, Bordeaux liquid or copper oxychloride.
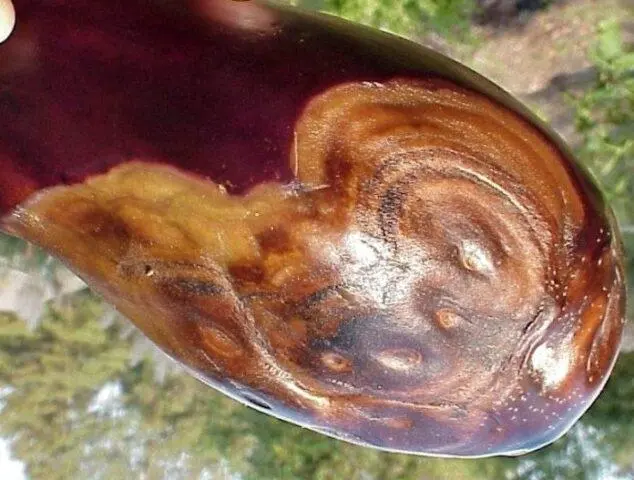

Fruit affected by Phomopsis is not suitable for human consumption.
Cerkosporoz
Cercosporosis is a disease that is often observed in a greenhouse. It affects leaves, shoots and stalks. Rounded chlorotic spots appear on them. Gradually, they increase in size, after which the affected leaves begin to fall off. At the same time, the fruits themselves become small and stop developing.
The pathology is associated with fungi that are carried with water and through contact with garden tools. The main preventive measure is compliance with the norm of irrigation, crop rotation rules. For treatment, Bordeaux liquid and fungicidal preparations are used.
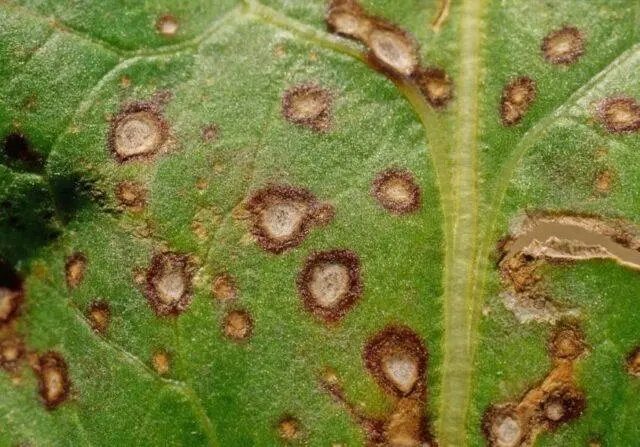

Signs of cercosporosis on foliage are easy to identify with the naked eye.
Fitoftoroz
A fungal disease that affects eggplants, peppers, tomatoes, potatoes in the greenhouse and in the open field. It manifests itself as brown-red spots with green edges on the outside of the foliage. A whitish coating appears inside, after which the fungus passes to the fruit. They begin to warp and rot.
The main way to treat this eggplant disease in a greenhouse is treatment with drugs:
- “Quadris”;
- Anthracol;
- “Consento”;
- copper sulfate.
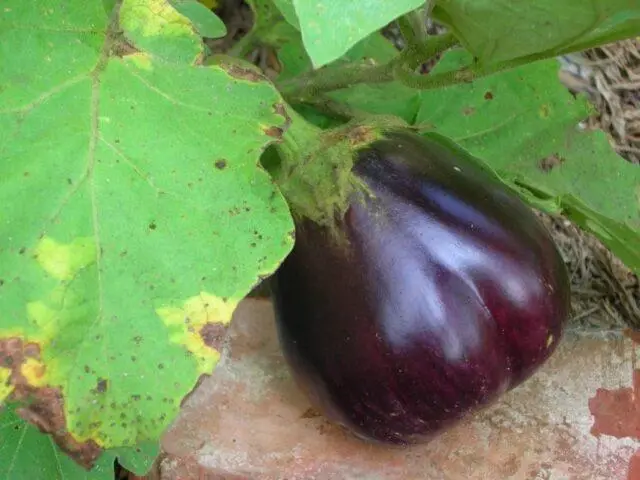

Signs of late blight – deformed fruits
White rot (sclerotinia)
Sclerotinia is another fungal disease affecting eggplants in the greenhouse. It affects first the roots, and then all other parts of the plant. The stems have a white coating. The internal parts are compacted, sclerotia are formed on them, after which they soften and interfere with the movement of water through plant tissues. Dark spots appear on the leaves and fruits. For treatment, it is necessary to remove the affected parts and sprinkle the sections with ash, and then treat with copper-containing agents.
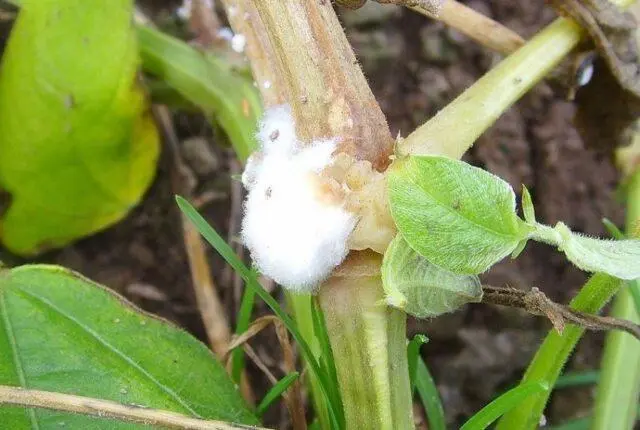

A stem affected by white rot is best removed from the site.
Gray rot (alternariosis)
Alternariosis is an eggplant disease that occurs in a greenhouse. It is of fungal origin. It can be identified by the following features:
- round brown spots on foliage and wet spots on ovaries;
- eggplants are pressed in, become soft;
- fruits acquire an olive-gray, black color.
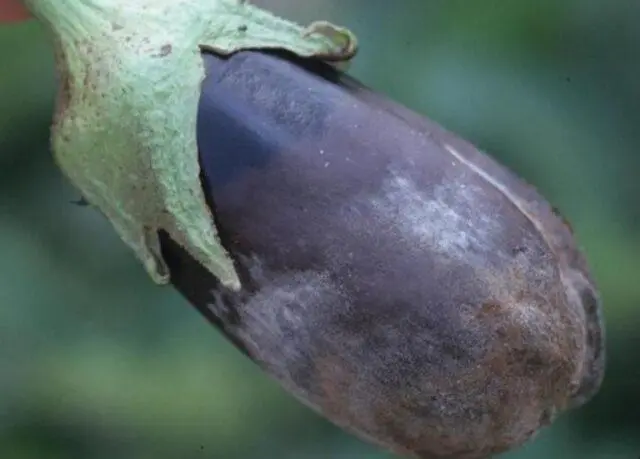

Signs of gray rot
The infection spreads through cracks, burns, and other lesions on the eggplant. The pathogen can live in the soil for up to two years. Affected plants must be dug up and carried away. For treatment, agents based on copper and colloidal sulfur are used. The main preventive measures are compliance with the norm of irrigation, crop rotation rules.
Dry rot (Phomopsis)
Signs of eggplant fomopsis in a greenhouse appear in hot, dry weather. The sprouts turn brown and rot, wet ring rot is noticeable on the seedlings. Rounded spots with brown edges appear on the leaves of adult plants. In the center, black dots are noticeable – these are the pycnidia of the fungus, the causative agent of the disease.
Spots appear on fruits. They increase in size, turn black, which is why the eggplant rots. To cope with the pathology, fungicides with active ingredients are used: prochloraz, mancozeb and chlorotolonil.
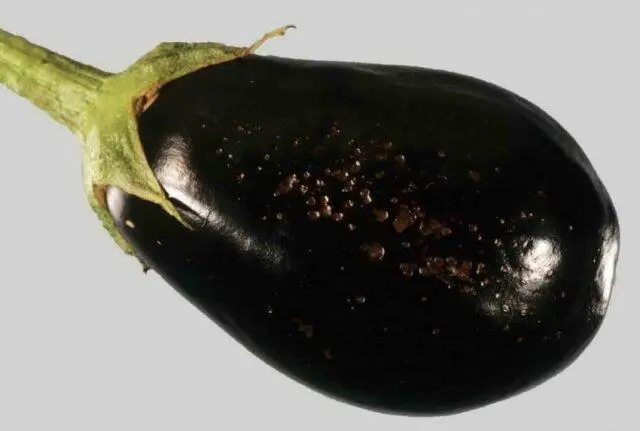

Fruit affected by Phomopsis
Verticillary wilting
Verticillosis is a fungal disease that damages eggplants in the greenhouse and less often when grown outdoors. Fungi penetrate the soil, release toxic substances. Provoking factors are warm weather and high humidity. The soil is watered with a solution of a biological preparation, for example, Fitosporin or Trichodermin.
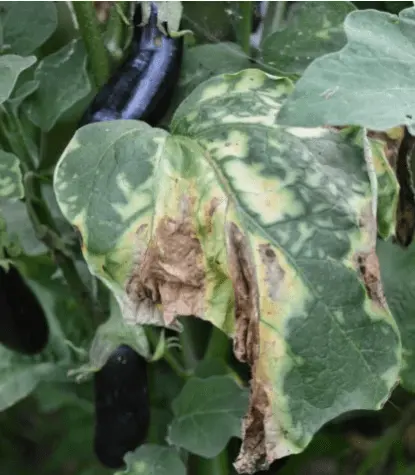

Treatment of verticillium is useless – the bushes can only be thrown away.
Tobacco mosaic
A common viral disease of eggplant in a greenhouse. The main signs are chlorotic, light green spots along the veins of the leaves. Part of the leaf plates acquires a mottled pattern, the veins lighten, become wrinkled. The fruits shrink, lose their normal shape. There are no adequate methods of treatment – the affected plants remain to be dug up and discarded.
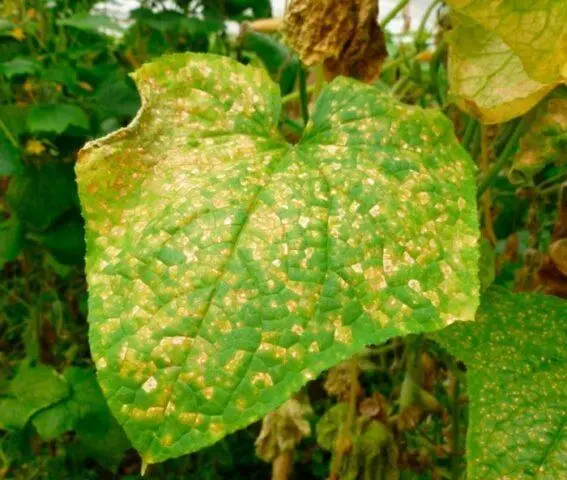

Signs of tobacco mosaic
Internal necrosis
Internal necrosis – the death of tissues of foliage, stems and other parts of eggplant. This disease develops both in the greenhouse and in the open field. It is associated with bacteria and fungi that come from the soil and release toxic substances. Pathogenic processes develop in conditions of high temperature and humidity.
Treatment is impossible, the plants will have to be dug up and destroyed. The surface layer of soil is discarded and replaced with a new one. Moreover, the soil is treated with biological preparations, for example, Fitosporin or Trichophyt.
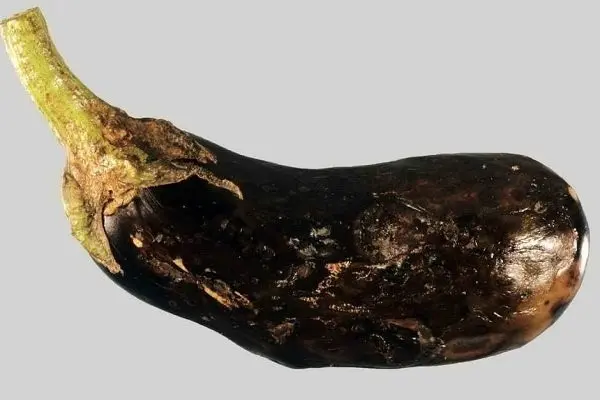

A fetus affected by internal necrosis should not be eaten.
Vertex Rot
Blossom end rot is a dangerous disease that affects seedlings and adult eggplant plants in a greenhouse. It manifests itself as light spots and rotten areas on the fruit.
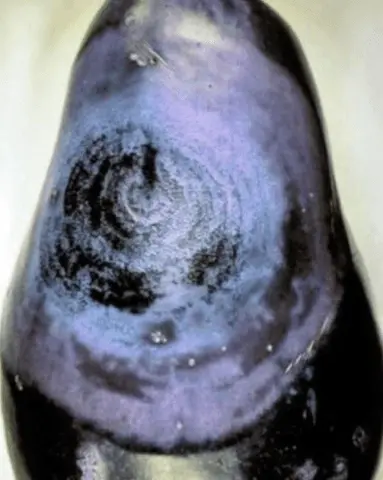
Blossom end rot may be due to calcium deficiency or pathogens.
Calcium nitrate is added (foliar method, 10 g per 10 l) or treated with drugs, for example, Fitolavin and Fitomycin.
Disease Prevention
To treat eggplant diseases in a greenhouse, it is necessary to determine the signs of leaf damage, as in the photo. To avoid the development of such symptoms, certain preventive measures should be observed:
- Carefully select a variety suitable for the climatic conditions of a particular region.
- Choose the right place for plants – do not plant after tomatoes, peppers, potatoes. Good predecessors are cruciferous, legumes, onions and carrots.
- Make landings with an interval of at least 50 cm.
- Plant seedlings only when the temperature reaches 15 degrees Celsius.
- Ventilate the greenhouse.
- Observe the watering rate.
- Loosen the soil regularly.
- Carry out preventive treatments with fungicides and insecticides.
Conclusion
Eggplant diseases in the greenhouse are often associated with improper care. Plants prefer regular watering, they are responsive to fertilizing. Water should be given so as not to flood the soil. It is important to ventilate the greenhouse and periodically inspect the plants. When the first signs of infection are detected, treatment is carried out.









