Contents
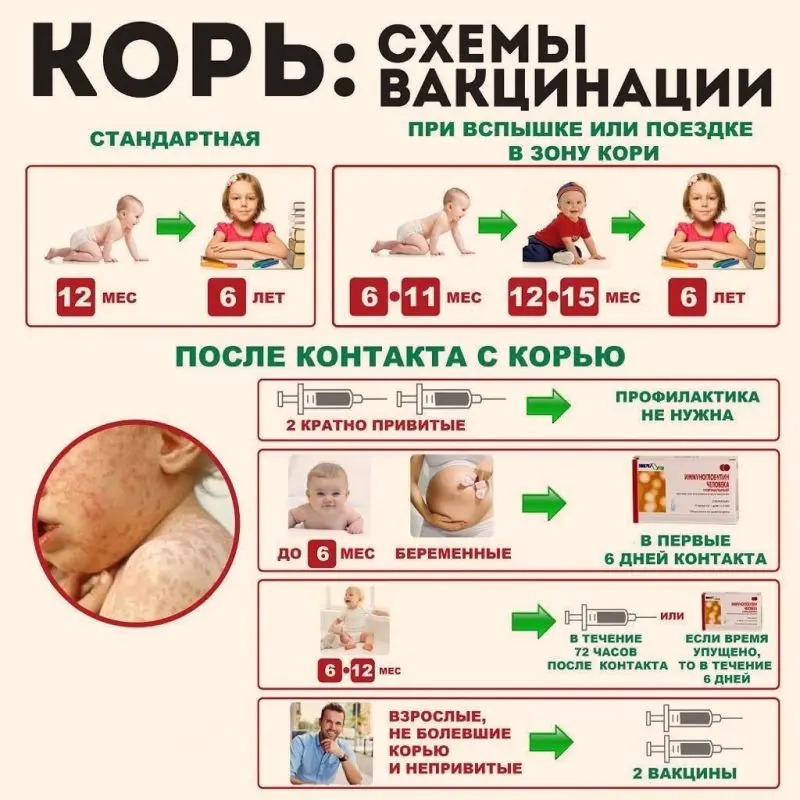
Measles vaccine is given to those children at the age of 12 or 15 months who have not had measles, a second vaccine is given to children at the age of six years. It is necessary for the formation of herd immunity, as well as in the case of weak immunity formed after the first vaccination.
According to the vaccination schedule, the measles vaccine is given at the same time as the mumps, rubella and hepatitis B vaccine.
The effectiveness of the measles vaccine
Subject to all the rules for vaccination, immunity is developed in almost 100% of cases in children of the second year of life about a month after the injection. Immunity lasts 25 years and only in a few cases can fade over time.
Vaccine Contraindications
Modern medical science has identified a number of contraindications that prohibit vaccinating a child.
Previously, this list was more extensive, but now it has been significantly reduced, due to a number of reasons:
Many years of experience in the use of vaccinations has shown that the consequences of refusing them are much more serious than the consequences of vaccination themselves. So, in children infected with tuberculosis, all diseases are very difficult. Premature babies infected with whooping cough can die from this infection. If a person has diabetes, then he has a severe course of rubella. Influenza leads to serious complications in patients with bronchial asthma. If such children are not vaccinated, their lives are in serious danger.
WHO conducted studies that made it possible to establish that in children with the listed diagnoses, the post-vaccination period does not differ from that in healthy babies. Moreover, vaccinations do not aggravate the course of the underlying pathology.
Modern vaccines are practically devoid of proteins and ballast substances that can cause severe complications. Egg white is not even determined in many solutions, since there is very little of it in them. Therefore, vaccinations can be given to children with an allergy to chicken protein.
Contraindications to vaccination can be of the following types:
True contraindications. They are included in the list of all instructions that are available for any vaccine. They are also clearly spelled out in all international recommendations.
False contraindications. They can not even be called contraindications in the full sense of the word. Although some doctors still do not vaccinate children with perinatal encephalopathy. While this contraindication has long sunk into oblivion.
Absolute contraindications. If there are any, then the child is not vaccinated.
Relative contraindications. They are also true, but the doctor has the last word. So, with an allergy to chicken protein, children are not given a flu vaccine. While during an epidemic outbreak, a child can be vaccinated, since the severity of an allergic reaction is not comparable to the severity of complications from influenza. In many countries, children with chicken protein allergy are required to be vaccinated against influenza, but specific preparation is carried out before the injection. It prevents the development of a severe allergic reaction.
Temporary contraindications. These include chronic diseases in the acute stage, SARS, etc. When the child recovers, he will be vaccinated.
Permanent contraindications. They stay with the child for life. An example of such contraindications is congenital immunodeficiency.
General contraindications. They are the same for all types of vaccines. For example, children are not vaccinated against the background of high body temperature, or during the acute phase of the disease.
Private contraindications. They are valid for some vaccines, but other vaccines can be given to a child.
True contraindications include:
Name of the vaccine | List of contraindications |
All vaccinations | After the introduction of the first vaccine, the child developed severe reactions: the body temperature rose to 40 ° C, there was an edema of more than 8 cm in diameter. This also includes anaphylactic shock, arthritis, angioedema, etc. |
Live types of vaccines | Congenital deficiency of immunity, cancerous tumors, the period of bearing a child. |
BCG | The weight of the child is less than 2 kg, the formation of a keloid scar at the site of the last injection, intrauterine infection of the child, severe neurological disorders, generalized BCG infection in the family history, hemolytic disease of the newborn, systemic diseases of the dermis, HIV in the mother, immunodeficiency of the child. |
DTP | Convulsions that happened to the child earlier, severe neurological pathologies. |
Measles, rubella, mumps | Allergy to aminoglycosides, anaphylactic shock, developing on the introduction of chicken protein. |
Hepatitis B | Allergy to baker’s yeast, prolonged jaundice in a newborn with a significant increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood. |
Complications of the measles vaccine

Measles vaccine rarely causes side effects. In most children, vaccination against measles does not cause any complications, and only about 10% of cases of vaccination are accompanied by fever, catarrh, and a small rash. With a tendency to allergic reactions, a rash may appear in the first hours after vaccination. On the second or third day, all reactions to the drug disappear. In any case, the child does not pose a danger to others.
In children with an increased allergic background, a rash, urticaria, Quincke’s edema may occur, in a very rare case, complications appear in the form of anaphylactic shock to chicken protein.
There have been cases in pediatrics of adolescent sclerosing panencephalitis in children who have not previously had measles and who were given the measles vaccine. The likelihood of developing such a complication is one case per million doses of the drug, which is significantly less than with pathology. In measles, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis occurs in 6–22 cases per million cases. According to a retrospective study conducted by the CDC, the vaccine helps prevent subacute sclerosing panencephalitis by reducing the number of measles cases.
Thrombocytopenia is extremely rare after the administration of a trivaccine, and cases of this disease are even more rare after a monovaccine is administered.
In medicine, a case of toxic shock is also described due to infection with Staphylococcus aureus after contamination of an opened ampoule of the drug.
It is important to understand what is meant by the phrase “local reactions” and “general reactions”. All of them are listed in the table.
Local manifestations | Common manifestations |
Such reactions develop due to the fact that aseptic inflammation develops in the injection area. It can be a reaction to the solution itself, or to injury to the skin and muscles with a needle. Inactivated vaccines contain a substance that stimulates a local reaction. This is necessary so that more blood flows to the place of its introduction, which will make the immune system stronger. |
More often than other reactions, children develop a rash and develop a high body temperature. A rash most often occurs after an injection for viral diseases (measles, rubella, etc.). This is due to the fact that the virus penetrates the dermis, but it does not cause harm to health. An increase in body temperature is a natural reaction of the body, which indicates the activation of immunity. When its cells come into contact with an antigen, they release pyrogens into the blood. It is these substances that are responsible for hyperthermia. |
Myths about the dangers of vaccines
There is a social movement in the world that points out that vaccines are unsafe and completely useless. This movement is called anti-vaccinationism.
The failure of vaccination campaigns was first discussed at the end of the 19th century. To date, the situation is complicated by the fact that commissioned reports from the media, as well as non-scientific articles on the Internet, continue to influence the minds of citizens. Many of them, having no medical education, do not understand at all what is at stake, but refuse to vaccinate their children. Moreover, they promote their false scientific beliefs among their inner circle.
The main myths that need to be debunked are:
Vaccines are given not for health, but because of the collusion of doctors and pharmacists. Many people are convinced that pharmacists and doctors make fortunes from vaccination campaigns. But why is this belief true of vaccines in particular? Any pharmaceutical industry allows someone to become richer, but this is not emphasized. Vaccines are produced to prevent serious diseases and their complications, and not for profit.
Vaccines are ineffective. This myth is refuted by dry statistics. Vaccinated people rarely get sick. If infection occurs, then the infection will have a mild course. When an unvaccinated person meets her, he will definitely get sick.
Vaccines are not needed. Most people who point out the failure of vaccination simply do not have an idea about the real frequency of occurrence of various infections. They think they are not common. Actually, it is not. Six years of vaccinating children against hepatitis B has yielded stunning results. So, out of 9 children per 100, no more than 000% per 1,6 are now sick. These figures are also overestimated because many parents refuse to vaccinate their children. As a result, a stratum of people appears in society, which has no immunity and is a source of the spread of diseases.
Vaccines adversely affect human health. You can find information that vaccines contain mercury, which causes autism in children. It is worth noting that the human body contains almost all metals, including mercury. Every day with food in the gastrointestinal tract, and a loan in the blood, various microelements and compounds enter, but in microscopic doses. There is even less mercury in vaccinations and it is needed to preserve the solution.
Mercury cannot cause autism. To understand this, one does not need to study the medical specialty. However, such statements negatively affect the consciousness of citizens, although they are absolutely anti-scientific. The same applies to epilepsy and other pathologies that vaccines allegedly can cause.
Vaccines undermine the immune system. Immunity after vaccination is activated, but not reduced. This is an obvious and scientifically proven fact.
What Parents Should Remember

You should not bathe the child on the day of vaccination and the next day. It is not recommended to walk with him during the same period. Hypothermia and contact with people can cause a respiratory infection. In the first two days, the immune defense actively produces antigens, so the load on it increases. Well, if the child at this time will be absolutely healthy.
If the child’s body temperature rises by more than 37,5 ° C, then you need to give him an antipyretic.
To reduce the intensity of local manifestations, it is necessary to take an antihistamine. However, before doing this, you should consult a doctor.
The child must be healthy on the day of the vaccine. From the moment of complete recovery from the previous disease, at least 14 days must pass. Before the procedure, the child must be examined by a doctor. It is advisable to donate blood and urine for analysis.









