Contents
Edematous disease of piglets is the cause of sudden death of vigorous and well-fed young pigs, which “have everything”. The owner takes care of his piglets, provides them with all the necessary feeding, and they die. It is unlikely that a consolation here will be the fact that a similar disease and under the same name is also found in lambs and kids.
Causative agent
Scientists themselves have not yet come to a consensus on which microorganism causes edematous disease in piglets. But most researchers “vote” for the fact that these are beta-hemolytic toxigenic colibacilli that cause specific poisoning of the body. Because of this, edematous disease has received the name “enterotoxemia” (Morbus oedematosus porcellorum) in veterinary medicine. Sometimes the disease is also called paralytic toxicosis. But among the people, the name “edematous disease” has taken root more.
Causes
The reasons for the development of enterotoxemia are no less mysterious than the true pathogen. If the causative agent of enterotoxemia is known to be one of the types of bacteria that constantly live in the intestines, then the cause with a high degree of probability can be called a decrease in immunity.
А вот спусковым крючком для падения резистентности организма у поросят могут послужить:
- stress due to weaning;
- premature weaning, when the intestines and the body’s defense systems have not yet fully developed;
- bad content;
- lack of walking;
- poor quality food.
Even a simple transfer of a piglet from one pen to another can cause stress, which will lead to a decrease in immunity.
Active enterotoxemia bacteria can be introduced by an ill piglet. The situation is similar to human tuberculosis: all people have a certain amount of Koch sticks in the lungs and on the skin. Bacteria do no harm as long as the body can defend itself or until a person with an open form of the disease appears nearby. That is, there will be a source of a large number of active bacteria nearby. In the case of edematous disease, such a “fountain” of active bacteria is a sick piglet.
Who is at risk: piglets or pigs
In fact, carriers of colibacilli in safe amounts for the body are the entire population of pigs on the planet. The disease is distributed throughout the world. But not everyone gets enterotoxemia. Well-fed and well-developed piglets are most susceptible to the disease, but only in certain periods of life:
- the most frequent cases on the 10-14th day after weaning;
- second place in suckling piglets;
- on the third – young animals older than 3 months.
In adult pigs, either the protective functions of the body are developed, or the nervous system is hardened, which does not allow the animal to fall into stress because of any little thing.

How dangerous is the disease
Often the disease occurs suddenly and the owner does not have time to take action. The usual mortality rate for edematous disease is 80-100%. With a lightning-fast form, 100% of piglets die. In chronic, up to 80% survive, but this form is recorded in “older” piglets with relatively strong immunity.
Pathogenesis
The reasons why pathogenic bacteria begin to multiply are still not known for certain. It is only assumed that due to violations in the feeding regimen and maintenance, colibacilli begin to actively multiply in the intestines. In the struggle for living space inside the piglet, toxigenic bacteria crowd out beneficial strains of E. coli. Dysbacteriosis occurs and metabolism is disturbed. Toxins begin to enter the body from the intestines. The amount of albumin in the blood decreases. This leads to the accumulation of water in the soft tissues, that is, to edema.
Развитию энтеротоксемии способствует и нарушение фосфорно-кальциевого баланса: при увеличении содержания фосфора и магния и уменьшение количества кальция приводит к увеличению проницаемости сосудов.
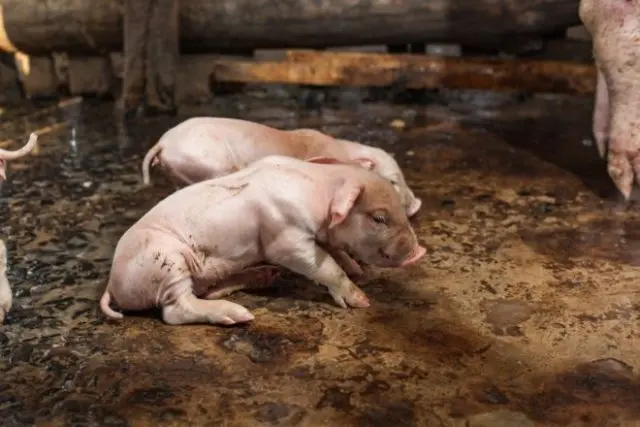

Symptoms
Инкубационный период длится лишь несколько часов: от 6 до 10. Непонятно, правда, как этот период вычисляли, если заболеть поросенок может в любой момент и совершенно внезапно. Единственная версия: заражали в лабораторных условиях.
But the latent period cannot be long either. It all depends on the rate of reproduction of bacteria, the number of which doubles per day already at a temperature of + 25 ° C. The temperature of a live piglet is much higher, which means that the rate of reproduction of microorganisms increases.
The very first sign of edematous disease is a high temperature (40,5 ° C). After 6-8 hours, it drops to normal. It is difficult for a private owner to catch this moment, since people usually have other things to do. This is the main reason why edematous disease occurs “suddenly”.
With the further development of enterotoxemia, other signs of the disease appear:
- edema;
- wobbly gait;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- photophobia;
- small hemorrhages on the mucous membranes.
But the name “edematous” disease was due to the accumulation of fluid in the subcutaneous tissue. When a piglet is ill with enterotoxemia, they swell:
- eyelids;
- forehead;
- back of the head;
- snout;
- intermaxillary space.
An attentive owner can already notice these symptoms.
Further development of the disease leads to damage to the nervous system. Piglets have:
- muscle tremors;
- increased excitability;
- movement in a circle;
- head jerking;
- the characteristic posture of a “sitting dog”;
- “Running” in the supine position;
- convulsions due to the most insignificant stimuli.
Стадия возбуждения длится лишь 30 минут. После нее наступает состояние депрессии. Поросенок больше не бьется в судорогах по пустякам. Вместо этого он перестает реагировать на звуки и прикосновения, испытывая сильное угнетение. На стадии депрессии у поросят появляются параличи и парезы ног. Незадолго до падежа отмечают появление кровоподтеков на пятачке, ушах, животе и ногах из-за ослабевания сердечной деятельности.
In most cases, the death of piglets occurs 3-18 hours after the onset of signs of edematous disease. Sometimes they can last 2-3 days. Piglets older than 3 months are ill for 5-7 days. Piglets rarely recover, and recovered ones lag behind in development.

Forms
Edema can occur in three forms: hyperacute, acute and chronic. Super-sharp is also often called lightning-fast for the characteristic sudden death of piglets.
Lightning
With a lightning-fast form, a group of perfectly healthy piglets yesterday completely dies over the next day. This form occurs in 2-month-old weaned piglets.
A hyperacute course is usually observed during an epizootic on a farm or in an agro-complex. Simultaneously with suddenly dead piglets, stronger individuals “acquire” edema and lesions of the central nervous system.
Sharp
The most common form of the disease. Piglets live a little longer than with a lightning-fast form: from several hours to a day. Mortality is also slightly lower. Although all piglets can die on the farm, in general, the percentage of death as a result of edematous disease is from 90.
In a general description of symptoms, they are guided by the acute form of the disease. Death in this form of flow occurs from asphyxia, since the affected nervous system no longer conducts signals from the respiratory center of the brain. The heartbeat before death increases to 200 bpm. Trying to compensate the body for the lack of oxygen that has ceased to flow from the lungs, the heart accelerates the pumping of blood through the circulatory system.
Chronic
Piglets older than 3 months are sick. Characterized by:
- poor appetite;
- dependence;
- oppressed state.
Difficulties in diagnosing
Symptoms of edematous disease are very similar to other ailments of piglets:
- hypocalcemia;
- рожей;
- Aujeszky’s disease;
- pasteurellosis;
- нервной формой чумы;
- listeriosis;
- salt and feed poisoning.
Piglets with edematous disease cannot be distinguished from pigs with other diseases either in the photo or during a real examination. External signs are often the same, and the diagnosis can be reliably established only with pathoanatomical studies.

Патанатомия
Основное отличие отечной болезни в том, что поросята погибают в хорошей кондиции. Подозрение на отечную болезнь возникает, если среди отъема вскоре появляются внезапные случаи падежа поросят с отеками органов брюшной полости и подкожной клетчатки. При других болезнях, кроме сильных отравлений, они нередко успевают похудеть.
On examination, bluish spots on the skin are found:
- heel
- ears;
- inguinal region;
- tail;
- feet.
При вскрытии трупа можно найти отек подкожной клетчатки на конечностях, голове и животе. Но не всегда.
But constantly there are changes in the stomach: swelling of the submucosa. Due to the swelling of the soft tissue layer, the wall of the stomach thickens greatly. The mucosa of the small intestines is swollen, with bruises. Fibrin strands are often found in intestinal loops. Accumulation of serous-hemorrhagic exudate in the abdominal and chest cavities.
In the liver and kidneys, venous congestion is noted. Due to tissue degeneration, the liver has an uneven color.
Light swollen. When cut, a frothy reddish liquid flows out of them.
Брыжейка отечная. Лимфатические узлы увеличенные и набухшие. Красные «кровавые» участки в них чередуются с бледными анемичными. Очень сильно брыжейка отекает между петлями ободочной кишки. В норме брыжейка выглядит как тонкая пленка, которая прикрепляет кишечник к спинной части животного. При отечной болезни она превращается в студенистую жидкость.
Сосуды мозговых оболочек наполнены кровью. Иногда на них заметны кровоизлияния. В спинном мозге изменений, заметных глазу, нет.
The diagnosis is established on the basis of the clinical picture of the disease and pathological changes in the body of the dead piglets. Bacteriological research and data on the epizootic situation are also taken into account.
Treatment of edematous disease in piglets
Since the disease is caused by bacteria, not viruses, it is quite treatable with antibiotics. Antibiotics of the penicillin and tetracycline groups can be used. At the same time, sulfa drugs are used.
As concomitant therapy, a solution of calcium chloride 10% is used. It is administered by intravenous injection of 5 mg twice a day. For oral use, the dosage is 1 tbsp. l.
Recommended administration of antihistamines:
- diphenhydramine;
- superstina;
- diprazine
Dosage, frequency and method of administration depend on the type of drug and the form of its release.
In case of heart failure, cordiamine is injected subcutaneously at 0,07 ml / kg twice a day. After recovery, probiotics are prescribed to all livestock to restore intestinal flora.
During treatment, errors in feeding are also eliminated and a complete diet is calculated. On the first day of edematous disease, piglets are kept on a starvation diet. For the speedy cleaning of the intestines, they are given a laxative. On the second day, the survivors are given easily digestible food:
- potatoes;
- beet;
- return;
- fresh grass.
Vitamin and mineral supplements are given according to the norms of feeding. Vitamins of groups B and D can be injected instead of feeding.
Preventive measures
Prevention of edematous disease – first of all, the correct conditions of detention and feeding. The correct diet is necessary for already pregnant pigs and, of course, lactating queens. Next, the piglets are fed according to age. Piglets begin to be fed with vitamins and minerals very early, from the 3-5th day of life. In the warm season, piglets are released for walking. You can not carry out too early weaning. One-sided feeding of piglets with concentrates can also lead to edematous disease. This diet should be avoided. At about 2 months of age, piglets are fed probiotics. The course of probiotics begins before weaning, and ends after.
The premises, inventory, equipment must be systematically cleaned and disinfected.

The vaccine
Against edematous disease of piglets in Our Country, the Serdosan polyvaccine is used. Not only piglets are vaccinated, but the entire population of pigs. For preventive purposes, piglets are given the first vaccination on the 10-15th day of life. The second time the piglets are vaccinated after another 2 weeks. And the last time the vaccine is injected after 6 months. after the second. With an outbreak of edematous disease on the farm, the piglets are vaccinated for the third time after 3-4 months. Immunity against pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli develops half a month after the second vaccination.
But the vaccination scheme in this case changes: the second vaccination is done 7 days after the first; the third – a week and a half after the second.
Conclusion
The edematous disease of piglets usually “wipes out” all the broods of the farmer, depriving him of his profit. This can be avoided by observing the rules of zoohygiene and properly compiling a diet. The blanket vaccination of all pigs will also prevent enterotoxemia from running wild.










Bastard of a disease
Sincerely
A pig farmer