Contents
- Types of ectopic pregnancy
- Who is at risk for developing an ectopic pregnancy?
- Why does an ectopic pregnancy happen: the reasons for its development
- Negative test result in ectopic pregnancy: what are the reasons?
- Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
- Do menstruation occur during an ectopic pregnancy?
- How can an ectopic pregnancy be distinguished from a normal one?
- Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy
- Signs of a ruptured fallopian tube
- Why does a fallopian tube rupture during an ectopic pregnancy?
- Is it possible to carry a child with an ectopic pregnancy?
- When does a fallopian tube rupture occur?
- Early fallopian tube rupture
- If the fallopian tube ruptured in late pregnancy
- Complications of an ectopic pregnancy
- Do I need to save the fallopian tubes during an ectopic pregnancy?
- Answers to popular questions

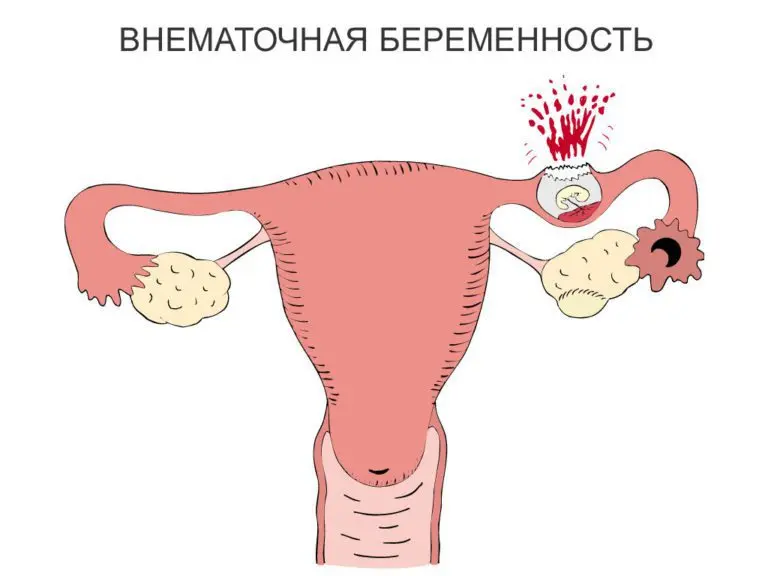
An ectopic pregnancy is a serious violation of the formation of the embryo after the fertilization of the egg. Pathology is characterized by the fact that the fetal egg begins its growth and development not in the uterus, but in the fallopian tube. Less commonly, the site of its implantation is the walls of the peritoneum or ovaries. Sometimes there is a situation in which the fetal egg comes out of the tube and remains in the cervix, getting stuck in it. Naturally, the embryo cannot survive as it grows and develops under such conditions. Medical science knows only isolated cases of abdominal pregnancy, which can be considered a miracle.
An ectopic pregnancy is associated with serious risks for a woman, as it threatens to rupture the tube and develop internal bleeding. If within a short time the victim does not get to the hospital, then she will experience extensive blood loss, which in 80% of cases will end in death. Therefore, every woman of reproductive age should know the main signs indicating an ectopic pregnancy and rupture of the fallopian tube.
It is not without reason that doctors consider ectopic pregnancy to be the most insidious pathology in the gynecological field. It ends with about 0,8-2,4% of all pregnancies. Moreover, the embryo is attached in the fallopian tubes in 98% of cases. After suffering a rupture of the appendage, the patient may forever remain infertile. Another ectopic pregnancy is called ectopic.
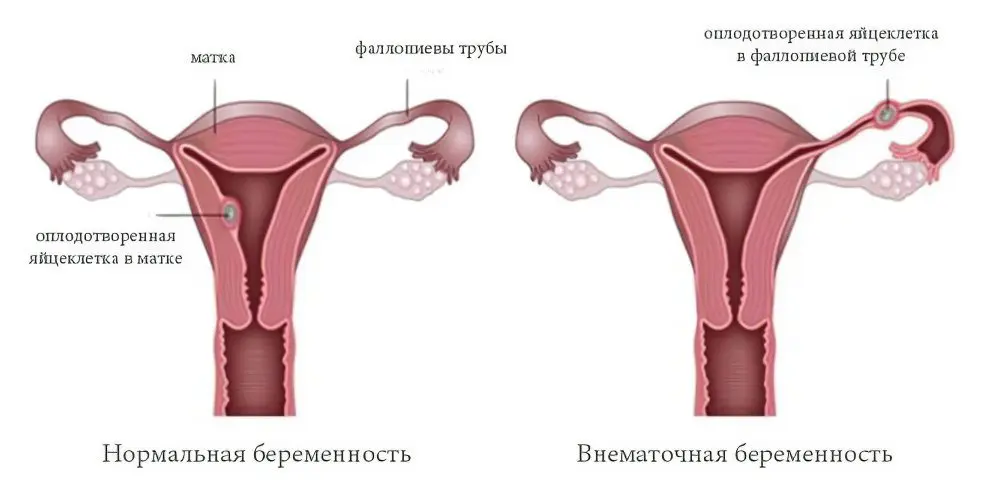
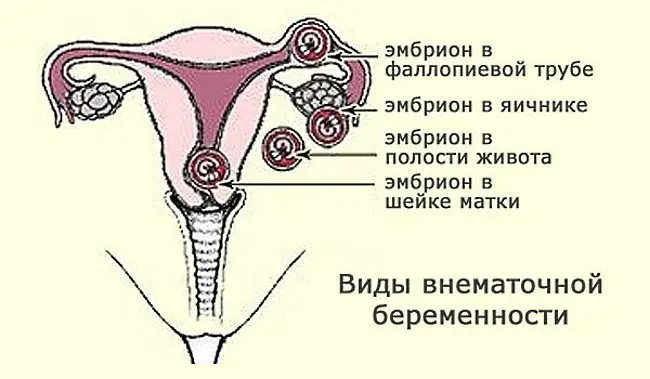
Types of ectopic pregnancy
A fertilized egg can attach itself outside the uterus in the following places:
In the abdominal cavity (abdominal pregnancy). This pregnancy can be primary (fertilization of the egg immediately occurred in the peritoneal cavity, where it remained) and secondary (the fetal egg came out of the fallopian tube and “settled” in the peritoneal cavity).
To the ovary (ovarian pregnancy). It is divided into pregnancy, which develops on the surface of the ovary, and one that grows inside the follicle.
To the inner surface of the fallopian tube (tubal pregnancy).
In the cavity of the rudimentary uterine horn.
There have also been cases of pregnancy when one embryo grows and develops in the uterus, and the second – outside its cavity. However, tubal pregnancy is the most common. Its most favorable completion is a spontaneous tubal abortion, when the fetal egg independently leaves the cavity of the appendage. In this case, the woman will be disturbed by bloody vaginal discharge.
Who is at risk for developing an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy is considered pathological, since the fetal egg is attached not in the uterine cavity, but in the tube. In the peritoneum, it is recorded extremely rarely (no more than 1% of cases of all cases of ectopic pregnancy). The embryo is not viable, and for a woman there is a real threat to life.
Most often, ectopic pregnancy occurs in women after 35 years of age, seeking to conceive a child for the first time. The risk group includes those women who are being treated for hormonal disorders, or for infertility.
Diseases such as mycoplasmosis, chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections can increase the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy in the future. Therefore, never forget about contraception.
Why does an ectopic pregnancy happen: the reasons for its development

In order for the pregnancy to develop normally, it is not enough only to fertilize the egg with a sperm. A prerequisite is its implantation in the uterine wall. Only this organ in the entire female body has the ability to stretch to fit a child. In addition, it is in the uterus that the fetus will receive all the necessary nutrients for its growth and development.
Sometimes it happens that the egg does not reach the uterus and is attached in the wrong place. As a result, an ectopic pregnancy occurs, which threatens the life of a woman. Therefore, when a fetal egg is found outside the uterus, doctors send the patient for emergency surgery. Otherwise, it will not be possible to avoid a rupture of the tube and the development of internal bleeding.
Reasons for an ectopic pregnancy:
Pathology of the fallopian tubes. If the tubes are covered with scars after suffering inflammation, induced abortions, many sexually transmitted diseases, then this will ensure that the fertilized egg will not be able to reach the uterus, but will settle in the wrong place.
Congenital anomalies of the fallopian tubes. Similar pathologies are often observed in women whose mothers abused alcohol during pregnancy, smoked or took drugs.
Wearing an intrauterine device for the purpose of contraception can lead to the development of an ectopic pregnancy.
Frequent abortions. Multiple abortions artificially contribute to the fact that adhesions will grow in the abdominal cavity and in the fallopian tubes. This violates contractility, leads to narrowing of the appendages. As statistics show, in 45% of cases, women who have had an abortion later suffer from an ectopic pregnancy.
Smoking. It has been established that the risk of ectopic pregnancy in women who smoke is 3 times higher than in non-smokers. Nicotine negatively affects the functioning of the fallopian tubes and uterus, leads to malfunctions in the immune system.
Malignant tumors of the uterus and appendages.
Sexual infantilism, in which the fallopian tubes are very long and curved.
The woman is over 35 years of age.
genital tuberculosis.
Oral contraceptive Mini-pill. All other drugs from this group are quite safe, and Mini-pill should be used to prevent unwanted pregnancy in women over the age of 35, nursing mothers, and only after consulting a doctor.
ECO. There are statistics that indicate that every 20th IVF ends with an ectopic pregnancy.
Hormonal disorders. If a woman’s body has an insufficient level of progesterone, then this can lead to the formation of an ectopic pregnancy. Against the background of a lack of this hormone, the fallopian tubes are not able to contract normally and move the egg into the uterus.
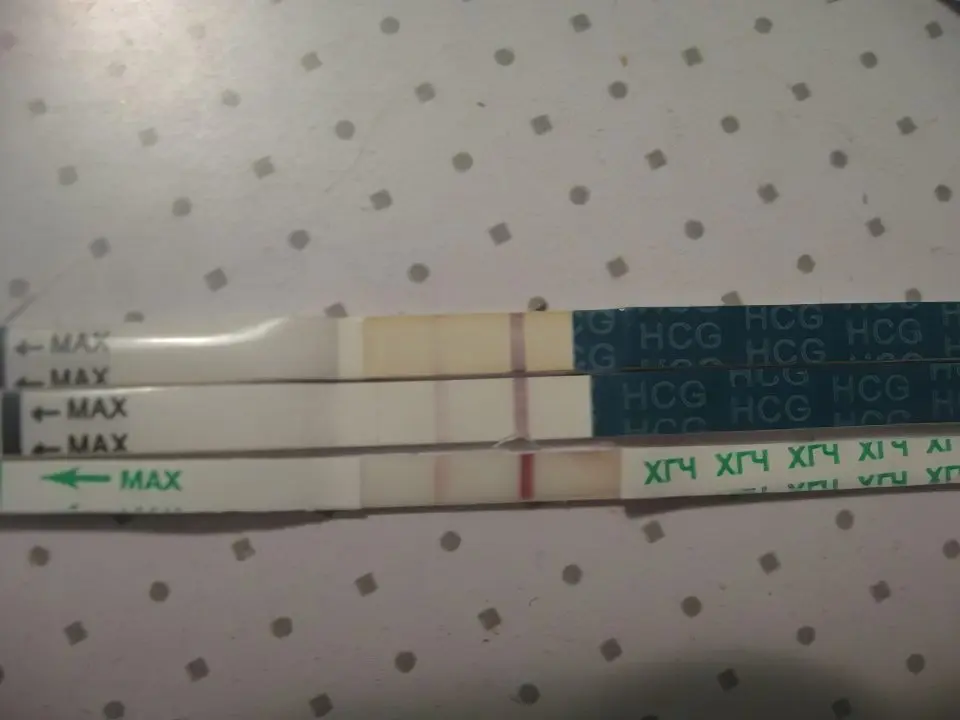
Negative test result in ectopic pregnancy: what are the reasons?
A pregnancy test responds to hCG levels by detecting the hormone in the urine. With an ectopic pregnancy, the test may be negative, or the second strip on it will appear dimly. Such a result should definitely alert a woman. She should retest in a week. When even after 7 days the result of a pregnancy test again turns out to be doubtful, you should not hesitate to contact the doctor.
The test for an ectopic pregnancy turns out to be negative due to the fact that hCG is produced in the body, but not in the same amount as during a normal pregnancy. Therefore, it is imperative to listen more carefully to your body: does it give any pathological signals, for example, in the form of pain in the lower abdomen.
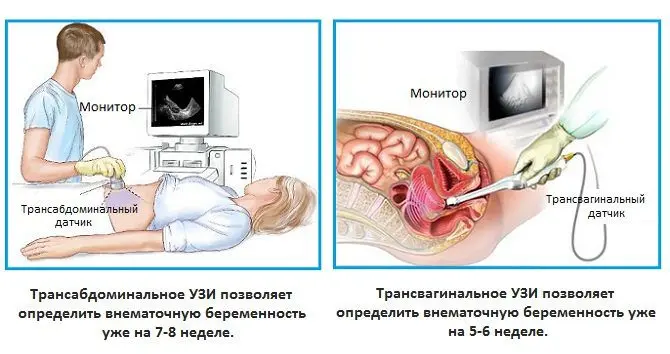
In general, ectopic pregnancy should not be judged solely on the basis of the test done. To make sure that there is no pathology, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound examination, which allows you to visualize the fetal egg and its location.
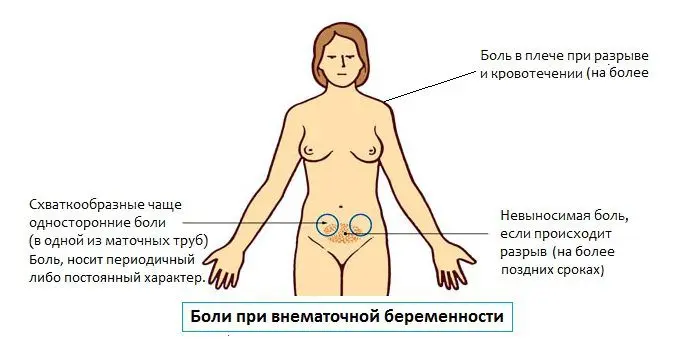
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
At the initial stage of attachment of the fetal egg outside the uterus, the symptoms of a pathological pregnancy will not differ from the signs of a normal pregnancy. It will be possible to detect that the embryo has not entered the uterus only during the passage of an ultrasound. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend seeking advice if menstruation does not come on time.
The fact that a woman develops an ectopic pregnancy will be indicated by minor pains that are localized in the lower abdomen. They are aching in nature and do not differ in high intensity. As the embryo grows, the pain will increase.
Do menstruation occur during an ectopic pregnancy?
After the onset of an ectopic pregnancy, menstruation stops, since the presence of an embryo in the body of a woman causes the onset of hormonal changes. As a result, menstruation does not come on time (in 75-92% of cases). For this reason, many women do not go to the doctor, believing that they had a normal pregnancy. Such negligence threatens with serious complications.
The appearance of discharge with blood in the early stages of an ectopic pregnancy most often indicates that a woman will soon have a miscarriage. If there is heavy bleeding, then this requires emergency medical attention.
How can an ectopic pregnancy be distinguished from a normal one?
It is almost impossible to independently distinguish an ectopic pregnancy from a normal one for a period of 1,5-2 months. However, doctors identify a certain set of symptoms that should alert a woman and make her see a doctor as soon as possible.
Features of the course of ectopic and normal pregnancy: comparative characteristics
Sign | Standard pregnancy | tubal pregnancy |
Body temperature | After conception, body temperature can rise to a subfebrile mark of 37,5 ° C | Body temperature remains elevated constantly and reaches a mark of 37,6-37,8 ° C |
Chills | Not visible | Occurs very often, it is accompanied by elevated body temperature |
Pain | Painful sensations can be aching in nature and are localized in the lower abdomen. Lumbar pains are absent. | The pain is often stabbing in nature, localized in the abdomen and pelvis, may occur in the side. The pain radiates to the lumbar region, radiates to the coccyx and intestines (in 35% of cases). Painful sensations are noted by 72-85% of all patients. |
Vaginal discharge with blood | They can only occur when there is a threat of spontaneous abortion. | From time to time there are secretions in a small volume. They are observed in 60-70% of cases |
Nausea, vomiting | This symptom is characteristic of early toxicosis. However, when women adjust their menu and devote more time to walking in the fresh air, nausea and vomiting recede. These symptoms are of concern mainly in the morning. | Occur at any time of the day, not amenable to correction with nutrition. It is not possible to get rid of vomiting even after taking medications. Early toxicosis in the form of nausea and vomiting is observed in 48-54% of cases. |
Pain while emptying the bladder | Pain during urination is extremely rare and is most often a sign of an infection in the urinary or reproductive system. | Pain occurs very often, tends to increase as the fetal egg increases in size |
Dizziness | Is a frequent companion of normal pregnancy | Often accompanied by an ectopic pregnancy |
When a woman has at least 2 symptoms, she should contact the doctor as soon as possible and be examined.
Fatigue that does not go away after a night’s rest, in combination with other pathological signs, may indicate an ectopic pregnancy.
Also, in a woman with an ectopic pregnancy, in 41% of cases, there is an increase and soreness of the mammary glands. However, this symptom is not pathognomonic specifically for tubal conception.
The fact that a woman develops an ectopic pregnancy will be indicated by pain in the shoulders at a later date. The pain occurs due to the fact that internal bleeding has opened, blood has entered the peritoneal cavity and irritates the diaphragm.
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy
After the woman comes to the doctor’s appointment and reports her problem, the doctor will definitely offer her an examination on the gynecological chair. With an ectopic pregnancy, he visualizes a softened cervix, which will have a bluish tint. However, this sign can indicate both normal and ectopic pregnancy. During palpation of the fallopian tubes, it is possible to detect an appendage enlarged on one side. At the same time, he himself will give pain during probing. The presence of education in the area of the appendage can be detected in 58% of cases, and pain occurs in 38% of cases. At the same time, the doctor fails to qualitatively probe the shape of the seal.
To confirm the assumption of an ectopic pregnancy, the gynecologist will refer the woman to undergo the following studies:
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs.
Determination of the level of hormones in the blood (the level of progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin is assessed). Indicators for an ectopic pregnancy will be lower than for a normal one.
Signs of a ruptured fallopian tube

Regardless of how long the fallopian tube ruptured, the symptoms will always be the same. Her muscle layer is damaged, which leads to the development of severe internal bleeding.
It is impossible not to notice the gap that has occurred, since it is accompanied by the following signs:
Drop in blood pressure.
Cold perspiration on forehead.
Paleness of the skin.
Nausea and vomiting.
Dizziness and pre-fainting (possible fainting).
Increased heart rate.
The strongest stabbing pain in the lower abdomen comes to the fore, which radiates to the rectum, to the lower back.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor visualizes the bluish cervix, the small size of the uterine cavity, which does not correspond to the actual gestational age. The posterior fornix of the small pelvis is smoothed out, which is due to the accumulation of blood in the abdominal cavity. On palpation, it gives pain. Blood from the uterus may not come out and appear only after the surgery.
If the doctor takes a puncture of blood from the peritoneum, it will have a dark color and will not clot. It is extremely rare to resort to puncture, and a rupture of the fallopian tube is diagnosed according to the available signs.
Why does a fallopian tube rupture during an ectopic pregnancy?
The fallopian tube ruptures when a woman does not see a doctor even though she knows she is pregnant. It is the untimely registration in 80% of cases that leads to this internal catastrophe against the background of an ectopic pregnancy. A woman does not pass the necessary tests, ultrasound does not pass in a timely manner, etc. If a patient comes to see a doctor at an early stage, he will be able to suspect an ectopic pregnancy, which will avoid serious health complications.
The fallopian tube, unlike the uterus, is not able to stretch, take the size of a growing fetus. The pipes are made of dense muscles and connective tissue, so it is absolutely not suitable for carrying a child. As the embryo grows, the walls of the tube stretch and it bursts.
Is it possible to carry a child with an ectopic pregnancy?

It should immediately be noted that the chance that the pregnancy can be saved is minimal. Science knows only a few cases when an ectopic pregnancy ended in childbearing, and all of them are under great doubt from official medicine. Proponents of this theory point out that this can happen when the fetus is fixed at the very end of the tube. As it grows, the fetal egg can simply push into the existing lumen, exit into the abdominal cavity and attach there to any organ.
However, in medicine, this condition is called a tubal abortion. As for the chances that the fetus will survive, they are extremely small. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend that patients remove the embryo. This will avoid an inflammatory reaction and many other complications.
When does a fallopian tube rupture occur?
Most often, the rupture occurs at a period of 8-12 weeks, although it is impossible to exclude damage to the tube by a growing fetal egg even at 4-6 weeks. Not a single doctor is able to name more exact dates. Therefore, a period of 4-12 weeks is considered dangerous.
It should be noted that there are certain factors that can affect the rupture of the fallopian tube, among them:
Individual structural features of the female body, in particular, the diameter of the fallopian tube;
The presence or absence of fetal pathology;
Individual characteristics of the growth and development of the embryo;
Women’s health status.
Early fallopian tube rupture
Sometimes a fallopian tube rupture occurs at an ectopic pregnancy less than a month old. However, this happens extremely rarely and only when the fetal egg is fixed in the narrowest part of the fallopian tube (in its isthmic part). A similar situation threatens that the appendage may burst even before the time when the woman finds out about her position. In this case, it will be possible to save the patient’s life only on the condition that she seeks medical help in a timely manner. Therefore, when signs appear that indicate a rupture of the fallopian tube, it is necessary to call a medical team as soon as possible.
If the victim will get to the hospital on her own, then it is best for her to be in a horizontal position. This will reduce pain and reduce bleeding.
If the fallopian tube ruptured in late pregnancy

A fertilized egg, which exceeds 5 mm in diameter, cannot remain in any part of the fallopian tube and will certainly lead to its rupture. The most favorable situation is one in which the fetal egg is fixed at the site of the transition of the tube into the uterus. In this case, there is a chance that the woman will find out about her position faster than the rupture of the appendage occurs. The fact is that it is in this section that the muscles of the pipe have maximum elasticity and the ability to stretch. Therefore, if a woman turns to a gynecologist on time, the risk of tube rupture will be minimal.
Statistics clearly indicate that most often the fallopian tubes are damaged for a period of 8-12 weeks, so timely registration is not a whim of gynecologists, but a careful attitude to one’s own health. In some cases, in this way a woman saves her life.
An ectopic pregnancy poses a real threat to the life and health of a woman, therefore, when the first signs of this pathology are detected, it is necessary to contact a gynecologist for an appointment.
Complications of an ectopic pregnancy
No doctor can guarantee that a woman will never have an ectopic pregnancy.
Its complications can be very serious:
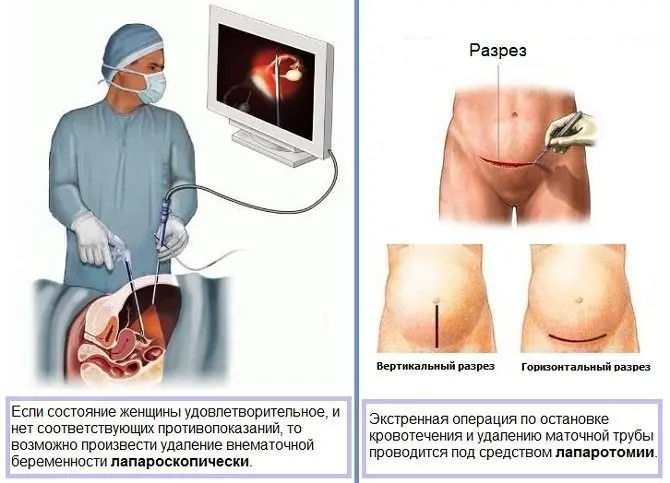
Removal of an appendage. The tube will be cut during the operation. It is necessarily removed in the case when the walls of the appendage rupture. In this case, an ectopic pregnancy is complicated by internal bleeding and can be fatal.
Infertility. If a woman has a tube removed, then the risks of her becoming infertile are very high. This is especially true for older women. While the body of young patients adapts much faster to the absence of one appendage. They can get pregnant even with one tube. What matters in this case is how well the ovaries function.
Recurrent ectopic pregnancy. It is possible that an ectopic pregnancy in a woman may recur, but the embryo will settle in the remaining tube. To prevent this from happening, the woman must undergo treatment. The risk of recurrent ectopic pregnancy after tubotomy is 4-13%.
Formation of adhesions in the pelvis after undergoing surgery.
Development of intestinal obstruction also not excluded.
Doctors without fail recommend women who have had an ectopic pregnancy to undergo anti-inflammatory therapy. During the rehabilitation period and after it, women should adhere to a healthy lifestyle, eat right and be protected from pregnancy for 6 months.
Do I need to save the fallopian tubes during an ectopic pregnancy?
Since an ectopic pregnancy requires emergency surgery, most doctors perform a salpingectomy, which involves removing the fallopian tube. It is not possible to save it, since it usually has serious deformations. Even if the appendage is retained, the next pregnancy carries a high risk of being ectopic again.
However, sometimes the surgeon decides not to remove the tube, but to make a longitudinal incision on it, remove the fetal egg and suture. It is possible to save the appendage when the fetal egg has a diameter not exceeding 5 mm, the woman feels well and shows a desire to have children in the future.
In some cases, the fetal egg can simply be squeezed out or sucked out of the appendage. But fimbrial evacuation is possible only if the embryo is located in the ampullary part of the tube.
Another option for the operation to remove the fallopian tube while preserving the appendage is its resection. In this case, a part of the pipe is cut out, and the ends are sewn together.
If an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed in the early stages of its development, then it is possible to eliminate it with medication. At the same time, Methotrexate is introduced into the cavity of the epididymis, which contributes to the dissolution of the embryo. Access to the tube is obtained through the posterior fornix of the vagina. The whole procedure is carried out under ultrasound control.
In order for a woman to have the opportunity to become pregnant naturally after the operation, the following conditions must be observed:
To prevent the formation of adhesions, the patient should be raised early and allowed to move. Also, the woman is shown physiological treatment.
Rehabilitation after surgery should be of high quality and comprehensive.
It is important to prevent the development of infectious processes after the surgical intervention.
Answers to popular questions

How to protect yourself from an ectopic pregnancy? With an increased risk of developing such a pathology, a woman is not recommended to install an intrauterine device and take progestin oral contraceptives (Mini-pill).
Can a pregnancy test determine the ectopic location of the fetal egg? No, a pregnancy test only indicates the fact that conception has happened.
The pregnancy test is positive, the delay in menstruation is 5 days, during an ultrasound scan, a fetal egg was not found in the uterus. What to do in this situation? It is necessary to pass an analysis to determine the level of hCG and conduct a second ultrasound after 7-14 days. It is likely that the fetal egg is still too small, so it cannot be visualized during the ultrasound examination.
Is there an increased risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy after a single inflammation of the appendages? Yes, the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy in women who have had ovarian inflammation is much higher than in healthy women. To minimize it, you need to undergo an examination and treatment, if necessary.
When can I start planning for conception after an ectopic pregnancy? You can think about children no earlier than after 6 months.









