Contents
What is liver echinococcosis?
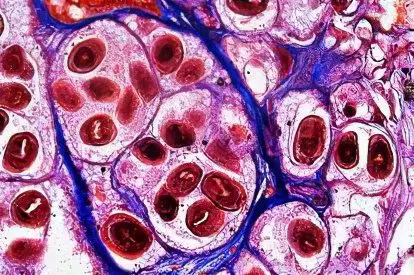
Liver echinococcosis in humans is caused by the introduction and development of tapeworm larvae Echinococcus granulosus in the liver.
Human liver echinococcosis can be of two types: alveolar or cystic. The distribution of liver echinococcosis is concentrated in Russia and neighboring countries. In Russia, these are the Omsk, Novosibirsk and Tomsk regions, as well as Yakutia and Siberia. Near abroad countries include Central Asia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Crimea.
In the case of cystic echinococcosis – or unilocular, racemose, hydatous – in most cases, the cyst forms in the right lobe of the liver, but sometimes there may be several cysts. All the pathogenic effects of echinococcus are determined by the fact that the echinococcal cyst exerts mechanical pressure on the liver and neighboring organs. Also, the parasite has a toxic and sensitizing effect.
Echinococcal cyst has the form of a bubble with a rather complex structure. Outside, the cyst is surrounded by a cuticle, or layered membrane, in some cases its thickness can reach 5 mm. Beneath this multi-layered cuticular sheath is the germinal, inner germinal sheath. This membrane forms brood capsules with scolexes and daughter blisters, but also gives strength for the growth of the layered membrane of the cyst.
Causes of liver echinococcosis
In human echinococcosis, the dog occupies a key position as the definitive host of the parasite. Dogs can get echinococcosis by eating meat scraps. Another possible source of infection for dogs can be hunting products. These are the affected organs or corpses of wild herbivores.
In humans, infection occurs mainly from dirty hands. Infection comes from contact with a dog, in which the accumulation of tapeworms of echinococcus may be on the coat or tongue. Animals can also be mechanical egg carriers. They get them from a similar contact with a sick dog.
It is possible that a person can become infected with echinococcosis through eating vegetables and fruits that have not been pre-treated or washed. On fruits and vegetables, the pathogen can get with the feces of dogs, which contained oncospheres.
Another source of infection can be wild carnivores. From them you can get an infection during hunting, as well as when cutting skins and making fur clothes. You can also get infected by eating unwashed wild berries and water from natural reservoirs.
At risk are those people who work in sheep breeding areas. These are shepherds, shepherds, shearing sheep and all those who have contact with these people are no exception and their families.
Symptoms of liver echinococcosis
In liver echinococcosis, two forms are distinguished – alveolar and hydatidosis (cystic).
The hydatidosis form of liver echinococcosis is a disease characterized by a larval, or cystic, form of development. For many years from the moment of infection, clinical signs of the disease do not appear in any way. The person during all this time feels absolutely healthy. All symptoms begin to appear when the hydatid reaches a relatively large size. After the hydatida reaches a certain size, aching or dull constant pains may appear in the right hypochondrium and epigastric region, as well as in the lower parts of the right half of the chest. If the size of the cyst is very large, then on examination it is possible to detect a bulging of the abdominal anterior wall in the region of the right hypochondrium. There is also a percussion increase in the borders of the liver upwards. On palpation of the liver, a round, elastic, tumor-like formation can be detected. Hepatomegaly is observed with the localization of cysts that are deep in the liver parenchyma.
According to its location, liver echinococcus can be divided into three types: it is anterior, descending, or abdominal, ascending, or thoracic. If the anterior cysts have a large volume, then the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe liver is greatly enlarged. Upper cysts are defined fluoroscopically due to the high condition of the diaphragm on the right with a dome-shaped highlight of the cyst location. If the cysts are lower, then the tumor is palpable in the abdominal cavity, while it moves when a person breathes along with the liver and has an elastic consistency. Cysts, which are located in the left lobe of the liver, are detected by palpation already in the later period of the course of the disease.
The state of health worsens due to the fact that an allergic reaction begins to develop in the presence of a live parasite in the body. An allergic reaction can manifest itself in the form of diarrhea, urticaria, etc. The main symptoms begin to appear when the tumor begins to compress neighboring organs.
In the hydatid form of liver echinococcus, complications are most common. They manifest as jaundice, rupture of the hydatid cyst or its suppuration. Obstructive jaundice is associated with the fact that the cyst compresses the bile ducts, or with a breakthrough of the cyst into the biliary tract, this occurs in approximately 5-10% of all patients. And ascites is quite rare, in 5-7% of patients, with compression of the portal vein.
The rupture of the hydatid cyst is accompanied by the outpouring of its contents into the abdominal cavity, into the bile ducts, into the pleural cavity, the bronchus and the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract.
The most serious complications are caused by perforation of the cyst into the abdominal cavity. This causes symptoms of anaphylactic shock and widespread peritonitis.
Suppuration of the cyst occurs because cracks form in the hydatid capsule, especially if there is a connection with the biliary tract. If suppuration of an echinococcal cyst occurs, then there are severe pains in the liver, hyperthermia, hepatomegaly, as well as other severe symptoms of purulent intoxication.
As for alveolar echinococcosis, it is always characterized by liver damage. Throughout the time, the invasion proceeds without the presence of clinical symptoms. The main symptom is hepatomegaly due to the development of a tumor-like node, but with an exceptional “wooden” density. A persistent and frequent symptom in this type of echinococcosis is jaundice. Perihepatitis of the liver develops, it limits the mobility of the liver. In a third or even half of patients, the spleen is enlarged. When the process is running, liver function tests are sharply disturbed.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing the hydatid form of echinococcosis, a complete history of the patient can help. Still, the decisive role remains with additional methods of research. With a general blood test, eosinophilia of up to 20% or more is often found in it. To determine echinococcosis, Koni’s intradermal reaction is performed. It shows a positive result in 89-90% of cases with echinococcus. The Koni reaction is a procedure for injecting 0,2 ml of sterile echinococcal fluid subcutaneously. If the reaction is positive, then redness will appear at the place where the injection was made, and after that a continuous and intense redness, or, in other words, skin anaphylaxis, will form. More accurate in diagnosing such tests as agglutination with latex and the reaction of indirect hemagglutination.
For the diagnosis of alveolar echinococcosis, a long-lived cyst in the liver, which has a very high density, is of great importance, as well as hypereosinophilia, positive allergic tests and a liver scan. When diagnosing this type of echinococcosis, the Koni reaction with the alveolar antigen is of great value.
[Video] Lecturer – Kalieva D.K. – Echinococcosis of the liver. Modern methods of diagnosis and treatment:










Саламатсыздарбы ушул оорудан кантип айыкса болот менда бул оору мн алышып келптам быйыл дагы ушул оору мн опереция болом 3 жолу тажап кеттим ушунчплык кантип оорубайтурган болуп жакшы болсом болот