Contents
Echinococcosis is widespread in countries with a hot climate, or in regions traditionally engaged in animal husbandry. The density of patients with echinococcosis in Russia is 1-4 recorded cases per 100 thousand people. A feature of the pathology is poor symptoms at the beginning of the development of helminthiasis and, as a result, late diagnosis of the disease.
Echinococcosis is a chronic helminthiasis caused by the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosis. The parasite invades the internal organs of humans and animals (most often the lungs and liver). Their functions are seriously impaired, echinococcal cysts are formed in the tissues. The area of development of the disease occupies the countries of Southern Europe (Italy, Cyprus, Greece, Bulgaria, Spain), the countries of South America (Brazil, Argentina). Echinococcosis is often found in the southern states of the USA, India, Japan, Australia.
In Russia, residents of regions and regions with a wide development of animal husbandry are most often susceptible to infection: Khabarovsk, Krasnoyarsk, Stavropol, Krasnodar, Altai Territory, Omsk, Tomsk Regions, Bashkiria, Tatarstan.
Reasons for the development of echinococcosis
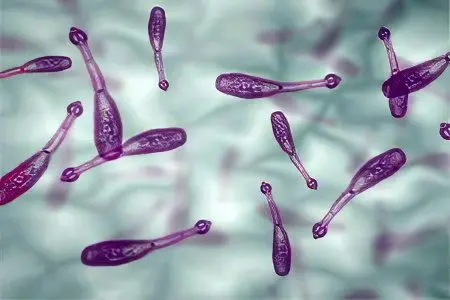
The cause of infection with echinococcosis is the introduction of the tape parasite Echinococcus granulosis into the body at the larval stage. This tapeworm from 2,5 to 8-9 mm long consists of 3-4 segments, a neck and a head with 50 hooks in 2 rows and four suckers.
The segments have different degrees of maturity:
1-2 immature segments;
hermaphroditic joint;
a mature segment containing a uterus with several hundred eggs.
In each of them there is a larva in the embryonic stage, which has 6 hooks. This larva (oncosphere) remains viable under the most extreme conditions: temperatures from -30°C to +35+40°C. It can be in the ground for several months at a temperature of +12 to +25°C. Only exposure to sunlight for a few days is detrimental to the larvae.
Sources of Echinococcus Infection

Final host:
Dogs,
coyotes,
Foxes,
lions,
wolves,
Jackal,
Lynx.
Intermediate host:
Sheep,
Proteins,
buffalo,
hares,
Horses,
pigs,
Person.
The placental barrier is not an obstacle to the transmission of helminthiasis from mother to fetus.
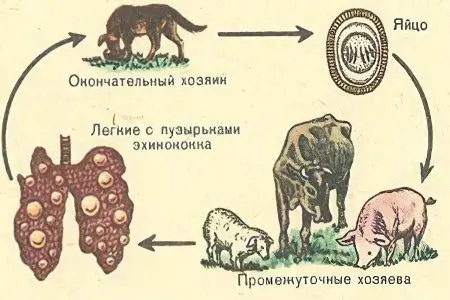
Scheme of the circulation of parasitic invasion:
Final owner.
Environment as a place of feces with segments and oncospheres.
Intermediate host or healthy definitive host.
A person does not excrete either eggs or helminth segments with feces, so he cannot be a source of echinococcosis.
Mechanisms of infection with echinococcosis
A person becomes infected with echinococcosis in two ways: alimentary and contact household. The introduction of parasites into the human body occurs when contaminated vegetables and fruits, contaminated water are included in the diet, picking up herbs and berries infected with animal feces, contact with the hair of the main and intermediate hosts (mainly dogs).
A short cycle of development of echinococcus in animals:
The final host (wolf, dog) eats the entrails of the intermediate host (pigs, hare, squirrels).
On the mucous membrane of the small intestine of the definitive host, an adult helminth develops, producing eggs.
With faeces, mobile segments with eggs of larvae enter the environment.
The eggs of the larvae are stored in the internal environment until they reach a new host.
A short cycle of development of echinococcus in humans:
Echinococcus eggs enter the human intestine orally.
From the oncosphere, the embryo enters the bloodstream, enters the internal organs through the portal vein.
In the lungs or in the liver, a single-chamber fluid-filled bladder is formed, consisting of a chitinous and germinal membrane. In the bubble, the stage of larval development occurs, additional daughter bubbles are formed.
Inside the cyst, scolex capsules form, sometimes detaching from the walls and floating in the fluid.
The total weight of blisters in one person can reach several tens of kilograms and contain up to 6-10 liters of liquid.
Pathological effect of echinococcus in the human body

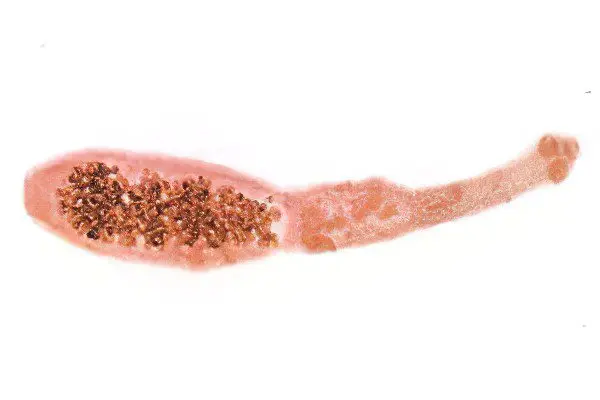
The main feature of echinococcosis is the formation of cysts in any organ. Most often it is lungs (20%), liver (80%). The cyst can be either singular or plural.
The consequences of the introduction of echinococci into the body:
Sensitization of the body (immediate or delayed allergic reaction, anaphylactic shock when a cyst ruptures).
Mechanical impact of an overgrown echinococcal cyst (atrophy and dysfunction of organs). Consequences – tissue fibrosis, pneumosclerosis of the lungs. The term for the formation of a bubble structure from the moment the larvae enters the body is on average 2 weeks. After 4-5 months, the size of the cyst can reach 5 mm. A cyst reaches a volume of several liters in a period of 10-20 years.
Decreased general and local immunity, re-infection due to a weak immune response of the body.
Symptoms of echinococcosis

Stages of development of echinococcosis:
Asymptomatic stage (from the onset of infection to the appearance of the initial cyst).
The appearance of minor symptoms of infection in a particular organ.
The appearance of a pronounced clinical picture of echinococcosis.
The development of complications of helminthiasis.
The stages are allocated conditionally, since the disease has a slow rate of development of symptoms, and cysts form extremely slowly.
Symptoms of liver echinococcosis

Common symptoms:
Nausea and vomiting;
Weakness;
Loss of appetite;
Pain in the epigastric region and right hypochondrium;
Skin rash and itching;
Diarrhea;
Hepatosplenomegaly (enlargement of the spleen and liver);
Isolation of the cyst during palpation;
Inflammation of the cyst when a bacterial infection is attached (hyperthermia, chills, pain);
liver abscess;
Obstructive jaundice in case of compression of the cyst of the bile ducts (dark urine, light stools, yellowing of the sclera of the eyes and skin, skin itching, an increase in the number of leukocytes and eosinophils).
When opening the cyst, the patient experiences a sharp pain, manifestations of allergies, symptoms of anaphylactic shock. A serious consequence of a violation of the integrity of the cyst is the seeding of the whole organism with echinococci, secondary echinococcosis.
Symptoms of echinococcosis of the lungs

Common symptoms:
Pain in the chest, in the projection of the lungs;
Dyspnea;
Hemoptysis;
Weakening of breathing;
Shortening of percussion;
Chest deformity with mediastinal displacement;
The development of exudative pleurisy with effusion of pleural fluid.
If the integrity of the cyst located in the bronchi is violated, the patient feels suffocation, a strong cough, severe allergic manifestations are noted, he has skin cyanosis. When a cyst breaks into the pericardial cavity and the pleural cavity, death occurs due to anaphylactic shock.
A complete blood count fixes leukocytosis with a shift towards stab neutrophils and eosinophils.
Symptoms of echinococcosis of the spleen, kidneys, central nervous system
It occurs extremely rarely when echinococci enter the systemic circulation. Symptoms – allergic urticaria, signs of damage to a particular organ.
[Video] “Live healthy” – Echinococcosis – a disease of dirty hands:
Prevention of echinococcosis

To prevent the spread of helminthiasis, the following measures are taken:
Examination for echinococcosis of persons at risk: livestock breeders, employees of meat processing plants and slaughterhouses, dog breeders, hunters.
Veterinary measures for the prevention of infection of animals: compliance with sanitary standards for slaughtering and cutting livestock, prevention of helminthiasis in dogs.
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene: thorough washing of berries, vegetables and fruits, drinking purified water, washing hands with soap and disinfectants after contact with dogs, caring for animals, before eating.









