Contents
Dysplastic nevus – This is one of the varieties of pigmented skin formations, which are often called moles. It is an intradermal or subepidermal accumulation of melanocytes – pigment cells, which are a subspecies of nerve cells and enter the skin during fetal development. Throughout a person’s life, these nevi begin to appear on the skin in the form of brownish spots. This type of nevoid formations deserves the closest attention among all types, since there is a very high risk of their malignancy with the transition to the most malignant tumor – melanoma. The term dysplastic itself means that it is a nevus that is not similar in external and internal features to typical moles.
Causes
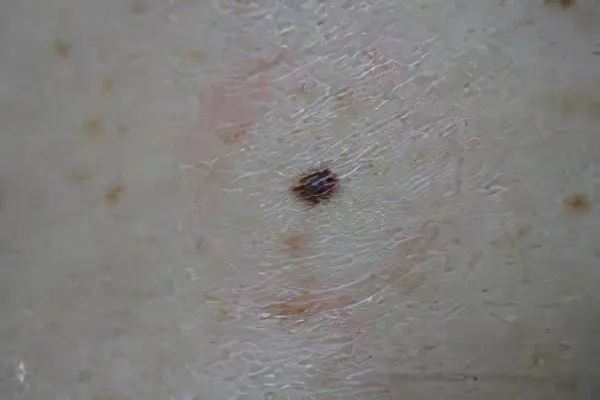
Do not confuse ordinary nevi, which, as a result of their injury, begin to show properties that degenerate into melanoma. Dysplastic nevus from the moment of its appearance has the properties of atypism, which distinguish it from ordinary moles.
The main reasons for the occurrence of such nevoid structures are:
Genetic predisposition;
Hormonal changes in the body and its active growth;
Excessive insolation and sunbathing;
Procedures associated with exposure to the skin of ultraviolet rays.
The role of heredity in the occurrence of dysplastic nevi
Scientists have unambiguously recorded that this type of mole has a clear family prevalence. An autosomal dominant type of their transmission from parents to children has been recorded. This means that in any case, there will be a tendency to the appearance of dysplastic nevi in children from parents who are their carriers. Whether they appear in the process of a child’s life or not depends on environmental factors and the characteristics of the functioning of a particular organism. The probability of the appearance of family-type dysplastic nevi is lower, the more distant relatives are.
The role of external influences and internal features of the development of the organism
Talking about these factors as the causes of the appearance of dysplastic nevi is caused by the presence of their sporadic cases. At the same time, neither close nor distant relatives of the carrier of such nevi have signs of mole dysplasia. This means that not only the hereditary factor contributes to their development. The maximum appearance of dysplastic nevi was recorded during puberty and in a young growing organism. This phenomenon can be explained by the influence of fluctuations of sex hormones on the degree of differentiation of skin melanocytes, which did not manifest themselves in the form of moles at an earlier date. External factors in the form of excessive exposure to direct sunlight and artificial sources of ultraviolet rays are of secondary importance and are unable to independently cause the appearance of dysplastic nevi.
Clinical manifestations
In most cases, it is not difficult to determine the specific type of nevoid skin formations with a detailed examination of them.
The following features of their appearance may suggest the idea of dysplastic nevi:
They acquire their atypical appearance from the moment of occurrence;
They can be both single and spread over the entire surface of the skin;
Most actively appear in puberty and young people
The appearance of dysplastic nevi is presented in the table:
Quantity | From 1-2 to 100 or more |
Favorite localization | Mainly arms and upper body |
dimensions | Always large (about a centimeter) |
color | It contains pigment elements with coloring of different intensity (from light light pigmentation to rich brown). Characterized by alternation of areas of different intensity within the same nevus |
Elevation above the surface of the skin | Slightly protrudes above the surface of the skin or is at its level |
Surface | Never smooth. It is characterized by a finely tuberous structure, reinforced in the central sections, especially with elevated types of nevi. Peripherals are less elevated and smooth |
Form | Often irregular, edges uneven and fuzzy |
Additional signs | Very often there is an increase in pathological hairs from the nevus (black, long, thick) |
The danger of dysplastic nevi
By themselves, moles of the dysplastic type do not belong to diseases. It is rather a kind of obligate precancer, which only in some cases can become a malignant neoplasm. Therefore, carriers of dysplastic nevi should be alert in this regard. But in no case should one succumb to panic, living in constant fear. Stress and psycho-emotional lability are one of the prerequisites for the transformation of dysplastic nevi into a malignant tumor.
Therapeutic and preventive measures

Unfortunately, it is not possible to prevent the appearance of dysplastic nevi. The only thing that remains is to carefully observe them, follow the recommendations regarding lifestyle and correctly respond to any changes in the nevi. Specific treatment for typical stable carriage of dysplastic moles is not required.
You can help in this way:
Mandatory registration with a dermatologist and oncologist;
Inspection by a specialist once a quarter;
Daily checkup of your skin. Be sure to note the characteristics of existing nevi and the appearance of new ones;
Mandatory and immediate contact with a specialist if any changes in nevi are detected;
Removal of suspicious dysplastic nevi. Only their excision is carried out surgically to the fascia. It is unacceptable to use different methods of physical influence (diathermocoagulation, laser, liquid nitrogen). Only by radical removal of the pathological area of the skin can the appearance of melanoma be prevented.









