Contents
What is dysentery
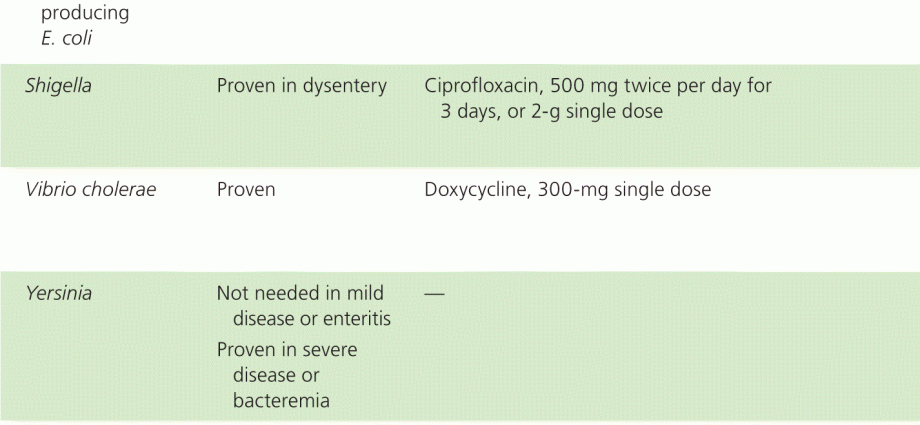
Dysentery or shigellosis is not just a poisoning that causes diarrhea, but a dangerous infectious disease, due to which the whole organism is intoxicated. With dysentery, the digestive tract, namely the large intestine, is especially affected.
The causative agents are Shigella bacteria, named after the Japanese scientist Shiga. Bacteria persist for a long time in food products, in soil contaminated with the feces of patients – up to 3-5 months, in cesspools and open water up to 50 days, in tap water – up to 1 month.
Causes of dysentery in adults
Shigella infection is transmitted in several ways:
Domestic – when caring for a sick person and through common household items.
Food – the use of products or the use of dishes on which the causative agent of dysentery has fallen. In the warm season (especially in summer and autumn), food is contaminated by flies that carry fecal particles containing bacteria. If hygiene standards are not observed in public catering, and food and utensils undergo insufficient heat treatment, then this is fraught with an outbreak of a group disease with dysentery.
Infection can occur when drinking water from open reservoirs or bathing in them. In some cases, tap or well water may be contaminated.
Symptoms of dysentery in adults
The incubation period of the disease ranges from 12-24 hours to 2-3 days.
Symptoms are very easy to confuse with symptoms of poisoning:
- headache;
- neck muscle tension;
- pain in the joints;
- retardation;
- frequent stools, which after a few hours acquires a typical dysentery character – there are few stools, but a lot of mucus and streaks of blood.
In the initial stage, the body temperature rises to 39 ° C, sometimes higher. Patients have pain in the abdomen, frequent loose stools with an admixture of mucus and blood appear, then it takes the form of grayish-green mucous lumps with streaks of blood.
Treatment of dysentery in adults
Treatment of dysentery is recommended in the hospital of the infectious diseases hospital. Urgent hospitalization is required if the disease proceeds in a moderate form, for children under 1 year old and preschoolers, catering and water utilities workers, people who live in communal apartments and dormitories.
In the acute period of the disease, it is necessary to follow the diet table number 4. Doctors prescribe to eat low-fat broths, chicken meat, low-fat fish, jelly, cereals, and drink green tea and rosehip broth in drinks. Such food restrictions are best observed within a month after recovery.
Diagnostics
To determine the pathogen in any intestinal infection, it is necessary to do a stool culture in order to find the most appropriate method of treatment. Shigellosis can be diagnosed only on the basis of clinical, epidemiological and laboratory bacteriological studies.
The disease can be mild, moderate or severe. A distinction is also made between acute and chronic dysentery. It can pass without symptoms, and the person can be just a carrier of the infection.
Modern treatments
When treating dysentery in a hospital, antibiotics and bacteriophages (the so-called “good” viruses that infect bacterial cells) are prescribed.
As mentioned above, in conjunction with drug treatment, a diet and bed rest are recommended.
But the main feature of the pathogen is that it quickly develops resistance to drugs. For example, if the same remedy is used for a long time within the same region, then after some time the pathogen may not respond to a particular drug. Therefore, the prescribed treatment can be adjusted taking into account this feature of the bacteria. Also because of this, there is always a risk of new mass outbreaks of dysentery.
Prevention of dysentery in adults at home
To protect yourself from infection, you must follow fairly simple rules of hygiene and maintain cleanliness in places where you eat:
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap, especially after using the toilet, before and during food preparation, before eating, after coming home from the street;
- drink boiled or drinking bottled water;
- observe the terms and conditions of food storage and the rules of heat treatment of food;
- wash fruits, berries and vegetables thoroughly under running water;
- rinse vegetables and root vegetables with water before putting them in the refrigerator. If the fruits are damaged by rot, they must be carefully cleaned, but it is better to throw them away;
- do not allow raw and cooked food to touch – use different cutting boards;
- keep the kitchen area clean;
- Always keep your kitchen free of insects and rodents.
Popular questions and answers
We asked for answers to typical patient questions related to dysentery Gastroenterologist Marata Zinnatullinа.
Why is dysentery dangerous?
After entering the human body, after 1-4 days, diarrhea begins (sometimes with blood), abdominal pain, tenesmus, symptoms of intoxication (high fever, general weakness), signs of dehydration may appear. In mild cases, the disease resolves spontaneously in 4 to 8 days, in severe cases in 6 to 8 weeks.
What are the complications of dysentery? Can you die from it?
Complications include the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, blood loss can lead to anemia, kidney damage.