What is a duodenal ulcer?
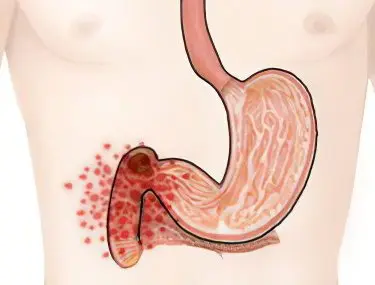
A duodenal ulcer is a deep inflammation of the mucous membrane or epithelium of the skin. Most often, the inflammatory defect is chronic and occurs due to an infection, mechanical injury, chemical or radiation exposure. Violation of the blood supply to tissues or nerve fibers can also cause an ulcer. With an ulcer, tissue is lost, and healing occurs with the formation of a scar.
People with hypersensitivity get sick due to exposure of the mucous membrane of the initial section of the small intestine to pepsin (an enzyme produced by the cells of the gastric mucosa) and stomach acid.
Peptic ulcer occurs with relapses: periods of exacerbation and remission alternate.
Peptic ulcers are predominantly men. On average, the world’s duodenal ulcer occurs in 10% of the population. In the duodenum, the formation of ulcers occurs more often than in the stomach. When an inflammatory defect simultaneously affects the stomach and duodenum, they speak of combined ulcers.
There are several types of duodenal ulcers. Acute inflammatory defects of the duodenum include ulcers with bleeding, bleeding and perforation (breakthrough outside the stomach or intestines), or without bleeding and perforation. Chronic ulcers may be unspecified with bleeding, unspecified with rupture of the ulcer outside the stomach or intestines, unspecified with bleeding and rupture, or without perforation and bleeding.
[Video] Surgeon Lovitsky Yu. A. – Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. What are the symptoms? How to determine? How to treat?
Prevention of this disease is proper nutrition, adherence to a healthy lifestyle, correct and timely treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. It is also important to try to avoid stressful situations and nervous tension.









