Contents
Dorsal hernia l5-s1 and l4-l5 is a protrusion of the contents of the intervertebral disc, directed into the space of the canal of the lumbosacral spine. So, l5-s1 is the fifth lumbar and first sacral vertebrae, and l4-l5 is the fifth and fourth lumbar vertebrae, that is, we are talking about a dorsal hernia that appeared in the intervals between them. It is from the direction in which the disc displacement is directed that the types of hernias are distinguished. A dorsal hernia, also called a posterior hernia, is directed towards the spinal canal. In this regard, there is a risk of infringement of the spinal cord and spinal nerves passing through it.
Its special soreness is associated with the direction of protrusion of the dorsal hernia. When the posterior longitudinal ligament is damaged, diffusion of the dorsal hernia occurs, which leads to severe neurological disorders, followed by paresis and paralysis of the pelvic organs.
According to statistics, it is in the lumbar region that dorsal hernias appear most often.
Causes of dorsal hernia l5-s1 and l4-l5
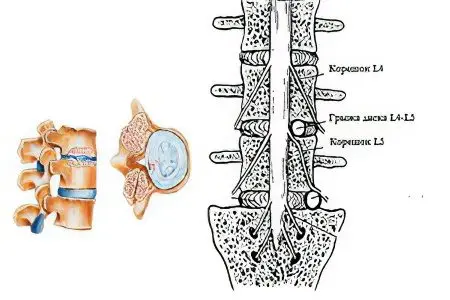
There may be several reasons leading to the formation of a dorsal hernia of the lumbar spine:
Dysplasia of the lumbosacral spine. This condition is a congenital developmental anomaly in the structure of the lumbar spine. In this case, the structure and shape of the vertebrae changes, ligaments are broken, cartilage tissue, blood vessels and nerves are destroyed. As a result, a dorsal protrusion is formed.
Osteochondrosis of the spine, leading to the destruction of the intervertebral discs and the appearance of protrusion.
Diseases of the spinal column associated with impaired posture – kyphosis, scoliosis and lordosis.
Injuries of the lumbar spine. This also includes transferred surgical interventions, falls, sharp turns.
Infections such as bone tuberculosis.
Excessive physical activity with weight lifting. Often, dorsal hernias occur in athletes. In addition, people who experience constant vibration, such as drivers, are at risk.
Violation of metabolic processes in the body, leading to malnutrition of cartilage tissue. In addition, a failure in metabolic processes leads to an increase in body weight. Particularly dangerous in terms of the development of a dorsal hernia are fatty deposits in the abdomen. They have a significant impact on the lower zone of the spine.
Regular intake of nicotine in the body significantly increases the risk of hernia formation.
Physical inactivity. In terms of the formation of a dorsal hernia, it is a sedentary lifestyle that is dangerous. Sellers, accountants, drivers, people of those professions who are forced to spend most of their working time sitting are in the zone of increased risk.
It is impossible to exclude the fact of a hereditary predisposition to the formation of a hernia.
Age-related changes that cause natural wear of discs.
Eating disorders that lead to inadequate intake of nutrients. In this case, all organ systems, including the spine, suffer. Since it is the lumbar region that experiences maximum stress, its vertebrae are destroyed before the rest.
Symptoms of dorsal hernia l5-s1 and l4-l5

Pain syndrome Until the hernia has reached a medium size, the pain syndrome will be mild. As it grows, there is an increase in pressure on the spinal nerves. As a result, any movement: raising the leg, changing the position of the body – all this will be accompanied by excruciating acute pain. In advanced cases, patients are not even able to cough without experiencing pain. It usually radiates to the buttocks and thighs.
Violation of sensitivity. In patients, the sensitivity of the legs and toes decreases, which is also associated with damage to the spinal nerves. There may be numbness of the coccyx, gluteal muscles. In addition, the lower limbs are more likely to swell.
spinal syndrome. This is a complex of symptoms, the appearance of which is associated with pain. Intuitively, a person tries to unload the lumbar and sacral regions, begins to stoop, lean forward. As a result, an incorrect posture is produced. In addition, the sense of balance suffers and the gait changes. Curvature of the spine leads to the development of problems in the work of internal organs.
Root Syndrome. As the muscle tissue atrophies, there is a violation of the sensitivity of the limbs, their weakness appears. The skin becomes dry, or, conversely, sweating may increase, which is associated with disruption of the sebaceous glands. As the hernia increases, the risk of paralysis of the lower body increases.
The more damaged the spinal cord, the higher the risk of developing life-threatening conditions for the patient:
Malfunctions in the reproductive system.
Violations of the functioning of the pelvic organs, which is expressed in constipation or diarrhea, urinary incontinence, etc.
Intermittent lameness.
Sciatica in the lumbar region and pelvis, with shooting pains all over the back of the lower limbs. (Read also: Causes and symptoms of sciatica)
Lasegue syndrome. The neuropathologist determines the presence of this syndrome. In a patient with a dorsal hernia, there is a complete or partial disappearance of physiological reflexes, in particular, knee and Achilles reflexes. But at the same time, new pathological reflexes are formed.
Complications of dorsal hernia l5-s1 and l4-l5
Sequestration of a hernia with a violation of the integrity of the disc and the exit of the nucleus pulposus into the lumen of the spinal canal. A person suffers from severe pain, which is explained by compression of the spinal nerves and spinal cord. As a result, the patient loses the ability to self-service, as he becomes unable to move.
As the hernia grows, a complete or partial paralysis of the patient may form with the assignment of a disability group.
Formation of an autoimmune inflammatory process. The reason for its manifestation is the protein content of cartilage and fibrin fibers, which trigger an autoimmune reaction.
Compression of the bundle of roots of the spinal nerves. In medicine, this complication is called a cauda equina symptom.
Violations of the act of urination and the process of defecation due to a malfunction of the pelvic organs.
Atrophy of the tissues of the lower extremities associated with loss of sensitivity.
So, a dorsal hernia, located at the level of l4-l5, can lead to paralysis of the legs and a complete loss of sensation in the feet, with all the ensuing consequences of this state.
Dorsal hernia, located at the level of l5-s1, can provoke serious disturbances in the functioning of the internal organs of the pelvis. Therefore, if the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately seek medical help.
Diagnosis of dorsal hernia l5-s1 and l4-l5
If you suspect the presence of a dorsal hernia in the lumbar region, it is necessary to conduct instrumental diagnostic methods. The most informative method in this case will be MRI. The picture will show the direction of the protrusion, its size, the degree of compression of the spinal canal.
If it is not possible to conduct an MRI, then the patient can be sent for a CT scan. However, according to its results, it will be possible to establish only the very fact of the presence of a hernial protrusion. X-ray examination in this case is not very informative, it will only allow us to conclude that there are no other sources of pain – curvature of the spine, its injuries or tumors.
Treatment of dorsal hernia l5-s1 and l4-l5
If a hernia has already formed, then you can get rid of it only through surgical intervention. However, doctors are in no hurry to send the patient to the operating table, as there are clear indications for this.
Conservative treatment of l5-s1 and l4-l5 dorsal hernia
Conservative treatment is to relieve the patient of pain and prevent the progression of the hernia:
In order to save the patient from pain, he is prescribed painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, among them: Diclofenac sodium, Ibuprofen.
To relieve muscle spasm, muscle relaxants are indicated, for example, Baclofen, Sirdalud, Mydocalm.
Non-narcotic analgesics – Ketanol, Baralgin, Ketanov.
Antidepressants and sedatives are aimed at eliminating the neurological disorders that often affect patients with spinal hernia. Among the most popular drugs are Desipramine, Doxepin, Amitriptyline.
The use of hormonal drugs helps to relieve inflammation, however, they are prescribed only in the absence of the effect of other drugs.
Vitamin therapy. It is advisable to take an increased dose of vitamin B, namely B1 and B12. It is possible not only to administer them intramuscularly, but also to take drugs orally, for example, Neuromultivit or Neurovitan.
The methods of conservative treatment also include:
Physiotherapy. You can start performing exercise therapy complexes only at the stage of remission of the disease, after you manage to get rid of the pain syndrome. The patient is recommended to perform exercises every day, without gaps. It is worth avoiding sudden movements, the load in the initial stages should be minimal.
Stretching of the spine. Modern medicine offers patients with a hernia to undergo traction using computerized devices that carry out the procedure according to the program embedded in them. The principle of this method is that the distance between the vertebrae is increased by a maximum of 2 mm. It is in this gap that a hernia that can partially retract. You can undergo the procedure only in specialized medical institutions so as not to harm your health (for more details, see the article: spinal traction: indications and contraindications).
Physiotherapy treatment. Among the most popular methods for relieving a patient of pain are drug electrophoresis (with the introduction of anesthetics, anti-inflammatory or hormonal drugs) and the use of diadynamic currents (helps relieve pain, relax and increase blood circulation).
Surgical treatment of dorsal hernia l5-s1 and l4-l5
As a rule, surgery is prescribed in no more than 20% of cases. The indication for the operation is the development of complications, the lack of effect of conservative therapy, a significant size of the hernia, severe pain. In addition, surgical intervention can be carried out with paralysis of the patient, as well as with violations of the internal organs.
Modern ways to get rid of protrusion are as follows:
Microdiscectomy, in which part of the hernia is removed and, if necessary, parts of the vertebra. The procedure is performed under a microscope. Already after 5 days, the patient can perform non-physical work, and after 3 weeks, his ability to work is fully restored.
endoscopy carried out using a special device – an endoscope. Thanks to him, the puncture on the skin that will be made to remove the hernia will not exceed 20 mm. The duration of the procedure does not exceed 45 minutes, it will require the introduction of local anesthesia. The hernia itself can be removed with a laser or cold plasma.
Laminectomy rarely used by modern surgeons. It is performed if the hernia is large. During the operation, the patient is removed part of the vertebra, as well as a fragment of the disc.
However, no matter what method of hernia removal is chosen, there is always a risk of recurrence of the disease.









