Contents
Any gardener wants to get an early harvest of vegetables. It will be possible to achieve such results only with the installation of a greenhouse. However, not every vegetable grower is able to afford high costs. It is easier to make a greenhouse by stretching a transparent film over the arcs, but such a primitive design is not able to provide garden plants with the proper microclimate. The best results were shown by high warm beds, allowing for 3 weeks to get a crop of vegetables faster.
Benefits of using technology
To figure out whether it is worth making warm beds on your site, let’s look at the advantages of this method of growing early vegetables:
- A warm bed is located above ground level. This is a big plus when growing vegetables in regions with a cold climate and frequent rainfall. Firstly, the soil inside the beds warms up faster. If frozen areas are still observed in the garden in the shade, then on a hill the fertile soil is ready to accept seedlings. Secondly, in a rainy summer, plants on an elevation of 100% will not get wet.
- When constructing warm beds, organic matter is used. From its decay, heat and nutrients for plants are released. The process lasts at least 5 years, and during this time early vegetables can be grown. In the future, the fertile soil does not lose its nutrients and is used to grow other plants, and new layers are poured inside the fence.
- Organics has a positive quality – it retains moisture well. If an ordinary earth embankment in a fence needs to be watered more often, then a warm analogue requires 1-2 waterings per week. When using drip irrigation, horticulture care is halved.
- During the decay of organic matter, a large amount of heat is released, which has a positive effect on the rapid germination of seeds. The plant that emerges from the grain immediately receives nutrients from the compost.
- The technology allows you to get ready-made compost without laying a separate pile. Organics are stacked in layers inside the fence, so warm beds are immediately ready for use in spring.
- You can arrange a warm bed in the open air or inside the greenhouse. The location does not affect the yield. Only if the bed is set up on the street, arcs are additionally installed above it and the film is stretched.
- The technology is convenient for the gardener in terms of growing vegetables. The soil covered with mulch during rain or watering is not sprayed with drops of water, contaminating the fruits. There are few weeds between cultivated plants, and they are easy to pull out of loose soil.
If you liked the arguments for the advantages of technology, then in the spring you can try to plant the first batch of plants on a warm bed with your own hands.
Proper laying of organic layers
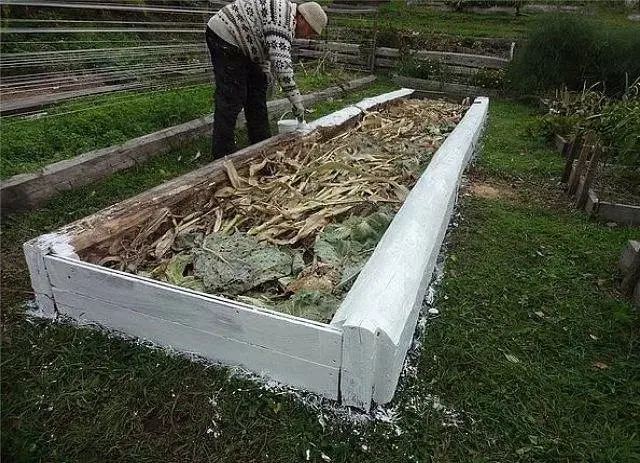
The question of how to make a warm garden bed in the spring is not entirely correct, since its contents begin to be prepared in the fall. But if you didn’t have time to fuss in time, this work can be done in the spring, only organic matter is harder to find. Depending on the depth of groundwater, the type of structure is selected. On arid lands, warm beds are immersed in the ground. They are obtained flush with the ground or slightly raised. On land with a high level of groundwater, high warm beds are made. In any case, a prerequisite for the proper manufacture of beds is its fencing. Any building material is suitable for the manufacture of boards. Most often, slate or boards are used.
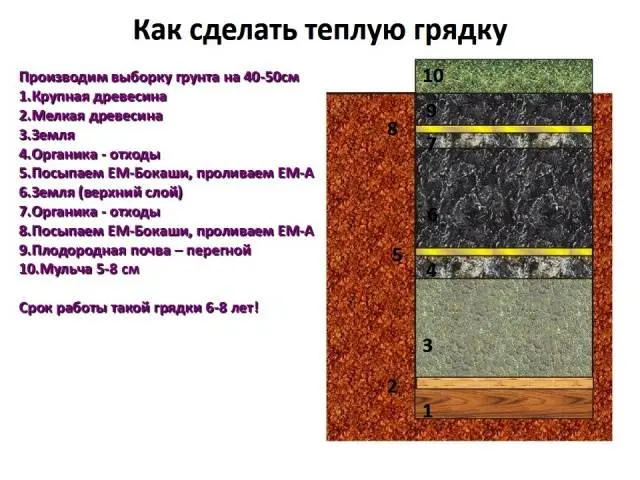
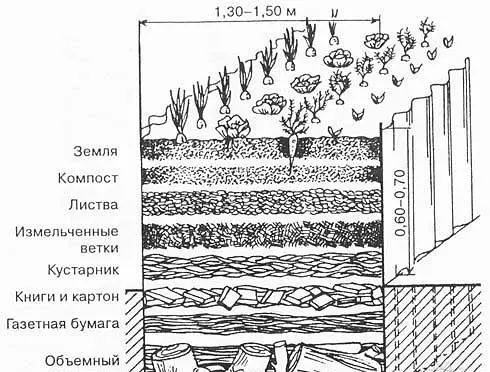
An important question remains after the construction of a warm bed with your own hands, what to put first on its bottom, as well as what is the further sequence of layers. To make good compost, there is a rule of order for laying organic matter. The photo shows the correct layer scheme, but it is quite complicated. Most often, gardeners lay the following layers:
- The bottom of the pit is covered with large organic matter, that is, thick wood. You can use uprooted stumps, branches, in general, everything wooden that is superfluous in the household. Wood is excellent at retaining moisture inside the compost heap. The larger the organics used for the bottom layer, the more years the warm bed will last.
- The second layer is laid small organic matter. For these purposes, the stems of garden plants, thin branches of shrubs, paper, leaves fallen from trees, grass, straw, etc. are suitable.
- The third layer is a stimulator of the organic decomposition process. Usually, manure or unripe compost is used for these purposes. The cut layers of turf are laid on top along with the grass, only with the roots up. The last top layer is covered with ready-made compost.
Each layer of a warm bed is moistened with water. The air between the elements of large organics and moisture will accelerate the process of decay and an increase in temperature inside the bed. Some vegetable growers, in order to accelerate the formation of compost, water a warm bed with biologically active preparations.
The video shows the filling of a warm bed:
Independent production of a warm bed

Now we will consider the step-by-step production of a warm bed with our own hands using a wooden box as an example. Wood is not the best material for boards in terms of long-term use, but it is an environmentally friendly material.
So, let’s see how the manufacturing process works correctly:
- It is important to immediately determine the size. You can take any length that the site or greenhouse allows. It is advisable to take a width of no more than 1 m, a maximum of 1,2 m. Otherwise, it will be bad to take care of crops. The depth of the pit depends on the level of groundwater and the composition of the soil. Usually they remove a layer of fertile soil 40–60 cm thick. The height of the sides is made up to a maximum of 70 cm.
- According to the size of the future warm beds, the box is knocked down from the boards. The structure is installed on the ground and markings are made for the pit along the contour from the outside of the sides on the ground.
- The box is set aside. Sod is removed from the marked area in layers along with grass. For these works you will need a sharp shovel. Pieces of turf are folded to the side. They come in handy for the top layer.
- When the hole is dug to the required depth, a downed wooden box is installed in it. Sometimes gardeners resort to tricks, additionally insulating the structure. To do this, the sides are covered with pieces of polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam, and the bottom is tightly covered with empty plastic bottles with twisted corks.

- Further, according to the arrangement of warm beds already considered, layer-by-layer laying of organic matter is performed. When all the layers are laid, the pile is poured abundantly with water, after which it is covered with PET film.
- If organic matter was planted in the spring, then after two weeks it is possible to sow grains of garden crops or plant seedlings on it. Immediately after planting, the soil is sprinkled with dark-colored mulch. In the spring, a dark surface will be better warmed up by the heat of the sun. When the summer heat sets in, a light-colored sawdust or straw mulch is used for backfilling. A light surface will reflect the scorching rays of the sun, preventing the root system of plants from overheating.
The video shows the device of a warm bed:
Now you know how to equip warm beds with your own hands in your summer cottage. This is done in the same way in spring or autumn. It’s just that autumn bookmarking is more profitable due to the large amount of fallen leaves and other organic residues.










