Contents
Intestinal diverticulosis is characterized by the presence of diverticula in it. From Latin, diverticulum is translated as “road to the side”, which characterizes this pathology in the best possible way. Intestinal diverticulosis may have no symptoms. A variety of factors lead to the development of the disease, but the main cause of the disorder is the weakness of the connective tissue. When many diverticula form in the intestine, they indicate the development of diverticulosis. Such a diagnosis is made to patients who suffer both from the pathology itself and from its complications.
Characteristics of the disease
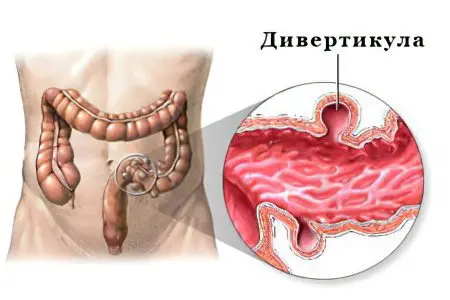
Diverticula form in the lining of the intestinal wall. Outwardly, they resemble a hernial protrusion. Most often, diverticula form in the intestines, but sometimes they can appear in the stomach and esophagus.
The disease develops due to a violation of the normal peristalsis of the intestinal wall. Often this happens due to errors in nutrition, as well as with low physical activity. Bloating and overflow of the intestines with gases leads to overstretching of its walls, since the accumulated gas bubbles contribute to an increase in pressure inside the organ. This provokes the formation of diverticula. Another reason for their occurrence is the weakness of the intestinal muscles.
There are 3 forms of diverticulosis:
Asymptomatic disease.
Diverticulosis with clinical manifestations.
Diverticulosis with complications.
Causes of diverticulosis
Causes leading to the development of diverticulosis:
Chronic constipation.
Overweight.
Flatulence and bloating.
Transferred intestinal infections.
The formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels that feed the intestines.
Leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Age over 60 years.
A burdened family history.
Violation of blood circulation in the intestines.
Chronic bowel disease.
Incorrect food.
Symptoms of intestinal diverticulosis

Often diverticulosis is not accompanied by any symptoms. A person for a long time does not even suspect that he has such a problem.
In other cases, the pathology is manifested by such signs as:
Pain in the abdomen on the left side.
Violation of the stool, alternating diarrhea and constipation.
Rumbling in the stomach.
Nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms are aggravated by inflammation of the diverticulum. At the same time, the patient’s body temperature rises, blood appears in the stool, and bloating increases. Pain during exacerbation of the pathology is concentrated in the iliac fossa on the left side. As the inflammatory response progresses, the symptoms increase, they are expressed as follows:
Alternating diarrhea and constipation.
Lack of appetite.
Vomiting and nausea.
Increased pain.
Increase in body temperature.
The appearance of mucus in the stool.
Increased heart rate.
The appearance of symptoms of peritonitis.
An increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood.
The appearance of fetid gases, bloating.
Increased urge to empty the bowels. After the act of defecation, the patient retains a feeling of incomplete emptying of the organ.
If a person is not provided with help in time, then the inflammation will increase, the intestinal wall will burst and spillage peritonitis will occur.
Why is diverticulosis dangerous?
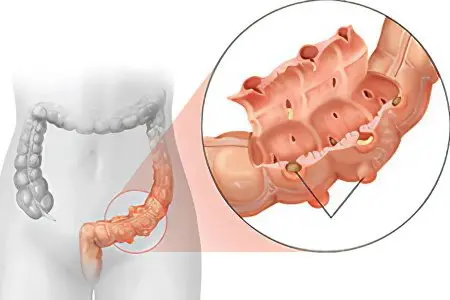
Since the intestines suffer greatly with diverticulosis, this threatens the development of such complications as:
Peritonitis.
Abscess.
Perforation of the intestinal wall.
Phlegmon of the retroperitoneal space.
Internal bleeding.
Fistula formation.
Intestinal obstruction.
Diverticulosis increases the risk of developing a malignant tumor in the intestine.
Diagnosis of diverticulosis
A patient with suspected diverticulosis is examined, his medical history is studied, and then they are given a referral to the following diagnostic procedures:
Donation of blood and urine for a general analysis.
Delivery of feces for a coprogram.
Performing a colonoscopy. The procedure is indicated for patients who are suspected not only of diverticulitis, but also of polyps, carcinomas or other neoplasms. Colonoscopy is prescribed for patients who are admitted to the hospital with rectal bleeding.
Conducting irrigoscopy. The procedure is carried out using a contrast agent. Pictures of the intestines are performed on an x-ray machine. The doctor gets the opportunity to track the movement of the contrast agent and its exit from the intestinal wall.
Ultrasound.
CT. This method is used in severe cases.
Scintigraphy. Perform a scan with technetium-labeled erythrocytes.
Treatment of intestinal diverticulosis

Treatment of diverticula in the intestine depends on the stage of development of the disease, the presence of complications and other factors.
Possible options for medical assistance:
If the diverticulum was discovered by accident, and it does not cause concern to the person, then the doctor prescribes dietary nutrition to the patient. The basis of the diet should be foods rich in fiber.
If the patient has symptoms of the disease, then in addition to the diet, he will need to take antibiotics. This will eliminate the resulting inflammation.
With the development of complications or at a high risk of their occurrence, the patient is referred for surgery.
Dietary food

The human diet should include food that is a source of soft fiber.
Basic nutritional rules to follow:
Increasing the proportion of foods that are a source of dietary fiber in the menu.
Refusal to eat foods that provoke an increase in gas formation.
The use of sour-milk drinks to prevent constipation.
Fractional food intake, refusal to overeat.
Products that should be present in the diet:
Bran bread.
Whole flour products.
Boiled porridge with vegetable oil.
Fresh and baked vegetables.
Low-fat dairy drinks.
Vegetable soups and fish broths.
Omelette for a couple of casseroles.
From the menu you need to remove products such as:
Muffins, sweets, products made from premium flour.
Pasta.
Rice and semolina.
Spicy, fatty and salty foods.
Alcoholic drinks.
Coffee, sparkling water.
It is not recommended to eat foods that are a source of coarse fiber. This applies to turnips, pineapples, radishes, persimmons. They are dangerous because they irritate the intestinal walls and can exacerbate the problem.
Medication

If the diverticula become inflamed but there are no pathological complications, the person may receive outpatient treatment.
In addition to following the diet, he will be prescribed medications such as:
Broad-spectrum antibiotics, butyric acid preparations, 5-aminosalicylic acid preparations.
Digestive enzymes (creon, festal, pancreatin, mezim and others).
Drugs that simulate the work of the digestive tract: Domperidone, Motilium, Passagex, Motilak, Metoclopramide, etc.
Antispasmodics: Drotaverin, No-shpa, Spazmol, Spazmonet.
Laxatives: Duphalac, Normaze, Portalac in syrup, Goodluck, Lactulose, Livoluk-PB.
If after 3 days from the start of therapy the patient’s well-being does not improve, then he is hospitalized. The doctor directs the patient for additional diagnostic tests. If necessary, he is operated on.
When is surgery indicated?
Indications for surgery for diverticulosis:
A history of 2 acute attacks of the disease and the absence of the effect of drug treatment. If the patient is over 40 years old, then he is sent for surgery with a single exacerbation of the pathology.
Massive intra-abdominal bleeding.
Intestinal obstruction.
The formation of phlegmon or the development of peritonitis.
Formation of an abscess, detection of fistulas.
The operation is reduced to the removal of the part of the intestine where the inflamed diverticulum is located. The course of the procedure depends on the individual characteristics of the course of the disease. In emergency cases, a stoma can be inserted into the abdominal wall.









