Contents
Potatoes are a permanent representative of the crops that gardeners add to the list of annual plantings. One of the issues that concern potato growers is the depth of planting potatoes.
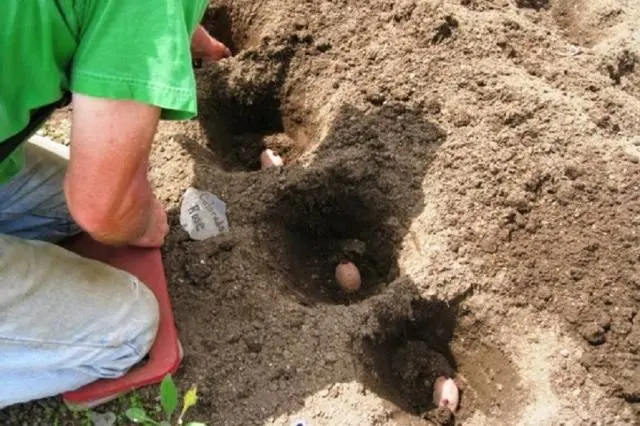

After all, this parameter is very important. Many gardeners consider it a good protection for tubers from frost. But how does depth affect the germination and yield of potatoes? Is it necessary to take into account the composition of the soil? How to plant potatoes, taking into account all the nuances? Do varietal characteristics depend on the depth of placement of tubers? All these questions are very important, especially for beginner potato growers.
In our article we will try to cover the above topics.
What is important to consider when planting potatoes

Of course, the composition of the soil and the region in which the crop is grown. Potatoes are planted from late March to May, depending on climatic conditions. The further south the area, the earlier they start landing. In the northern regions, work should begin in May.
Tuber planting depth
Potato planting depth is an important factor on which many plant growth indicators depend:
- will there be enough moisture;
- is there enough heat for development;
- whether it will be possible to provide soil aeration.
The depth of planting is determined depending on the type of soil and the size of the seed. Small tubers should not be buried deep.
Divide the deep, medium and shallow depth of planting potatoes.
- Deep. This is considered a planting in which the tubers are placed in the ground by 10 cm or more. As a result, the plants are well formed, but it will be more difficult to harvest. Therefore, it is well suited for sandy soils and dry areas. It is also used in cultivation technologies without hilling bushes.
- Average. With this type of planting, the tubers are deepened by 5-10 cm. It is good to maintain this parameter on loams and heavy soils.
- Small. Embedding parameters – from 5 to 7 cm. Recommended for clay soils and small seeds.
There is another interesting planting technology, in which the tubers are placed on top of loosened soil and covered with mulch on top. The best options are for shelter:
- rotted sawdust with sand;
- a mixture of humus and straw;
- compost;
- peat.
To improve the nutrition of potatoes, mineral components (fertilizers) are added to the mulch. This method is especially good for clay soils. To protect the tubers from greening, the mulch is added again at a plant height of about 25 cm.
When choosing the depth at which potatoes will be planted, the temperature of the heating of the earth should also be taken into account. In early spring, when it is still not warm enough, the planting is done to a depth of no more than 5-6 cm. If the planting dates are strictly observed, the tubers are buried 6-8 cm into the ground. And if you slightly shifted the deadline to a later time, then the earth is already quite warm and dry, it is well ventilated, so a depth of 10 cm will be the most suitable. On sandy soils, this figure can be safely increased to 12 cm.
Based on the foregoing, it is possible to determine the run-up in terms of the depth of planting potatoes from 5 cm to 12 cm. The main thing is not to forget to maintain the same depth of the tubers in the entire area allocated for potatoes.
The ratio of tuber size and planting depth can also be determined:
- Non-standard and small ones have a small margin of strength, therefore they are planted to a depth of at least 6 cm and not more than 12 cm. When planting potatoes in ridges, the minimum depth is 8-9 cm.
- Large potatoes are supplied with a sufficient supply of nutrients. Therefore, they develop faster and are able to easily overcome a planting depth of 10 to 12 cm. For Dutch varieties, a planting depth of 20 cm in ridges is acceptable, but local varieties are not ready for such a load.
- In the case of planting potatoes in parts, be sure to ensure that there are sprouts on each segment. This technology requires deepening only to a shallow depth in order to prevent rotting of the planting material.
How to plant seeds correctly
What does right mean? This concept includes not only the term and depth, but also the scheme for planting potatoes. There are several species that are successfully used by potato growers. At the same time, planting density is maintained depending on the composition of the soil.
- Potatoes of early varieties are planted thicker and on fertile soils. This option works well for small or chopped potatoes.
- Poorly fertilized and poor soils require a more rare planting of potatoes. This scheme is also used for large tubers.
It is very important what distance between rows will be maintained when planting potatoes.
Basic landing options
On the crest
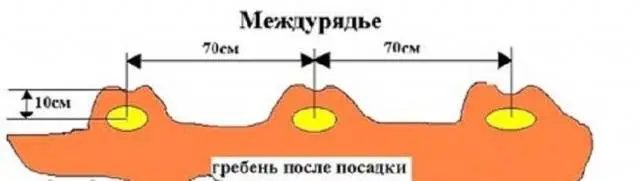
A common method since ancient times. The layout of the tubers 70×30. With this method, they dig up the selected part of the site, mark even furrows with a cord and lay them with a depth of 5-10 cm. Humus (0,5 spades) and wood ash (1 tablespoon) are introduced into the furrow. The dose is repeated every 30 cm of the furrow. Lay potatoes on top and cover with earth. It is better to do this on both sides to get a comb in the shape of the letter “M”. The height of the comb is 9-10 cm, the width is about 22 cm.
This option requires a one-time hilling of potatoes in the process of growth with simultaneous weeding. The final height of the comb is 30 cm. It protects the potatoes from drying out during the dry season and from the accumulation of moisture during the rains.

Technology advantages:
- early landing possible;
- good heating of the ridge under the sun;
- rapid pace of cultural development;
- the formation of powerful and healthy bushes;
- ease of harvesting;
- yield increase by 20%.
Under the shovel
The most common and simple method of planting potatoes.
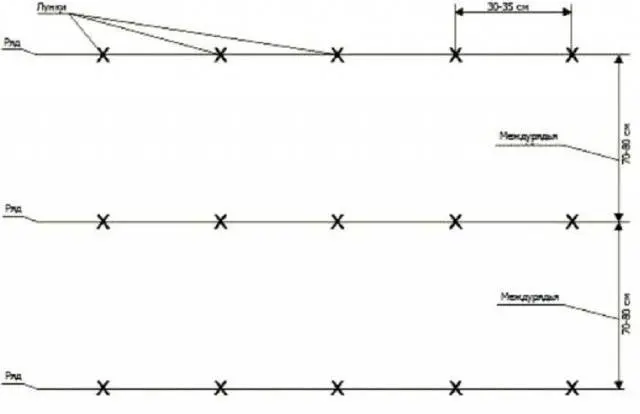
The depth of the furrows that are made on the ground is 5 cm. The arrangement of the rows is at least 70 cm apart, and the distance between the tubers is 30 cm. But look at the number of sprouts. The more of them, the longer the distance between the tubers must be maintained.
It will be optimal to plant potatoes when the temperature reaches 8 ° C on the surface of the soil, then you can be sure that at a depth of 30 cm it has already completely thawed. If you skip this period, then the moisture useful for potatoes will go away, and the yield will noticeably decrease. It should be noted the disadvantage of the method is the dependence of the state of tubers on weather conditions. Even at such a shallow depth, waterlogging of potatoes is possible. This threatens with the death of roots at the beginning of the season and a decrease in the quality of storage after harvest. And during the growth period, plants are susceptible to fusarium (with heat and humidity) and rhizoctoniosis (cool end of summer).
In the trenches
It is good to plant potatoes with this method in a dry region.
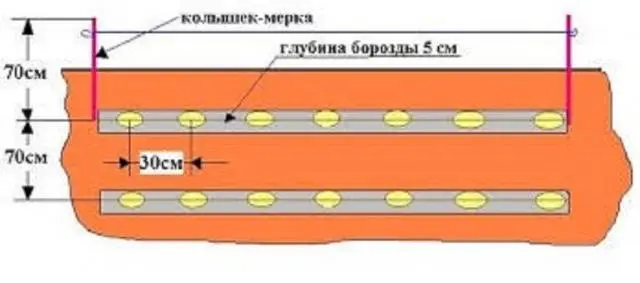
Trenches are prepared in the fall, digging them to a depth of 25-30 cm and filling them with organic matter. Mixture is used:
- manure;
- compost;
- ash;
- wet hay.
A distance of 70 cm is maintained between the trenches. In the spring, the depth of the trench will be 5 cm after the humus settles. Potato tubers are placed in a trench at a distance of 30 cm from each other, sprinkled with soil. Potatoes do not require additional nutrition when planting in trenches. It was introduced in autumn in sufficient quantities. In addition, organic matter provides heating for tubers. The trenches are lightly covered with earth and a layer of mulch is added to retain moisture. The thickness of the mulch layer is maintained no more than 6 cm. As the bushes grow, it can be sprinkled. The disadvantage of this method are:
- Waterlogging of potatoes during heavy rainfall. To avoid this, in regions with high humidity, grooves are laid along the edge of the ridges to ensure water flow. The depth of such grooves is from 10 to 15 cm.
- Labor intensity. Trenching requires significant labor and a large amount of compost and mulch.
Organic in a container
For this method, it is necessary to create stationary container beds. The height of the structure is about 30 cm, and the width is 1 meter. The location in length must be observed from north to south. The walls of the container are laid out from logs, bricks, slate, boards. Passages from 50 to 90 cm are maintained between containers, which must be mulched (sand, sawdust). Fill the container with organic matter:
- the bottom layer is plant residues;
- next – manure or compost;
- upper – soil from the passages.
The number of rows of potatoes in one container is no more than two. Tubers are planted in a checkerboard pattern with an interval of 30 cm. Advantages:
- Plants get enough light. Each row is located on the edge of the container. This leads to an increase in yield.
- Decorative landings.
- The duration of the operation of the ridges. After harvesting potatoes, the container is sown with green manure, and before winter it is filled with organic matter.
- Preservation of nutrients. They are protected by the walls of the container from being washed out.
- Ergonomics and aesthetics. Care of ridges is simple and convenient. Hilling and digging is not required. Enough loosening. The plants do not get sick and the tubers after harvesting are very clean and well stored.
- Possibility of early boarding.
Conclusion
Many gardeners choose to plant potatoes under non-woven materials, in barrels, and other extraordinary methods. In any case, you need to follow the recommended planting depth, depending on the potato variety, soil composition and climatic conditions.

The harvest will surely justify all the efforts expended.









