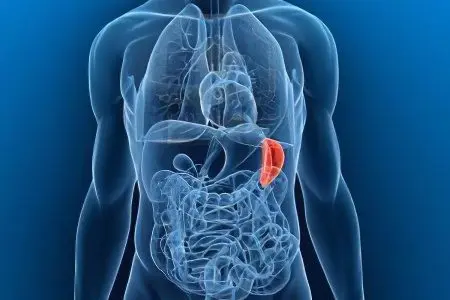
The spleen is a large lymphoid organ. It has an oval, slightly flat shape. The spleen is located in the region of the left hypochondrium, behind the stomach. It is in close proximity to the pancreas, colon, left kidney and slightly in contact with the diaphragm. The size of the spleen reaches 10-14 cm in length, 6-10 cm in width, and the thickness of the spleen is 3-4 cm.
The main part of this unique organ is represented by the so-called white and red pulp. The white pulp is lymphoid tissue, where lymphocytes originate, and the red pulp is filled mostly with erythrocytes. In addition to the important hematopoietic function for the human body, the spleen also produces antibodies, and also detects unnecessary harmful microorganisms and other foreign elements in the blood stream.
Since a certain decay of blood cells is constantly observed in the human body, the main function of the spleen is considered to be the necessary restoration of the number of cellular elements in the blood.
The spleen, as well as its adjacent organ – the pancreas, is most active in the morning from about 9 to 11 hours. If symptoms such as weakness in the legs, constant daytime sleepiness, loss of appetite are observed, but at the same time, the desire to taste sweets, memory impairment and general exhaustion of the brain, we can talk about problems associated with these organs.
Spleen diseases
As a rule, primary diseases of the spleen are quite rare, much more often it is affected secondarily, and more often than it happens with other organs. The following are the main dysfunctional conditions of the spleen that can be diagnosed as a disease.
Congenital malformations. There are cases when a person does not have a spleen from birth. There are also cases when the size of the spleen does not fit into the usual framework, its shape and structure are non-standard. Sometimes additional spleens are determined, there may even be several. If the position of the spleen is poorly fixed due to weak abdominal muscles, it can move in the abdominal cavity; this phenomenon in medicine is called “wandering spleen”, and it occurs more often in women than in men.
Spleen infarction is a phenomenon that occurs quite often, however, the area of infarction is usually very small. Leukemia and some other infections contribute to the occurrence of a heart attack.
Torsion of the spleen (or twisting of the leg) requires the mandatory intervention of a surgeon, as it leads to a serious violation of the blood circulation of this organ.
Abscesses. The causes of a spleen abscess can be different – it can be a spleen infarction or typhoid fever. As a rule, this process proceeds painlessly, which in most cases ends in self-healing.
Cysts. Different types of cysts can be observed in the spleen, however, epithelial cysts are extremely rare. But serous cysts are observed more often, but they usually occur, like ruptures, as a result of a person receiving an injury.
Various degenerative irreversible processes. In old age, atrophy of the spleen often occurs.
Tumors. A typical tumor of the spleen is lymphosarcoma. Primary malignant tumors rarely affect the spleen, and metastases to the spleen are even rarer.
Enlargement of the spleen (so-called splenomegaly). This may be due to various pathological conditions of the human body. With an increase in lymph nodes, with fever or jaundice, with an increase in the liver or severe anemia – in all these cases, splenomegaly can be detected. In the case of certain cardiovascular diseases, in infectious diseases – it can be measles, meningitis, scarlet fever, malaria, etc., in blood diseases – leukemia or hemolytic jaundice, an enlarged spleen may also occur.
Since splenomegaly is only a reaction of the body to another disease, first of all, it is necessary to establish what caused this pathological condition of the organ.
Diagnosis of diseases of the spleen
How to diagnose this or that disease of the spleen? There are several medical methods for doing this.
Survey. When compiling the necessary anamnesis, it is necessary to pay attention to all chronic infections that the patient has had, and which could lead to an increase in the spleen in size. Also, serious cardiovascular diseases, blood diseases, dangerous pathological conditions of the liver, etc. cannot be discounted. – if any have ever taken place in the patient’s medical history.
Inspection. This method is not very effective, since it allows diagnosing an enlarged spleen only in case of its significant change in size upwards. With such a pathology, the spleen emerges from under the ribs and on the left raises half of the abdominal wall so much that it can be seen by any person even with the naked eye.
Palpation. This is the main method of examination of the spleen, which must be diagnosed. Palpation is best done with the patient lying on his right side or on his back; to relax the abdominal muscles, it is better to lie with your legs tucked in. With the help of the left hand, which must be placed in the region of 7-10 left ribs, it is necessary to fix the sternum in a fixed position. The right hand should lie flat on the stomach, at a right angle to the ribs. In this case, with your fingers in a bent position, you need to slightly press on the abdominal cavity.
When the patient takes a deep breath, the spleen moves towards the palpating hand and is directly under the fingers, so you can feel the lower edge of the organ well.
As a rule, if you can feel the edge of the lymphoid organ with your fingers, you can assume that there is a pathological increase in its size. Although in practice, in some cases, in people with an excessively thin physique, especially in women, it is possible to determine the edge of a completely healthy spleen.
When carrying out the palpation method, one should focus on what are the available volumes of the spleen, its consistency, mobility, what kind of edge (serrated or even), how great is the sensitivity, etc.
X-ray examination. In the presence of a large amount of gases in the large intestine and stomach, the spleen and its edges are seen much better. For this purpose, when performing X-rays of the spleen, the stomach or large intestine is tried to be artificially inflated.
Spleen puncture. This method is used with a large increase in the body in size. Before making a puncture to the patient, he must take a deep breath and hold his breath. If this important condition is not met, the spleen is displaced to the side, and damage to the capsule can occur and heavy bleeding can begin.
Due to the similar insecurity of this diagnostic method, it is used only in cases of emergency and with extreme caution. The puncture is made with a very thin and sharp needle. As a result of the puncture, a few small drops of blood are obtained. Blood smears obtained from the spleen help determine the nature of the changes that have occurred in it.
Blood test. With a fairly large increase in the size of the spleen, it is imperative and necessary to conduct a complete blood test.
Disease Prevention
To prevent spleen disease, first of all, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, not to start infectious diseases, to take the necessary measures to strengthen immunity – in general, to monitor the general condition of your body. Particular attention should be paid to protecting the abdomen and chest from various injuries and injuries. The most serious damage is caused to the spleen in the event of a severe bruise, a blow received in a fight or as a result of a serious traffic accident.
It is also necessary to periodically take blood tests and check the status of its indicators, it is also advisable not to forget about the correctness of your diet. Do not exhaust yourself with diets that lead to anemia and general depletion of the body. You should limit yourself to drinking alcohol, especially not of very high quality.
If problems with the spleen have already arisen, you should increase the volume of the following foods in your diet: walnuts, beef liver, sea and river fish, beets and carrots, lingonberries, decoction of rowan berries.









