Contents
Food begins to break down in the mouth. If a person develops a disease of the oral mucosa (OMD), then the enzymes contained in saliva will not work at full strength. This can provoke disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the digestive system, cause bad breath. Even brushing your teeth does not allow you to freshen your breath for a long time, as purulent defects form in the oral cavity. They give a person pain, itching and burning. Therefore, soft tissue inflammation should be treated as soon as possible.
Causes
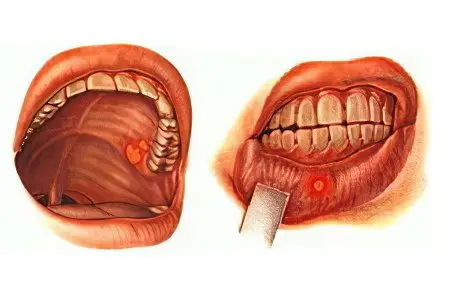
There are the following reasons leading to the development of diseases of the oral cavity:
Poor hygiene. Sometimes a person simply rarely brushes his teeth, sometimes he does it wrong, and sometimes he even uses poor-quality products to treat the oral cavity.
Smoking.
Alcohol abuse. Alcoholism leads to failures in metabolic processes in the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Eating too hot foods and drinks. Microburns violate the integrity of the mucous membrane and reduce its protective functions.
Alternating hot and cold foods or drinks. This contributes to the destruction of tooth enamel.
Excessive consumption of sugary foods. Violation of the acid-base balance in the oral cavity leads to the reproduction of harmful flora and irritation of the mucous membranes.
Diseases that increase the likelihood of damage to the oral mucosa:
Diabetes. If the level of glucose in the blood is elevated, then this can cause suppuration of the soft tissues. When its values are low, it is manifested by bleeding gums.
Deficiency of fluorine, calcium and phosphorus. This leads to fragility of capillaries and thinning of tooth enamel.
Frequent colds.
bacterial infections.
Dysbacteriosis.
Viral diseases.
Fungal infection of the oral cavity. Low hemoglobin level.
Diseases of an autoimmune nature.
tissue hypoxia.
Avitaminosis.
Chronic and acute inflammatory processes.
Violations in the functioning of the immune system, which may be due to HIV, rheumatoid diseases, STDs, etc.
Allergy.
Symptoms to watch out for!
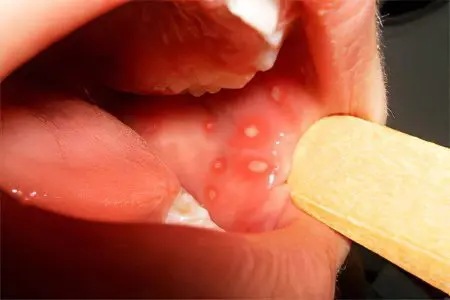
Discomfort in the oral cavity is a reason to visit the dentist’s office. The doctor will diagnose and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Symptoms that require medical advice:
Bad breath.
Swelling of the gums, their bleeding.
The appearance of rashes, ulcers and other defects in the mouth.
Pain and burning of the mucous membranes, which are aggravated by eating.
Increased salivation or dry mouth.
Classification of ORM diseases
SOPR classification:
Depending on the form of the course of the pathological process, acute and chronic diseases are distinguished. In turn, chronic disorders can worsen and enter a phase of remission.
Depending on the stage of development of the disease, there are: initial, acute and neglected form.
Depending on the causative agent of the disease, viral, bacterial and fungal infections are isolated. Also, diseases of the oral mucosa can be autoimmune and traumatic in nature.
Depending on the method of transmission of the disease, infections are distinguished, sexually transmitted, domestic, airborne. Also, the pathology may be of an allergic nature or occur due to hypothermia of the body. Inflammation, accompanied by suppuration, is often the result of dirt getting into microscopic wounds on the oral mucosa.
Depending on the place where the inflammation is concentrated, diseases of the lips, gums, tongue, and palate are distinguished.
Depending on the type of affected tissues, infections are distinguished that are concentrated on the mucous membranes, on soft tissues, and on the bone structures of the oral cavity.
Traumatic lesions

The oral cavity suffers all the time due to exposure to various irritants. They can be mechanical, physical or chemical. If such factors are not too intense, then the mucous membranes cope with them on their own. When local immunity is not enough, irritation and inflammation appear in the mouth.
Mechanical damage to the oral cavity. Injury can be obtained due to a blow, when biting soft tissues with teeth, or when injured with sharp objects. A bruise, abrasion, erosion, or other deep defect occurs at the site of injury. If bacteria enter the wound, it will transform into an ulcer and take a very long time to heal.
Chronic injury. These are the most common lesions of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. Sharp edges of teeth, chipped fillings, broken crowns, dentures and other orthodontic structures can lead to their occurrence. Swelling and redness occur at the site of injury. Then this area is transformed into erosion, and then into a decubital ulcer. The ulcer hurts a lot, has an even base, it is covered with a fibrinous coating on top. Along the edges of the ulcer is uneven, if it is present in the oral cavity for a long time, then its edges become dense. Chronic or acute inflammation leads to an increase in regional lymph nodes in size. When they are probed, a person experiences pain. If left untreated, such an ulcer can develop into a malignant tumor.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases
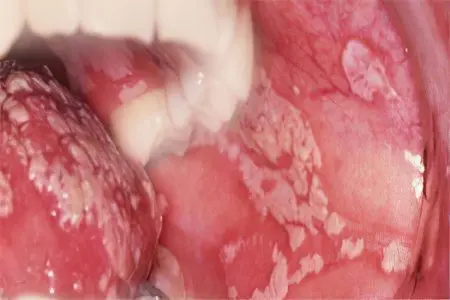
Infectious and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity develop due to the multiplication of viruses or bacteria. Most often, people are diagnosed with gingivitis, glossitis, pharyngitis, stomatitis. Errors in oral hygiene, poor-quality care for the gums, tongue or teeth lead to inflammation. Other risk factors include diseases of the digestive system, namely: gastritis, enterocolitis, stomach ulcers and duodenal ulcers.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis can be diagnosed at any age.
Doctors distinguish several varieties of stomatitis, including:
Aphthous stomatitis. The patient swells and reddens the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, then ulcers form on it, which will be covered with a white coating. These defects hurt a lot.
Ulcerative stomatitis. This disease is accompanied by the formation of erosions in the oral cavity. The patient’s body temperature may rise, the lymph nodes become painful. General health is deteriorating. To find out the cause of inflammation, you need to check the condition of the organs of the digestive system. Often these patients are diagnosed with enteritis or stomach ulcers.
Catarrhal stomatitis. The main symptom of the disease is swelling and redness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. A white patch appears at the site of infection. It is difficult for the patient to talk and eat. From the mouth of a person, an unpleasant odor begins to emanate, salivation intensifies.
It will not be possible to independently diagnose the type of stomatitis, in order to understand what kind of disease a person develops, you need to visit the dentist’s office.
Glossitis
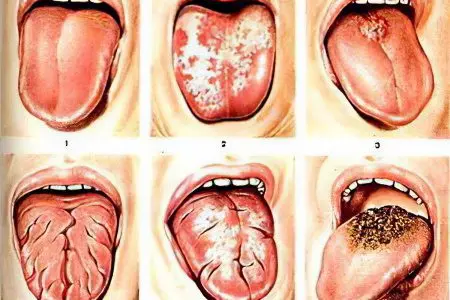
Glossitis is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the tongue, which can be caused by viruses or bacteria. At risk are people who neglect oral hygiene.
Often inflammation is caused by streptococci. However, these are not the only microorganisms that can provoke the disease. Increases the likelihood of penetration of pathogenic flora into the thickness of the tongue resulting in burns and injuries. Glossitis often develops in people who use sprays to freshen their breath, as well as in people who abuse alcohol.
Symptoms of glossitis:
Burning tongue, the appearance of a sensation of a foreign body in the thickness of the organ.
Redness of the mucous membranes of the tongue, increased salivation.
Distortion of taste.
Glossitis can occur in such forms as:
Superficial glossitis. Symptoms of the disease resemble stomatitis. Only the mucous membrane of the oral cavity suffers. Inflammation has an uncomplicated course and responds well to correction.
Deep glossitis. The entire surface of the tongue suffers, along its entire thickness. Often, abscesses and areas of abscess appear on the organ. Treatment must be started immediately, otherwise the infection may spread to the neck. This is a direct threat to human life. Deep glossitis requires surgical intervention.
Separately, non-inflammatory forms of glossitis are distinguished:
Desquamative glossitis. Often it develops in women who are carrying a child, in people with diseases of the digestive system, with blood pathologies. Also, risk factors leading to its occurrence are: metabolic disorders, rheumatism, helminthic invasions. The patient on the back of the tongue and on its sides begins to collapse the epithelium. This leads to the formation of foci of bright red color. They alternate with the unchanged mucosa of the organ, so when examining it, it seems that the tongue resembles a geographical map. Therefore, this type of gloss is called “geographical language”.
Rhomboid glossitis. This disease refers to congenital pathologies, it occurs due to anomalies in the development of the fetus. It is also called median glossitis.
Villous glossitis. In patients with this form of the disease, papillae grow on the tongue, which cover its entire surface.
Folded glossitis. This developmental anomaly is characterized by the appearance of folds on the back of the tongue. The deepest groove runs along the central part of the organ. The disorder is diagnosed in children immediately after birth. As a rule, it does not cause any discomfort to a person, so treatment is not carried out.
Gunther’s glossit. A person’s tongue acquires an unnatural smoothness, papillae disappear on it, so it looks polished. Gunter’s glossitis is a symptom of a deficiency in the body of vitamin B12 and folic acid, that is, it is a sign of anemia.
Interstitial glossitis. This disease develops against the background of progressive syphilis. The tongue becomes dense, the patient cannot move it normally.
Gingivitis
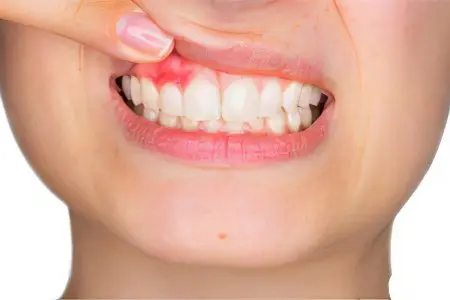
Gingivitis is characterized by inflammation of the gums. In this case, only their surface layer suffers. They talk about gingivostomatitis when ulcers form not only on the gums, but also on the surface of the cheeks. Most often, this form of the disease is diagnosed in children.
The main cause of gingivitis is called poor oral hygiene. Often, men who lead an unhealthy lifestyle suffer from gum disease. If there is no treatment, then gingivitis will progress and turn into periodontitis, which is associated with the risk of tooth loss.
You need to take good care of your teeth. If you do not clean out the remnants of food, then bacteria begin to multiply in them. The more of them, the higher the likelihood of inflammation of the gums. Gingivitis can be acute or chronic. In some people, the inflammation is recurrent.
Dentists distinguish several types of gingivitis:
Ulcerative gingivitis. The disease develops acutely, the gums swell, become bright red. An unpleasant odor comes from the patient’s mouth.
Catarrhal gingivitis. This inflammation is manifested by swelling, pain and bleeding of the gums. However, the lesion is superficial, gum pockets do not suffer.
Hypertrophic gingivitis. The disease is accompanied by swelling and compaction of the gingival papillae, the gum pocket hurts, becomes red. Hypertrophic gingivitis can be edematous and fibrous. The edematous form of inflammation leads to severe bleeding of the gums, they fill up and increase in size. With fibrous gingivitis, the gum tissue thickens, but the person does not complain of pain, there is no bleeding. It will not be possible to cope with hypertrophic gingivitis with drugs, the patient will need the help of a surgeon.
Pharyngitis
With pharyngitis, the mucous membrane of the throat becomes inflamed. A person experiences perspiration and pain in the throat, eating and drinking is accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
Viral diseases
Viral diseases of the oral mucosa imply infections of a bacterial and fungal nature. This also includes ulcerative necrotic stomatitis and sexually transmitted infections, which are manifested by various symptoms.
Most often, the oral cavity suffers from the herpes virus. It quickly spreads through the tissues, so it will be difficult to cope with the disease on your own. The help of a doctor is required.
Herpetic infection is manifested by ulcers localized in the sky, on the cheeks, on the inner surface of the lips. The disease can have an acute and chronic course. Suffer, including the gums. Symptoms of infection proceed according to the type of acute catarrhal gingivitis.
Fungal pathologies
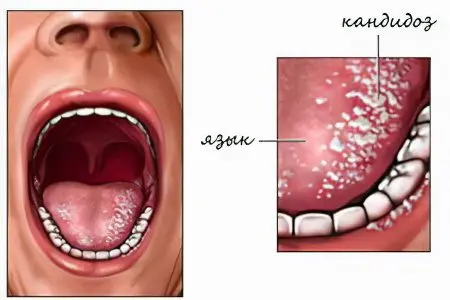
When a fungus of the genus Candida is activated in the mouth, a person develops signs of inflammation. These yeast-like organisms are normally always present in the oral mucosa. However, their growth is constrained by beneficial microflora.
Fungi are activated for the following reasons:
Decreased immunity.
Past illnesses.
Subcooling the body.
Inflammation in the mouth.
Active reproduction of fungi leads to damage to the mucous membranes, that is, a person develops candidomycosis.
Yeast-like fungi can cause pathologies such as:
atrophic candidiasis. The disease is acute, the mucous membranes in the mouth are dry and red. The affected areas are covered with a white coating, the skin peels off in the corners of the lips.
Atrophic chronic candidiasis. Most often, this form of the disease manifests itself in people using removable dentures-plates. The person experiences dry mouth, the mucous membranes are highly inflamed.
Pseudomembranous candidiasis. The disease is diagnosed quite often. It has an acute course. The mucous membranes of the oral cavity are covered with a coating that resembles cottage cheese. While eating, a person experiences pain and itching. If the food is spicy, then a burning sensation may join.
Hyperplastic candidiasis. The acute stage of the disease quickly transforms into a chronic form. The oral cavity is inflamed, plaques and nodules spread through it, which will be covered with a dense coating. When you try to remove it, the inflammatory reaction only intensifies. Under the plaque, a bleeding wound is formed.
Other pathologies
In dental practice, one has to deal not only with common, but also with rare diseases.
Dysbacteriosis
Oral dysbacteriosis often develops due to uncontrolled intake of antibacterial drugs or local antiseptics. They are often used to treat colds.
The first signs of dysbacteriosis may go unnoticed. A person has bad breath, cracks can form in the corners of the lips. As the pathology progresses, periodontal disease develops, the teeth become shaky. A plaque forms on them, which destroys the enamel. If there is no treatment, then the receptors of the tongue, vocal cords, tonsils will suffer.
Leukoplakia
With leukoplakia, keratinization of a certain area of the oral mucosa occurs.
Contribute to the development of leukoplakia factors such as:
Smoking.
Damage to a section of the mucous membrane with something sharp, such as a chipped tooth or prosthesis.
Reception of hot and cold dishes.
Alcohol abuse.
Therapy with certain drugs.
To cope with the disease, you need to eliminate the cause that provoked damage to the mucous membrane. The oral cavity is sanitized, applications are applied to the affected areas.
Sialoadenitis
This disease is infectious. The salivary glands are affected. Infection can be brought into them during surgery, or with an injury to the glands.
The main symptom of the disease is swelling in a characteristic place, suppuration of the gland and necrosis. A person’s body temperature rises, there are pains in the mouth.
Antibiotics are required to treat sialadenitis. The oral cavity is treated with antiseptic compounds. Vitamins are prescribed to increase immunity.
Xerostomia
Xerostomia is characterized by dry mouth. This disorder can develop against the background of diabetes mellitus or due to a malfunction of the salivary glands. Other causes of xerostomia include allergic reactions of the body, endocrine pathologies.
The disorder is manifested by dry mouth, inflammation, itching and burning. The oral cavity as a whole suffers. Sometimes the patient’s salivary glands and lymph nodes located under the jaw become inflamed.
red lichen
This disease is characterized by the appearance of blisters, ulcers and plaques in the mouth. The areas of inflammation differ from the rest of the mucosa in a bright red color. Sometimes characteristic rashes appear not only in the mouth, but also on the skin. Often red lichen is combined with pathologies of the liver or stomach, with diabetes.
Immunity disorders become the basis for the development of pathology. Also, doctors are of the opinion that the tendency to red lichen can be inherited.
The acute stage of the disease is said in the case when the lichen appeared less than a month ago. Subacute illness lasts no more than six months. The chronic form of lichen lasts more than 6 months.
Cancer of the oral mucosa
The oral cavity, like other parts of the body, is prone to cancerous tumors. The disease can affect the cheeks, tongue, palate, alveolar process and other areas.
There are three forms of oral cancer:
Knotty cancer. A seal appears on the tissues, which has clear boundaries. The color of the node may not differ from the surrounding mucosa, and may be white. Tumor growth is quite intense.
Ulcerative form. One or more ulcers form in the oral cavity, which cause pain to a person. They ooze blood. Defects exist for a long time and do not go away.
papillary form. The tumor will be dense, hanging down. Its color does not differ from the color of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
At risk for developing cancer are people with low immunity, as well as smokers. The neoplasm of the oral cavity is dangerous with early metastasis. First of all, the daughter cells of the tumor penetrate into the submandibular lymph nodes. In addition, metastases can be found in the liver, brain, and lungs.
Occupational pathologies
Occupational diseases of the oral cavity develop due to the fact that certain pathological factors influence the body. Moreover, they will be associated with the conditions of human labor activity.
Various harmful substances, for example, salts of heavy metals, can negatively affect the oral cavity. Under their influence, a person develops stomatitis, which will have a certain set of symptoms. Doctors distinguish stomatitis mercury, bismuth, lead, etc.
To cope with occupational diseases is most often possible only after a change of workplace. When the negative factor ceases to influence the body, the disease recedes. Sometimes a person needs an antidote.
The general principles of treatment are: sanitation of the oral cavity, relief of inflammation, elimination of pain. Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat it later. Therefore, you need to remember about preventive measures.
Prevention

The main preventive measure is regular visits to the dentist. An examination by a doctor should be done at least 2 times a year.
In addition, the following guidelines must be followed:
You need to brush your teeth every morning and evening. The procedure should last at least 3 minutes.
After eating, the mouth should be rinsed. The rinse aid should not be too cold or too hot.
You should not eat a lot of sweets. After using them, rinse your mouth with water.
Do not drink hot drinks and sweet foods at the same time.
The diet should contain foods that contain a sufficient amount of vitamins.
Diseases of the oral mucosa can be both mild and quite serious. The sooner a disease is detected, the sooner it can be dealt with. Alternative methods of treatment help to get rid of only the symptoms of the disorder. They can also be used prophylactically. However, professional medical assistance is required to eliminate the disease.









