Contents
All pathologies of the cardiovascular system should be treated after a thorough diagnosis under the guidance of a physician, using both therapeutic and surgical methods. In order to navigate the variety of diseases of the heart and blood vessels, as well as to understand when an immediate call to the ambulance team is required, and when you can get by with a visit to the local therapist, you should know the main symptoms of these diseases.
List of heart diseases and their symptoms
Cardiovascular diseases are classified into the following categories:
Arrhythmia – changes in the rhythmic and sequential contraction of the atria and ventricles;
Ischemic heart disease – circulatory disorders and the formation of scar tissue;
Myocarditis, pericarditis, endocarditis – inflammatory diseases of the heart muscle;
Heart disease – congenital and acquired dysfunctions of the valve apparatus of the ventricles;
Cardiovascular insufficiency is a group of diseases, which are based on the failure of cardiac activity in terms of ensuring normal blood circulation;
Vegetovascular dystonia – violation of vascular tone;
Hypertension is a systematic increase in blood pressure.
All these diseases of the heart and blood vessels have different causes of their development, symptoms, methods of treatment and prognosis of recovery.
Arrhythmia
Normally, the heart rhythmically and consistently contracts its atria and ventricles. This activity is closely related to the functioning of the conduction system, which directs impulses to the heart muscle.
Causes of arrhythmia:
Structural changes in the conducting system;
electrolyte imbalance;
Vegetative changes in the central nervous system;
endocrine diseases;
Side effects of drugs;
Complications caused by ischemic disease.
Diagnosis of arrhythmia is carried out using a cardiogram, the treatment of this pathology is quite complicated and is carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of the organism.
Types of arrhythmias:
Ventricular asystole – manifested by flickering and trembling of the ventricles, occurs as a complication of heart disease, due to electric shock, an overdose of glycosides, adrenaline, quinine (in the treatment of malaria). Prognosis – sudden clinical death is possible due to a cessation or a sharp drop in cardiac output. To stop an attack of ventricular asystole, resuscitation should be started immediately with the help of external heart massage and artificial respiration. It is necessary to call the cardiological ambulance team;
Atrial fibrillation – manifested by atrial fibrillation and flutter (250-300 times per minute), chaotic and non-rhythmic contraction of the ventricles. Occurs as a symptom of mitral valve disease, thyrotoxicosis, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, due to an overdose of glycosides, alcohol poisoning. The patient may not feel arrhythmia, mistaking it for a rapid heartbeat. The prognosis is the occurrence of thromboembolism;
Paroxysmal tachycardia – manifests itself as a sudden onset and sudden ending attack of rapid heartbeat, heart rate – 160-220 beats per minute. Additionally, there is profuse sweating, increased intestinal motility, slight hyperthermia. If the attack lasts for several days, these symptoms are joined by angina pectoris, weakness, fainting, and an increase in heart failure. Help with paroxysmal tachycardia – massage of the carotid artery area, activation of the vagus nerve by pressing on the eyes and the solar plexus area, as well as holding the breath, a strong turn of the head. If these techniques are ineffective, then there is a ventricular tachycardia or myocardial infarction – immediate medical attention is required;
Sinus tachycardia – manifested by a sinus rhythm frequency of more than 90 beats per minute, occurs with a sharp decrease in blood pressure, a significant increase in temperature, anemia, myocarditis. The patient experiences increased heart rate. Help – holding the breath, massage the solar plexus and the area of the carotid arteries, pressure on the eyeballs;
Sinus bradycardia – is manifested by a decrease in heart rate with a rhythmic sinus rhythm of less than 60 beats per minute. Occurs with myocardial infarction, as a consequence of certain infectious diseases and side effects of drugs. The patient feels a slowing of the heartbeat, his limbs become cold, fainting may occur or an attack of angina pectoris may occur;
Extrasystole – manifested by premature contractions of the ventricles, which the patient feels like a sinking heart or its increased beat. After that, reflexively there is a desire to take a deep breath. Frequent systoles require treatment, as they lead to atrial and ventricular fibrillation;
Heart blocks – are manifested by a slowdown or complete cessation of the transmission of an electrical impulse through the conduction system of the heart. The patient’s heart rate slows down, he faints due to the fact that the brain is not sufficiently supplied with blood, convulsions occur, and heart failure is diagnosed. Prognosis – with intraventricular (complete transverse) blockade, sudden death is possible.
Coronary heart disease
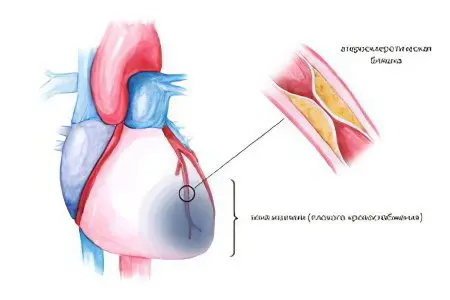
With this severe heart disease, which is based on a violation of the blood supply to the heart muscle, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris and cardiosclerosis occur.
Myocardial infarction is an acute violation of the blood supply to the heart muscle, resulting in focal necrosis of its sections. Due to the necrosis of part of the myocardium, the contractility of the heart is impaired. A heart attack occurs due to thrombosis of the arteries that supply the heart with blood, blockage of blood vessels by atherosclerotic plaques. The acute period of a heart attack is characterized by very severe retrosternal pain, the intensity of which is not stopped by Nitroglycerin. Additionally, there is pain in the pit of the stomach, an asthma attack, hyperthermia, increased blood pressure, frequent pulse. Prognosis – the patient may die from cardiogenic shock or heart failure. Emergency care before the ambulance arrives – taking painkillers, Aspirin and large doses of Nitroglycerin.
Angina (“angina pectoris”) – manifests itself as a sudden pain behind the sternum due to insufficient blood supply to the myocardium. The main cause of angina is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. Pain in angina pectoris is paroxysmal, has clear boundaries of appearance and subsidence, is almost immediately stopped by Nitroglycerin. The factor provoking an attack is stress or physical overstrain. Compressive and pressing pain occurs behind the sternum, radiates to the neck, lower jaw, left arm or shoulder blade, may be similar to heartburn. Additionally, there is an increase in blood pressure, perspiration appears, the skin becomes pale. If rest angina pectoris is diagnosed, these symptoms are accompanied by suffocation, a feeling of acute lack of air. An attack of angina pectoris lasting longer than 30 minutes is a suspicion of myocardial infarction. First aid – Nitroglycerin under the tongue twice with a break of 2-3 minutes, accompanied by taking Corvalol or Validol to suppress headaches, then you should call a cardiological ambulance.
Cardiosclerosis – damage to the myocardium and heart valves by scar tissue resulting from atherosclerosis, past rheumatism, myocarditis. Symptoms are arrhythmias and conduction disturbances. The prognosis is the formation of an aneurysm, the formation of chronic heart failure and heart defects.
Myocarditis, pericarditis, endocarditis
This group of diseases is characterized by inflammatory processes in myocardial tissues caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Their negative impact is complemented by allergic reactions and autoimmune processes of the formation of antibodies to the tissues of one’s own body.
Types of inflammatory heart disease:
Infectious-allergic form of myocarditis – occurs after an infectious disease or during it. Symptoms: general malaise, heart rhythm disturbances, pain in the heart area, shortness of breath, joint pain, slight fever. After a few days, the phenomena of myocarditis increase and increase. Heart failure is formed: cyanosis of the skin, swelling of the legs and abdomen, severe shortness of breath, liver enlargement;
Rheumatic, autoimmune, radiation myocarditis – distinguish between acute and chronic forms, manifested by the following symptoms of intoxication: fatigue, hyperthermia, skin rash, nausea and vomiting. If you do not see a doctor in time, there is a deformation of the fingers in the form of drumsticks, as well as a deformation of the nails in the form of convex watch glasses.
Endocarditis – inflammation of the endocardium, that is, the inner lining of the heart that covers the valvular apparatus.
Pericarditis – inflammation of the membrane that covers the outside of the heart (pericardial sac).
Such manifestations require immediate medical attention, bed rest. The cardiologist will prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Indomethacin), glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone), diuretics and antiarrhythmic drugs. The prognosis for the development of carditis is a complete cure with timely therapy.
Heart disease
These diseases include dysfunctions and abnormalities in the structure of the valvular apparatus: stenosis (inability to fully open the valves), insufficiency (inability to fully close the valves), a combination of stenosis and insufficiency (combined heart disease). If the defect is not congenital, it occurs due to rheumatism, atherosclerosis, syphilis, septic endocarditis, and organ injury.
Types of heart defects:
Mitral valve defect (stenosis and insufficiency) – determined by listening to the heart by a cardiologist, characterized by the appearance in patients of a bright blush and a scarlet hue of the lips. Additionally, shortness of breath, palpitations, swelling of the extremities, enlargement of the liver are diagnosed;
Aortic valve disease (stenosis and insufficiency) – at the 1st and 2nd stages of the disease, there are no complaints, at the 3rd stage angina pectoris, dizziness and decreased visual clarity are diagnosed. At the 4th stage, even the most insignificant load leads to disorders of cerebral and cardiac circulation: arrhythmia, shortness of breath, cardiac asthma;
Aortic valve insufficiency – at the 1st and 2nd stages there are no complaints, at the 3rd stage of the defect angina pectoris, pulsation of the arteries of the head, carotid artery, abdominal aorta, which is visible to the naked eye, are diagnosed. At the 4th stage, pronounced heart failure and arrhythmia appear. At the 5th stage, the symptoms of the disease are even more intensified;
Tricuspid valve defect – can be diagnosed by pulsation of the cervical veins, enlarged liver, swelling of the arms and legs. There is a direct relationship – the stronger the pulsation of the veins, the more pronounced valvular insufficiency. Valve stenosis does not give a pronounced pulsation.
Cardiovascular insufficiency
This general term refers to diseases that lead to the fact that the heart is not able to pump blood normally. Cardiovascular insufficiency is acute and chronic.
Types of acute heart failure:
Cardiac asthma – a consequence of cardiosclerosis, hypertension, myocardial infarction, aortic heart disease. The basis of the pathology is stagnation of blood in the lungs, since the left ventricle cannot provide normal blood flow in the pulmonary circulation. In the vessels of the lungs, blood accumulates, stagnates, its liquid fraction sweats into the lung tissues. As a result, the walls of the bronchioles thicken, their vessels narrow, and the air penetrates worse and worse. Vivid symptoms of cardiac asthma: cough, called “cordial”, wheezing, shortness of breath, fear of death, blue lips and skin. Heart palpitations and high blood pressure complete the overall picture. First aid – give the patient a semi-sitting position, put Nitroglycerin under the tongue, give Corvalol, provide hot foot baths. Before the ambulance arrives, to facilitate the work of the heart, you can put rubber bands on the thighs for 15-20 minutes, trying to press them not on the arteries, but on the veins. Prognosis – in the absence of the effect of resuscitation procedures, pulmonary edema occurs;
Pulmonary edema – failure to provide timely necessary assistance for cardiac asthma leads to the fact that the liquid fraction of blood sweats not only into the bronchi, but also into the alveoli and accumulates in them. The air, which nevertheless penetrates in a small amount into the lungs overflowing with liquid, beats this liquid in the pulmonary vesicles into foam. Symptoms of pulmonary edema: painful suffocation, pink foam protruding from the mouth and nose, gurgling breathing, rapid heartbeat. An excited patient has a fear of death, he is covered with a cold, sticky sweat. Elevated blood pressure drops sharply as the situation progresses. First aid should be provided quickly – the patient is placed reclining, a hot foot bath is made for him, tourniquets are applied to his legs, 1-2 tablets of Nitroglycerin are placed under the tongue. Intravenously or orally, 2-4 ml of Lasix or Furosemide are administered. The patient needs fresh air, they lighten tight clothes to the maximum, open the windows. Before stopping an attack of pulmonary edema, transportation to a hospital of such a patient is impossible;
Right ventricular failure – develops as a result of incorrect transfusion of blood and its substitutes, lung diseases (asthma, pneumonia, pneumothorax), as well as against the background of pulmonary embolism. There is an overload of the right parts of the heart, there is a spasm of the pulmonary circulation. The resulting stagnation of blood weakens the functioning of the right ventricle. Symptoms: shortness of breath, drop in blood pressure, cyanosis of the lips and skin of the face, severe swelling of the veins in the neck;
Thromboembolism – the above symptoms are accompanied by severe pain behind the sternum, expectoration of blood during coughing. Pathology occurs due to the ingress of a blood clot into the vessels of the pulmonary artery. Prognosis – blockage leads to death. In this condition, urgent thrombolytic therapy is needed, the introduction of thrombolytics (Eufillin, Lasix, Strophanthin) before the arrival of the ambulance. The patient at this time should be in a semi-lying position;
Collapse – the condition occurs with a sharp expansion of blood vessels and a decrease in the volume of circulating blood. Causes of collapse: an overdose of Nitroglycerin or drugs that lower blood pressure, poisoning, the effects of certain infections, vegetative dystonia. Symptoms – sudden weakness and dizziness, shortness of breath, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, emptying of the veins, thirst and chills. The patient’s skin becomes pale and cold to the touch, loss of consciousness may occur. Help before the arrival of “emergency help” – raise the legs above the head to provide the brain with blood, cover the body, give hot strong coffee to drink for the speedy rise in blood pressure.
Hypertension

The true cause of the development of hypertension is not fully understood. Its appearance is provoked by mental trauma, obesity, a tendency to salty foods, a hereditary predisposition.
Stages of hypertension:
At the first stage pressure rises to values of 160-180 mm Hg. Art. at 95-105 mm Hg. Art. An increase in pressure is characteristic of climate change, physical or emotional stress, weather changes, and the inclusion of spicy dishes in the diet. Additional symptoms: headaches, tinnitus, insomnia, dizziness. At this stage, there are no changes in the work of the heart and impaired renal function;
At the second stage pressure indicators increase to 200 at 115 mm Hg. Art. During rest, it does not fall to the norm, remaining somewhat elevated. There are changes in the left ventricle (hypertrophy), a decrease in renal blood flow, spasms of cerebral vessels;
At the third stage pressure rises to values of 280-300 mm Hg. Art. at 120-130 mm Hg. Art. During this period, strokes, angina attacks, hypertensive crisis, myocardial infarction, pulmonary edema, and retinal lesions are not excluded.
If at the first stage of hypertension it is enough to revise the lifestyle and diet so that the blood pressure indicators return to normal, then the second and third stages should be treated with pharmaceuticals as prescribed by a doctor.
Diagnosis of heart disease
According to medical statistics, about 60% of premature deaths are due to cardiovascular diseases. Diagnostic examination of the state of the heart muscle and its functioning will help to make the correct diagnosis in time and start treatment.
Common diagnostic methods:
Electrocardiogram (ECG) – fixation of electrical impulses emanating from the body of the subject. It is carried out using an electrocardiograph. Only a specialist can evaluate the results of an ECG. He will be able to detect arrhythmia, absence or decrease in conduction, coronary disease, myocardial infarction;
Ultrasound of the heart or echocardiography is a highly informative study that allows you to evaluate the cardiovascular system in a complex, identify signs of atherosclerosis, see blood clots, and monitor blood flow. Patients who have had a heart attack, echocardiography is performed regularly. The procedure helps to detect heart defects, aortic and ventricular aneurysms, and oncological processes in time. With the help of ultrasound of the heart, it is possible to measure the thickness of the walls of the heart muscle and pericardium, to control the activity of the heart valves;
Magnetic resonance imaging – helps to determine the source of noise in the heart, find the site of myocardial necrosis, identify vascular dysfunction;
Scintigraphy of the heart muscle – is carried out using a contrast agent, which, after entering the bloodstream, helps to assess the characteristics of blood flow;
Cardiomonitoring according to Holter – observation of daily changes in the work of the heart and blood vessels using a mobile device attached to the belt of the subject. It helps to determine the cause of abnormal heart rhythm and chest pain.
You can go through such studies on your own initiative, but only a qualified cardiologist can correctly interpret their results.
Prevention of heart disease

The main factors provoking the occurrence of cardiac pathologies:
Elevated blood cholesterol levels;
Sedentary lifestyle;
Smoking and alcohol abuse;
Elevated blood sugar;
Excess in the diet of refractory animal fats, salt;
Prolonged psycho-emotional overstrain;
High blood pressure;
Obesity.
To eliminate the risk of heart and vascular diseases, cardiologists suggest following simple rules in everyday life:
Follow the principles of a healthy diet, reduce the amount of fat in the diet and increase the amount of fiber;
Stop smoking, do not abuse alcohol;
Limit the time spent without movement, more often engage in physical education in the fresh air;
Get enough sleep, avoid stress, treat difficult situations with humor;
Use a minimum of salt in the cooking process;
Replenish the reserves of potassium and magnesium in the body by taking a complex of trace elements;
Know the age and sex norms of blood sugar, blood pressure, body mass index and strive for such indicators.
If there are prerequisites for the development of pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, risk factors should be immediately eliminated, preventing the occurrence of serious diseases.
[Video] Dr. Berg – Prevention of heart disease. How to avoid a heart attack:









