Contents
A strong and large bird as a chick is very vulnerable not only to infections. Any young animals are susceptible to infections because of the immunity that has not yet been formed. But goslings are also very sensitive to improper diet and lack of exercise.
Coming very young to a new owner from a goose breeding farm, goslings can bring with them infectious diseases that they contracted in an incubator or received from their mother goose.
Diseases of goslings, with which chicks come to a new owner, can deprive the happy purchaser of 70% of the newly acquired herd. And sometimes all the goslings die.
The diseases of young animals that goslings can bring with them from the incubator include:
- salmonellosis, aka paratyphoid:
- viral enteritis, often the result of salmonellosis;
- pullorosis;
- colibacillosis, aka colisepticemia;
- pasteurellosis.
Enteritis caused by a viral disease and which is a complication of the disease usually manifests itself starting from the 5th day after birth. The maximum period during which signs of “incubation” enteritis may appear is up to 3 weeks.
The intestines of goslings may become inflamed later, but this will already be a consequence of keeping with the new owner, and not a consequence of the disease brought from the incubator.
Colibacillosis
The disease has so many names that it is easy for inexperienced owners to get confused in them. Colibacillosis is also called coliinfection, colidiarrhea, colisepsis, avian coliseptimia. In the West, another name is common: escherichiosis.
The causative agent of the disease are various pathogenic varieties of the bacterium Escherichia coli, belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family. The bacterium is able to survive in the external environment for up to 4 months, but is sensitive to disinfectant solutions.
The causative agent of the disease is transmitted through the litter of a sick bird, inventory, feed, water and other similar methods. Sick birds remain a source of the disease for a long time, so the egg itself from a sick goose may already be infected. The hatched chick will become infected with colibacillosis right in the incubator.
In birds, including goslings, colibacillosis occurs in the form of septicemia (symptoms of “blood poisoning”), affecting the internal organs: air sacs, lungs, liver, outer shell of the heart, and joints. Arthritis develops in the joints. Because of the pain, the birds sit on their feet and refuse to walk. As a result of a lack of air due to a lung disease, the goslings limit their movement – they “go to rest” with signs of drowsiness. In fact, this is a sign of lack of air.
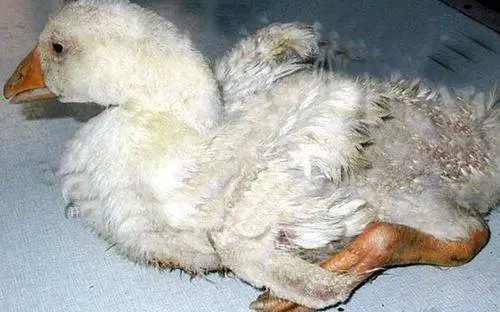
Enteritis (inflammation of the intestine) with septicemia is not always observed. But in the case of the development of inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, goslings experience diarrhea. Sometimes with blood.
In the acute course of colibacillosis, up to 30% of birds die. In surviving goslings, productivity and the ability to develop immunity when vaccinated against infections are further reduced.
Treatment of the disease
Unlike many other infectious diseases of birds, in which an ax is strongly recommended as a panacea for all diseases, colibacillosis is treated.
Colibacillosis in goslings must be distinguished from salmonellosis, pullorosis, pasteurellosis and enteritis caused by poor-quality feed.
The isolation of the causative agent of the disease is carried out in the laboratory, but since it is impossible to wait so much time (a week for sowing), treatment is started at the first signs of the disease.
Goslings check the diet by putting birds on a diet that prevents the development of enteritis. For treatment, broad-spectrum antibiotics and antibacterial drugs are used: sulfonamides and nitrofurans.
If the herd of goslings is too large and it is not possible to catch all of them, it will not be possible to personally dispense medicines, spraying antibiotics in the air in the form of aerosols is used.
In parallel with the main treatment of the disease, symptomatic treatment is used to maintain the gastrointestinal tract of birds and prevent dehydration and intoxication.
disease prevention
In the case of birds, the main prevention of the disease is the thorough disinfection of the room and the incubator with formaldehyde vapor. These control measures are relevant only for nurseries.
When buying goslings on the side, they should not be mixed with the rest of the herd until the chicks grow up and they develop immunity.
salmonellosis
Not only birds, but also mammals are susceptible to the disease. But salmonellosis is caused by different types of Salmonella. Salmonella persist in the external environment for a long time. Without the use of disinfectants, one cannot be sure of the destruction of the causative agent of the disease. Therefore, if last year the goslings on the farm died from salmonellosis, it is better to wait a year before buying new birds.
Mostly young goslings are ill, adult geese are more resistant to the disease. More precisely, their salmonellosis is asymptomatic. In this case, the goose can carry already infected eggs.
In goslings under the age of 20 days with an acute course of the disease, salmonellosis is characterized by fever, toxicosis, intestinal damage (enteritis). In the chronic course of the disease, lung damage and joint disease are observed.
Symptoms of the disease
The latent period of the disease lasts from 1 to 3 days. In birds, salmonellosis occurs acutely, subacutely and chronically. In the acute course of the disease, goslings under the age of 20 days lose their appetite and desire to move, anemia, diarrhea, and purulent conjunctivitis are observed. Nervous seizures appear, expressed in convulsions, during which the goslings make chaotic head movements, fall on their backs, and move their limbs. Mortality in the acute form of the disease can reach 70%.

A subacute course of the disease is observed in older goslings. Signs of a subacute course of the disease are purulent conjunctivitis, runny nose, diarrhea, inflammation of the joints. Inflammation of the joints leads to the fact that the goslings fall to their feet.
Goslings most easily tolerate the chronic form of the disease, which they suffer from at the age of 2 months. The chronic form of the disease is characterized by diarrhea and developmental delay.
Treatment of the disease
For the treatment of the disease, antibiotics are used in combination with antibacterial drugs, according to the instructions attached to the medication or issued by the supervising veterinarian. In addition to drug treatment of the disease, symptomatic support for goslings is carried out by adding vitamins and drugs that increase immunity to the feed.
disease prevention
In the case of poultry, the main measure to prevent the disease is the thorough disinfection of premises and areas where geese are kept, and the purchase of new livestock only from farms free of salmonellosis.
If you can get it, you can vaccinate geese with a live recombinant salmonella vaccine for birds used abroad.
Pasteurellosis
A disease caused by a pathogenic bacterium. The properties of Pasteurella of different serotypes vary greatly and largely depend on the type of animal from which they were isolated.
In the external environment, Pasteurella can be stored from several days to 4 months. The deadline is for animal carcasses.
The main modes of transmission of Pasteurella are through the respiratory tract and through the gastrointestinal tract. Infection occurs through contact with a sick and recovered bird, with food, through rodents. A goose that has been ill with pasteurellosis carries infected eggs, in which the embryos die on the 9th – 15th day of incubation. If the embryo survives, the hatched gosling becomes a virus carrier.

Symptoms of the disease
The incubation period for the disease is 2 to 4 days. In birds, the disease is very severe, with signs of general blood poisoning. The course of the disease in birds can be hyperacute, acute and chronic.
The superacute course of the disease is expressed in the sudden death of the bird and, most often, the owner only has to shrug. In the acute course of the disease, which lasts no more than 3 days and is observed, the following symptoms are most often noticeable:
- lowered wings;
- exhaustion;
- thirst;
- temperature 44°C;
- foam from the beak and nose;
- diarrhea;
- death after 18 – 72 hours.
In the chronic course of the disease, only rhinitis, viscous discharge from the nose and eyes is observed.
Treatment and prevention of the disease
Birds are not cured. If pasteurellosis was previously recorded on the farm, the birds are vaccinated against pasteurellosis according to the instructions. Particular attention is paid to compliance with sanitary and veterinary rules for keeping livestock and poultry and regular disinfection of premises and territory.
Pulloroz
A bacterial disease that is especially susceptible to young birds. Goslings show signs of general blood poisoning and inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, that is, enteritis.
The causative agent is a bacterium from the Salmonella family. In the soil can be stored for more than a year, dried for 7 years. Sensitive to disinfectants.

Symptoms of the disease
With congenital pullorosis, that is, when goslings are hatched from infected eggs, the incubation period of the disease is from 3 to 10 days. Such goslings have general weakness, refusal to feed, the yolk is not completely retracted into the abdominal cavity, white liquid droppings. The fluff around the cloaca is glued with droppings.
When infected after leaving the egg due to keeping together with sick chicks, the incubation period of the disease is 2-5 days. Postnatal pullorosis can be acute, subacute and chronic.
In the acute course of the disease, general weakness, upset digestion, slimy white diarrhea, and a beak open for breathing are observed.
Subacute and chronic course of the disease can be observed from the 15th day of life of the gosling: developmental delay, intestinal upset, inflammation of the joints of the legs. Mortality in the last two types of the course of the disease is low.
Treatment of the disease
Only conditionally healthy birds are treated, prescribing antibiotics of the terramycin group and maintenance therapy. The sick bird is destroyed.
Preventive measures for pullorosis are compliance with veterinary rules for incubating eggs and rearing young animals.
Viral enteritis of geese
Caused by a DNA virus. Adult geese are immune to the virus, only goslings suffer.

Symptoms of the disease
The incubation period lasts from 2 to 6 days. The course of the disease is acute. The illness can last from 2 days to 2 weeks. From 60 to 100% of goslings die. Symptoms of the disease: weakness, thirst, loss of appetite, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, diarrhea, accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Goslings under the age of 10 days have chills. They huddle together trying to keep warm. Older goslings lie without reacting to stimuli and lower their wings, pluck each other, and lag behind in growth. At 7 weeks of age, the course of enteritis is chronic. No more than 3% of goslings die, growth stops completely.
Treatment and prevention
The classical regimen for the treatment of the disease requires the presence of serum from convalescent geese. Today, for the treatment of enteritis, and in fact to help the body, since viruses are not treated, hyperimmune sera are used that stimulate the natural immunity of goslings. Antibiotics are used to suppress secondary infection.
Preventive measures are applied according to the instructions for combating goose viral enteritis.
Aspergillosis
A disease caused by the mold Aspergillus. It looks like a black coating on the walls and household items. Present everywhere. It does not cause problems, provided that the immune system is good. When immunity is weakened, the fungus begins to multiply in the respiratory system.
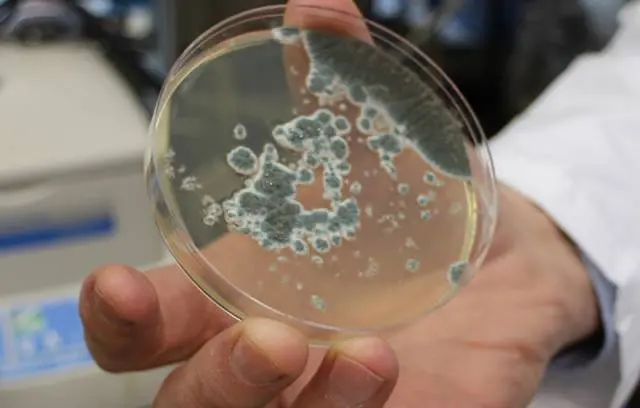
The disease affects old birds with weakened immunity and young animals in which immunity has not yet been formed.
aspergillosis in birds
The reasons for the development of aspergillosis are the keeping of goslings in a damp, dark room and feeding them with moldy grain. The spores of the fungus, getting into the lungs, begin to germinate, causing the disease.
Symptoms of the disease
The mold makes it difficult to breathe, so the goslings try to cough up the disturbing object. Breathing labored, with open beak. Trying to “push through” a piece, the bird stretches its neck. The mold grows into other internal organs, causing diarrhea, convulsions, and conjunctivitis.
There is no cure for aspergillosis. A sick bird is slaughtered, the room is freed from animals and carefully treated with mold preparations.
Helminthiasis
Geese become infected with worms by swallowing larvae near water bodies.
Amidostomatosis
Geese are infected with this nematode by directly swallowing the larvae with grass or water.
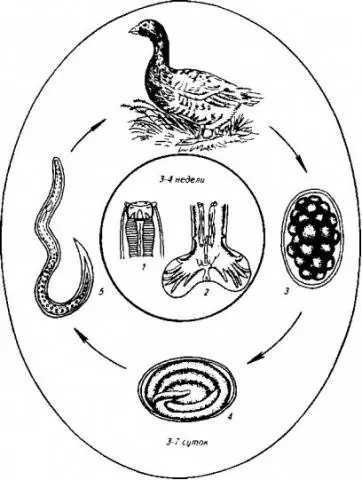
Symptoms of the disease
Goslings are especially sensitive to the parasite. When infected with a nematode, the gosling becomes inactive, often sits on its paws, and poor feather growth is observed. The gosling lags behind in development. With mixed invasion, cases of death of goslings are not uncommon.
Hymenolipedosis
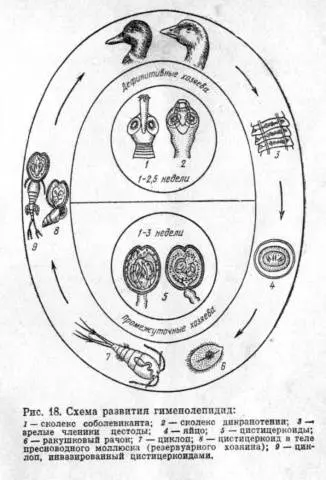
The causative agent of the disease is one of the types of cestodes. Geese become infected by ingesting plankton or molluscs. When infected with a cestode, emaciation, stunting, gait uncertainty, convulsions, sometimes paralysis of the limbs and, as a result, falls are observed. Litter liquid, with an unpleasant odor.

Prevention of diseases associated with helminths consists in regular deworming of the entire livestock.
Diseases of little goslings are not limited to infectious diseases. Often, goslings die from non-communicable diseases that could have been avoided if the chicks were properly kept and their diet was properly prepared.

Owners of newly hatched goslings often get two problems: cannibalism and the death of goslings when walking them along with the goose.
Cannibalism
As the cause of cannibalism, a version of the lack of animal protein or trace elements in the diet of goslings is considered. But when the goslings are still very small, this factor is unlikely to really matter. Also, cannibalism may be due to the stress of keeping birds too crowded. Experienced goose breeders have another explanation.
From the first day of life, the gosling must walk and pluck the grass. In the brooder, he simply has nothing to do and the goslings begin to pluck each other until they bleed. Goose breeders fight against manifestations of cannibalism in a very interesting way, presented in the video.
The second problem is the death of goslings after being in the pond. The point here is that in the early days there is little fat on the down of the caterpillar. And, more precisely, there is no fat at all. After a long stay in the water, the fluff gets wet and the chick dies from hypothermia.
The problem of rickets
Goslings are very fast growing birds. At 4 months, they already differ little in size from their parents. For rapid growth, goslings need not only high-quality feed, but also a long walk in the fresh air. In an attempt to protect the chicks from disease, owners often keep the birds indoors without walking.
In such conditions, the goslings begin to bend their paws. Unable to walk on their trembling legs, the goslings fall to their feet. This situation can be avoided if, from a very early age, the chicks are provided with a long walk with the possibility of active movement. At the same time, such a paddock in the presence of grass will solve the problem of cannibalism in geese.
Rickets is not the only developmental problem facing goslings. The video shows an example of wings that began to bend under the influence of external factors and the timely correction of the problem.
Conclusion
It must be borne in mind that falling on your paws is not a disease in itself. This is a symptom of some more serious disease. On closer examination, the owner will certainly notice other signs of illness in the caterpillar.









