Contents
Rabbits would be an excellent investment and a very profitable business, if it were not for the fact that the mortality of these animals often reaches 100%, bringing only losses to the owner. Before starting rabbits, it is better for a beginner to find out in theory what to feed rabbits so that they do not have bloating, and what are the diseases of rabbits and their treatment.
Like any other animal species, diseases of rabbits can be divided into infectious, invasive and non-infectious.
The main economic damage to the owners of rabbit farms is caused by infectious diseases, especially the scourge of all rabbit breeders: viral haemorrhagic disease of rabbits and myxomatosis. Also, animals often die from bloating, which is actually not a disease, but a symptom of a number of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
VGBK and myxomatosis
Both of these diseases are extremely contagious with a high mortality rate. Mortality rates in patients with HBV often reach 100%.
All the so-called folk methods of curing these diseases are symptomatic relief of the well-being of a sick rabbit. As a rule, they “work” with myxomatosis, where the mortality rate is lower than with VGBK.
In fact, the treatment of viral diseases has not been developed even for humans. There are only immunostimulating drugs that help the body cope with the virus at the expense of its own immunity. The virus does not die, but remains in the living cells of the body, which is why surviving rabbits are a source of infection for healthy animals for a long time.
Viral hemorrhagic disease
It is caused by a virus that affects only the European rabbit, from which the domestic rabbit is descended. Accordingly, domesticated rabbits are also susceptible to this disease.
The incubation period for the virus is no more than 48 hours. The course of the disease can be hyperacute, acute and subacute.
With subacute, symptoms of the disease can be noticed:
- lethargy;
- lack of appetite;
- heat;
- cramping;
- death.
In the subacute course of the disease, you can try to stretch the rabbit by injecting it with an immunostimulating serum, but this can only be done if the rabbit lives alone, being a pet. In the presence of several heads, such an action does not make the slightest sense. Even if the rabbit survives, it will be a carrier of the infection, capable of infecting not only rabbits in neighboring cages, but even on neighboring farms.

In hyperacute and acute course of the disease, there are no symptoms. The rabbit just suddenly falls and after a few agonizing movements freezes.
Sometimes dead rabbits may notice bleeding from the nose, mouth, or anus.
Mortality in rabbits with VHD is 50 to 100%. Moreover, according to the observations of practicing veterinarians, the last figure is much closer to the truth.
With any sudden death of a rabbit, it is imperative to do an analysis for the presence of HBV, since the virus is extremely resistant to adverse environmental conditions and can survive up to six months at room temperature and more than 9 months at temperatures close to 0.
The virus is transmitted by almost any means:
- through inanimate objects: car wheels, inventory, staff clothing, shoes;
- by contact with an infected rabbit or contaminated feces;
- through farm products: meat, skins, wool;
- through people who have been in contact with infected animals;
- through rodents, blood-sucking insects and birds.
There is no cure for this disease. The only way to prevent HBV is to prevent the disease.
First of all, you need to follow the vaccination schedule. Rabbits do not develop immunity to VHD, so vaccinations must be repeated every six months. The first three times the vaccine against VGBK is injected according to a special scheme:
- 45 days from birth;
- 115 days from birth;
- Six months after the second vaccination.
Further, the vaccine is always pierced every 6 months.
Measures to prevent VGBK:
- quarantine of a newly acquired rabbit for 5 days;
- disinsection of the premises where rabbits are kept;
- keeping rabbits indoors, since on the street they are more likely to meet with a carrier of the virus;
- purchase of fodder from areas that are safe for VGBK;
- special clothing and footwear for working with rabbits;
- systematic treatment of cells and cellular equipment with disinfectants.
When a disease appears on the farm, the entire livestock of animals must be slaughtered.
Myxomatosis
The homeland of the virus is South America, from where it was specially brought to Europe to fight the breeding of wild rabbits that did not have immunity to the disease. As always, they did not think about the consequences.
The virus is transmitted by direct contact with a sick animal or by blood-sucking insects that do not care who bites: a wild rabbit or a domestic one. As a result of the rapid spread of myxomatosis and the high virulence of the virus in Europe, it came to panzootic.

The myxomatosis virus is quite stable in the external environment. In the corpse of an animal, it can be stored for a week, at a temperature of about 20 ° C in a dried rabbit skin up to 10 months, in the external environment at a temperature of 9 ° C – 3 months. When heated to 55°C, the myxomatosis virus is inactivated after 25 minutes. Does not withstand the virus and treatment with disinfectant solutions.
The incubation period of the disease can be 20 days long and largely depends on the immunity of the rabbit.
Treatment with folk remedies, such a dangerous disease as myxomatosis, is essentially a profanity. Those animals that would cope with the virus survive. But the “doctors” endanger not only their own rabbits, but also neighboring animals.
Actually, the whole treatment of the disease comes down simply to alleviating the condition of the rabbit during the illness, pain relief and waiting for the animal to survive or not.
The requirements of the veterinary services when myxomatosis appears on the farm are the slaughter of livestock.
Forms of myxomatosis
Myxomatosis can be edematous or nodular. The first begins with conjunctivitis and swelling of the head.
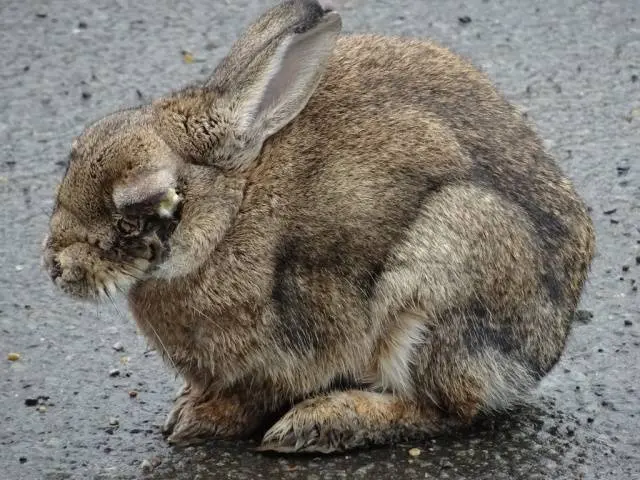

The head acquires a characteristic shape, nicknamed the “lion’s head”. At the same time, solid formations appear in the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe head and anus.
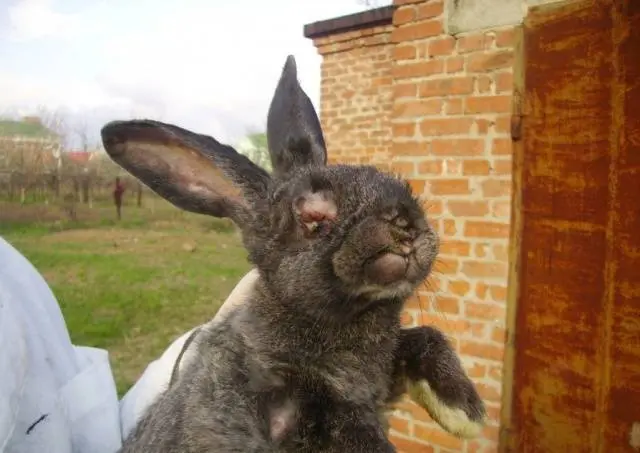

With the nodular form of the disease, hard, reddened tubercles appear on the body of the rabbit. Owners usually notice these formations on the ears, as the ears lack thick hair and the nodules are clearly visible.
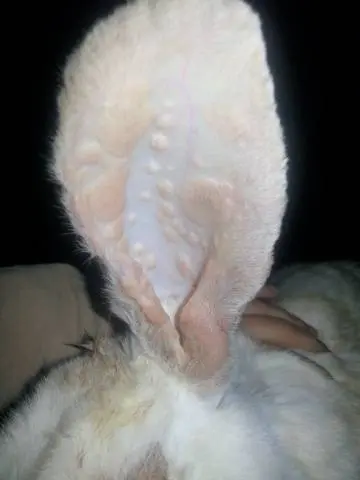
Both forms are characterized by a sudden increase in body temperature of rabbits up to 40-41 °.
In addition to the two “classic” forms, as a result of the mutation of the myxomatosis virus, a third one also appeared: an atypical form of the disease, characterized by the fact that it affects the respiratory system. As a result, this form of the disease is easily confused with bronchitis, pneumonia, or pneumonia. However, with a long course, it is inflammation of the lungs that this form of the disease causes.
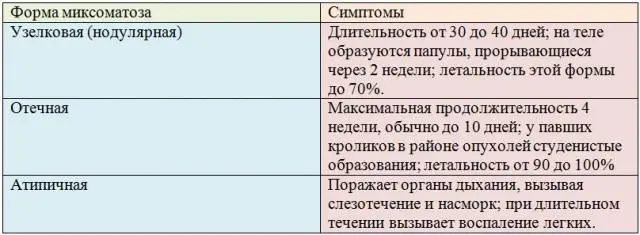
According to the rate of flow, myxomatosis is also divided into forms.
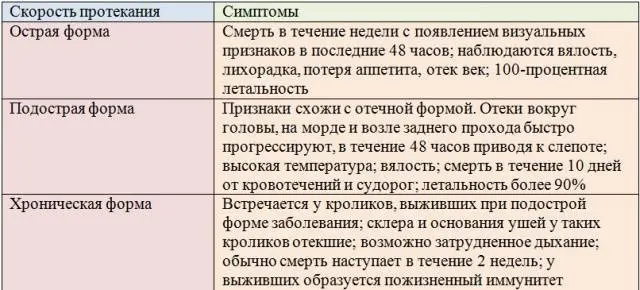
Myxomatosis treatment
As already mentioned, myxomatosis is not cured, and experienced rabbit breeders are advised to immediately slaughter the animals, but if the rabbit lives alone in an apartment and is a pet, you can try to help him cope with the disease. If the rabbit continues to live alone, then the fact of the disease will not play any role.
To alleviate the condition of the animal, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used to destroy a secondary infection, which usually “sits” on open purulent wounds. Mandatory injections of immunostimulating drugs. To facilitate breathing, apply drops from the common cold. The eyes are washed with saline and instilled with antibiotic eye drops.
At the same time, unlike VGBK, myxomatosis can be dealt with with little blood. Rabbits that have been ill acquire immunity to myxomatosis for life, remaining, however, carriers of the virus.
To get rid of this disease, it is enough to vaccinate 30-day-old rabbits once with the Rabbivac-B vaccine, made on the basis of a live attenuated myxomatosis virus.
In the case of using a bivalent vaccine against myxomatosis and HBV, the vaccine is punctured according to the vaccination schedule for HBV.
We must also remember that the vaccine does not give a 100% guarantee. Sometimes there is a “breakdown” of vaccination and the rabbit becomes ill with myxomatosis, although in a milder form.
Rabbit breeders often have the question of whether it is possible to eat the meat of rabbits with myxomatosis. There are no restrictions. This disease is not dangerous for humans. Therefore, you can eat. But it’s disgusting.
Other infectious diseases
In addition to myxomatosis and VHD, rabbits also suffer from rabies, which is caused by a virus. Since the rabies virus is transmitted only with the saliva of a sick animal, it is enough to exclude mice and rats from access to cages with rabbits in order to be practically calm about rabies. For a guarantee, you can vaccinate the whole livestock once a year.
Bacterial diseases
Bacterial diseases in rabbits and their symptoms are often confused with non-contagious diseases. This is the particular danger of pasteurellosis or salmonellosis.
Purulent conjunctivitis with pasteurellosis can be confused with advanced dacryocystitis, discharge from the nose can be attributed to a draft, and diarrhea can be attributed to eating unusual food.
The edematous form of pasteurellosis, in general, is very similar to rabies.
Symptoms of pasteurellosis in four different forms of the course of the disease

At the same time, subacute and chronic forms of the disease are divided into types according to the location of Pasteurella:
- in the intestinal form of the disease, the symptoms are dark diarrhea mixed with blood, lack of appetite, thirst;
- with the chest form of pasteurellosis, purulent discharge from the nose, a dry cough, which later turns into wet and labored breathing, are observed;
- in the edematous form of the disease, the rabbit develops saliva from the mouth due to difficulty swallowing and heart failure. But this is already a consequence of swelling of the limbs, abdomen, tongue, larynx, eyes, neck and other parts and organs of the body.
Most often in rabbits, the breast form of pasteurellosis is observed. Since this bacterium is always present in a living organism, but is not able to develop with normal immunity, pasteurellosis can be considered a sign of immunity failure. Immunity usually decreases against the background of stress and the unsanitary state of the cells.
Pasteurella can also affect the inner ear, causing what is known as a twisted neck.

Pasteurellosis is transmitted by contact of a healthy rabbit with a sick animal. To prevent pasteurellosis, it is necessary to systematically treat cells with disinfectant solutions. It is better to use several methods at once. You can treat the cells first with a blowtorch, burning crawling insects, then with disinfectant solutions, destroying especially resistant viruses and bacteria. In addition, it is good to disinfect the premises from flying insects.
To prevent pasteurellosis, rabbits can be vaccinated with one of the vaccines: Pasorin – OL or CUNIVAK PAST. Vaccination is carried out according to the schemes, separate for each of the vaccines.
If the rabbits still fell ill with pasteurellosis, then they will have to be treated with antibiotics for a course of 14 to 30 days. After treatment, due to dysbacteriosis, the rabbit may develop diarrhea or bloating.
The treatment regimen for pasteurellosis is prescribed by a doctor. It is not recommended to treat the disease with folk methods. Pasteurella also parasitizes humans.
Since pasteurellosis can be transmitted to humans, the meat of sick rabbits should not be eaten. Animal corpses are burned. In the settlement where pasteurellosis is found, quarantine is announced.
Invasive diseases of rabbits with photos, symptoms of diseases and their treatment
Part of the invasive diseases refers to diseases of rabbits dangerous to humans. In particular, it is cysticercosis – one of the types of helminthiases and dermatomycosis, popularly united under the general name “lichen”.
With regard to dermatomycosis, the people are partly right, since all types of these fungi are treated in the same way.
Symptoms of various types of dermatomycosis

Fungi are bad because no matter how they are herbs, they easily return, as they are transmitted not only from animal to animal, but also from object to animal. Or per person.
When choosing how to treat a surface infected with a fungus, you have to take into account that it is necessary to treat not only the room, but also the animal. Accordingly, the preparation must be such as to destroy the fungus without harming the mammals.
A possible option for processing the premises is presented in the video.
In the video, a cowshed is being treated, but in the case of dermatomycosis, the type of animals does not matter.
Helminthiasis
Common signs of the presence of worms is the exhaustion of the animal with increased appetite. But worms are not only intestinal. With the pulmonary form of helminthiasis, the rabbit may look good and only cough. And in the presence of parasites in the liver, the animal will show signs of hepatitis, but not exhaustion.
Of all helminthiases, cysticercosis is the most dangerous for humans. The description of this disease is similar to the symptoms of peritonitis and hepatitis. Cysticercosis is caused by larvae of carnivorous tapeworms, which parasitize everywhere in the rabbit’s body, including the brain.
For humans, cysticercosis is dangerous because one of the species of these larvae is the larvae of the tapeworm, the final owner of which is a person. Infection occurs by eating poorly processed meat.
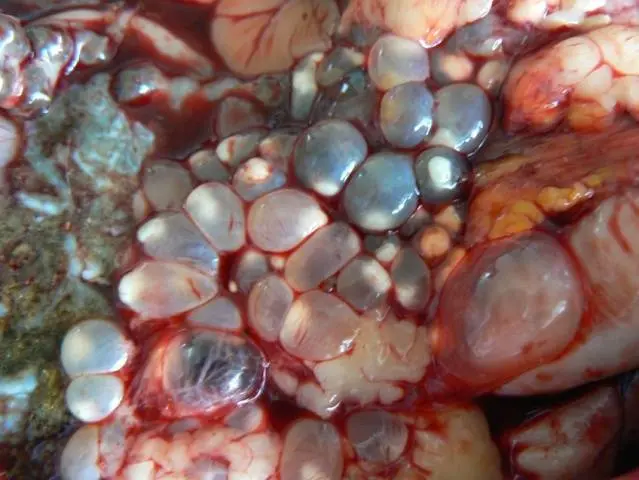
The second way of infection: airborne eggs of mature larvae, which the rabbit excretes along with feces. In this case, a person becomes an intermediate host for the tapeworm, and the Finn stage of the tapeworm passes already in the human body, leading to severe illness or death.
Bloating in rabbits
It is not a separate disease. It is a symptom of a number of other diseases, sometimes infectious, sometimes non-contagious. Mostly non-infectious.
Of the infectious diseases, bloating is caused by coccidiosis and enteritis.
Coccidiosis is a common invasive disease for several species of mammals and poultry. As a rule, signs of coccidiosis appear in rabbits after weaning them from their mother. Therefore, immediately after weaning, the rabbits need to drink coccidiostats according to the instructions attached to each type of drug.
For non-infectious tympania caused by a recent course of antibiotics, pre- and probiotics are given to rabbits. In the case of mild colic, the animal can be driven a little so that gases come out of the intestines.
But in any case, it is necessary that the veterinarian establishes the cause of tympania as soon as possible. In some cases, the account may go to the clock. With problems in the gastrointestinal tract, part of the intestine may even begin to die.
Therefore, rabbit owners often simply slaughter sick animals.
Conclusion
Rabbits are very delicate animals, prone to many diseases, and often die simply from inappropriate food. But if you are not afraid of vaccinations and medications, preaching environmental friendliness and naturalness, then losses among the rabbit population can be reduced to a minimum.









