Contents
Until a vaccine against diphtheria was invented, a huge number of children died from this disease every year. With the introduction of the vaccine into the national vaccination calendar, the disease receded. Humans have no intrinsic immunity to corynebacteria. These microorganisms are extremely dangerous. They are able to damage internal organs, provoke the development of a shock state and death of the patient.
Modern vaccines have made it possible to cope with diphtheria in 96% of cases. Detection of the disease is not difficult, since the causes and symptoms of the pathology are well known.
What is diphtheria?
Diphtheria is a dangerous infectious disease caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae. This microorganism is characterized by increased survival outside the human body. The microbe retains its activity after drying, is not afraid of low temperatures, feels great in an apartment. To destroy the bacteria that live in water, it must be boiled for at least a minute. It can be removed from household items only with the use of chlorine-containing agents, phenol or chloramine. Moreover, the processing should last at least 10 minutes. Diphtheria bacteria have various forms, but this does not affect the symptoms of pathology and the characteristics of therapy.
The disease is spread by airborne droplets. It is accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx and oropharynx, general intoxication. Diphtheria affects the cardiovascular, nervous and
Causes of diphtheria
Diphtheria develops due to the penetration of a pathogenic microbe into the body. Occurs after contact with an infected person. If he suffers from acute symptoms of pathology, then the probability of infection is 10 times higher than when in contact with a person who carries the infection. At the same time, Professor VF Uchaikin points out that about 97% of Russians are vaccinated against diphtheria, so contact with a patient with diphtheria can happen as an exception. Carriers of infection remain the main sources of spread of the disease.
There are 2 ways of transmission of pathology:
Airborne. Bacteria are released into the external environment along with sputum and particles of mucus during a conversation, coughing, blowing your nose. They get on the wounds of a healthy person and on his mucous membranes, causing illness.
Contact household. Infection occurs when using common household items or clothes of an infected person. Joint food intake is dangerous in this regard, since microbes are able to settle on the surfaces of various objects.
People who have received the vaccine do not get diphtheria. The same applies to healthy individuals with normal immunity.
For the disease to develop, some predisposing factors are necessary:
The vaccine was not delivered on time. This applies to DPT and DTP vaccinations.
Children’s age from 3 to 7 years. At this time, the woman already stops breastfeeding the child and there are no protective antibodies in his blood. Own immunity during this period is just beginning to form.
Weakened immunity. This can happen for a variety of reasons: HIV, cancer, the end of the menstrual cycle, previous infections, etc.
A significant period of time that happened after the vaccine was given, the lack of contact with sick people. All this weakens the immunity formed against diphtheria.
Bacteria are very stable in the external environment, because they quickly spread in groups, passing from one person to another.
Risk groups for the spread of diphtheria:
People without vaccination who are gathered in groups.
Children in orphanages and boarding schools.
University students, schoolchildren.
People who serve in the military.
The population of 3 countries of the world, refugees.
People who are in hospitals and psycho-neurological dispensaries.
Diphtheria spreads quickly, so an infected person should be isolated from society as soon as possible. Such patients are placed in semi-boxes. These rooms have their own toilets and baths. In the conditions of boxing, the patient should be until such time as the bacterium is completely eliminated from his body.
When does a person become contagious?
The incubation period after infection is 10 days. When the last day of the incubation period comes, the patient becomes contagious. It remains contagious until the bacteria are completely eliminated from the body. This must be confirmed by test results.
Symptoms of diphtheria, depending on the form of the disease
In many people, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, since they have a vaccine against it. Once a bacterium enters the body, it simply lives in it. Such people pose a threat to healthy unvaccinated individuals. However, the probability of infection upon contact with them is 10 times less than upon contact with a patient with acute diphtheria. When a bacterium enters the body of a person who has not been vaccinated, an infection develops. Its initial symptoms are:
Hyperemia of the tonsils.
The occurrence of intense pain while swallowing food.
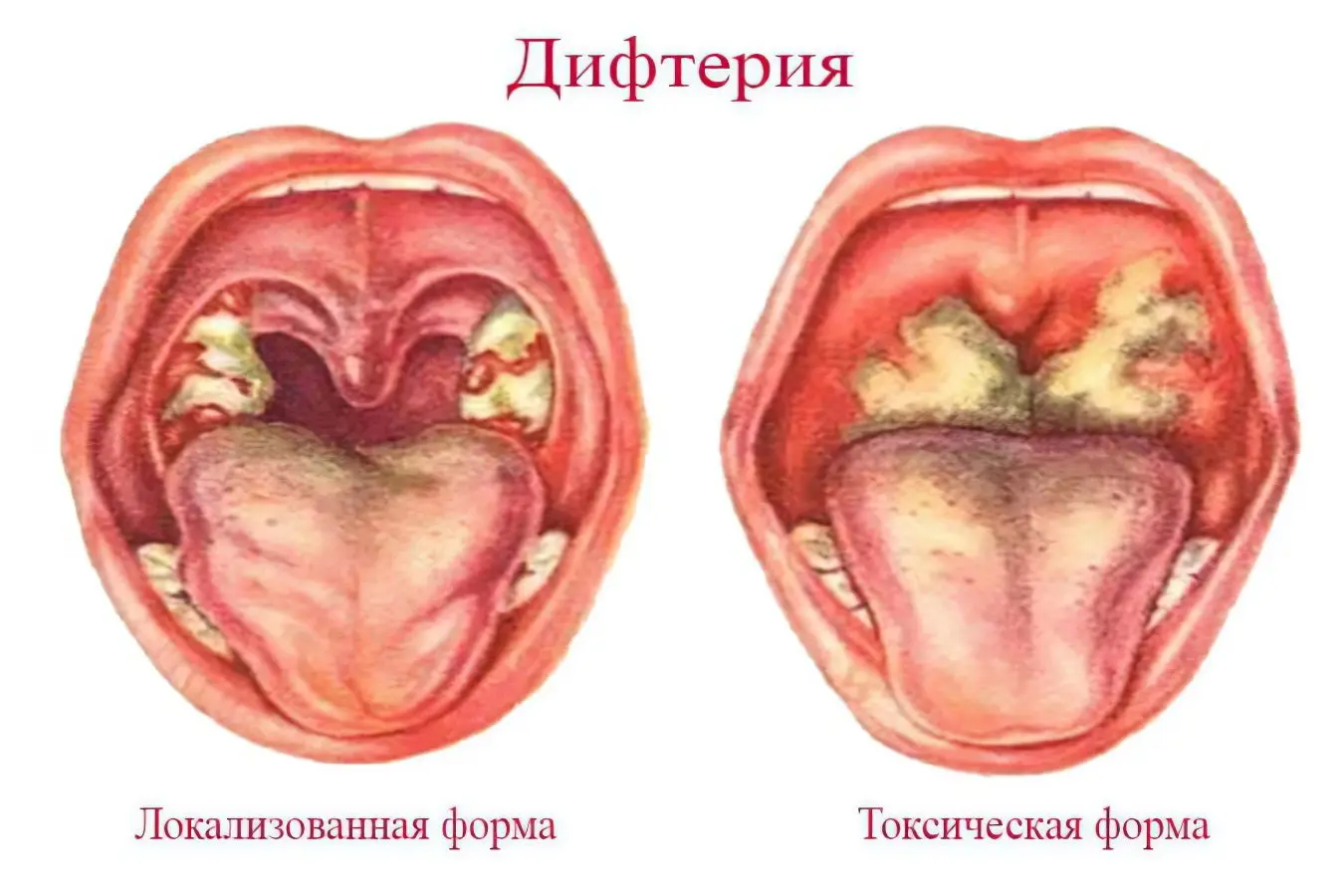
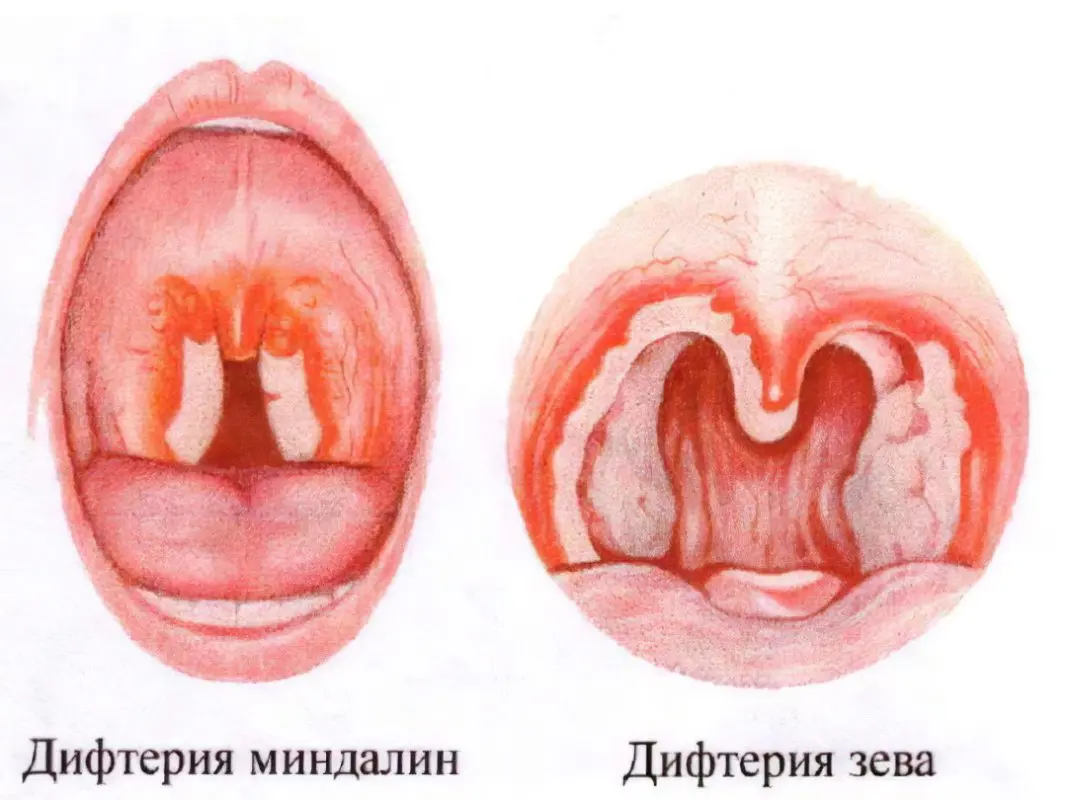
Formation of diphtheria films. They are smooth and shiny, and may be whitish, yellow or gray in color. It is difficult to remove the film from the surface, since it is firmly bonded to it. If a person nevertheless tears it off, then a wound with oozing blood will be visible under it. After some time, the film will appear on the surface of the skin again.
As the pathology progresses, the symptoms of diphtheria become more diverse. It depends on the specific form of the disease. They must be distinguished in order to determine the optimal therapeutic regimen.
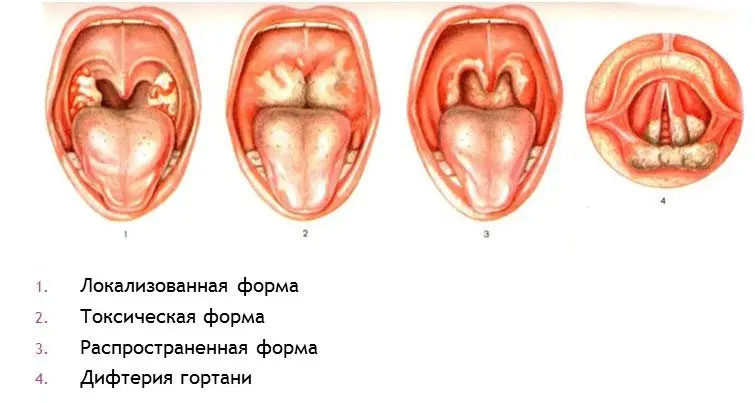
Diphtheria pharynx localized
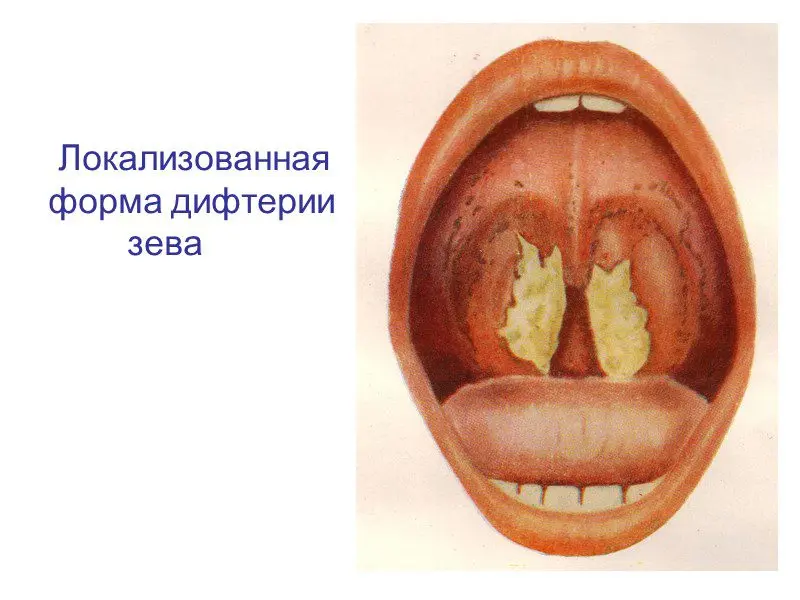
With localized diphtheria of the pharynx, the symptoms are mild. Most often, children who receive the vaccine get sick with this form, but their own immunity is very weak. There is no marked deterioration in well-being. Perhaps increased lethargy, decreased appetite, lack of sleep. Patients complain of headache.
In 35% of people, body temperature remains within the normal range. In other cases, it can rise to 38-39 ° C. After 3 days from the onset of the disease, the body temperature returns to normal, and other symptoms of the disease persist.
They include:
Pain in the throat, which occurs in the process of swallowing food.
Slight redness of the tonsils and their swelling.
An increase in the size of the lymph nodes, their slight pain on palpation. This applies to those nodes that are located under the jaw and under the chin.
The appearance of a film characteristic of diphtheria.
To palpate the lymph nodes, you need to put your fingers under the person’s lower jaw. Having collected soft tissues, it will be possible to feel the lymph node, which is enlarged in size and responds with pain. Palpation must be done carefully.
Localized diphtheria of the pharynx can be island-shaped, in which the film covers the tonsils not completely, but partially. The films themselves resemble the appearance of a pin head. There may be many such formations, or there may be 1-2 pieces.
The membranous form of the disease is characterized by the fact that the films cover the tonsils completely.
Dealing with localized pharyngeal diphtheria is not difficult. After 14-18 days, the person fully recovers.
Diphtheria pharynx common
With this form of the disease, the symptoms resemble those that are characteristic of localized diphtheria of the pharynx, but there are still differences. Common diphtheria develops infrequently. It is mainly diagnosed in children aged 5-7 years. As a rule, they were not vaccinated.
A distinctive feature of widespread diphtheria is the abundance of films that go beyond the tonsils. They pass to the palatine arches, to the tongue, to the soft palate and to the pharynx.
Body temperature always rises to feverish levels. It develops 4-5 days after the onset of the disease. A person suffers from severe intoxication of the body, he loses the desire to eat, and his head hurts badly.
The prognosis for recovery is favorable, but only on condition that the treatment is provided in full.
Diphtheria pharynx subtoxic
The subtoxic form of the disease is more severe than the previously described types of diphtheria. A person has intense headaches, body temperature rises to feverish levels and persists for 5 days (if the patient was not injected with antitoxic serum).
Lymph nodes hurt a lot, swell, become larger in size. The film extends beyond the tonsils and covers the mucous membranes surrounding them.
The patient is placed in a box for up to 30 days, but not less. At the same time, he will need to observe bed rest for 25 days. It is possible to cope with the subtoxic form of diphtheria, but it will not be possible to stop the symptoms of the disease earlier than after 30 days.
Diphtheria pharynx toxic
If the child has not been vaccinated and has a weak immune system, then there is a possibility of developing toxic diphtheria of the throat.
In the first days of the development of the disease, a significant amount of toxins enter the bloodstream, which provoke the occurrence of symptoms such as:
A sharp jump in body temperature. It reaches 39 °C. At the same time, parents can tell exactly when the temperature began to rise. The accuracy is down to the minute.
Immediately, a film forms on the patient’s tonsils.
A person suffers from severe weakness, he vomits, intense headaches develop.
The heartbeat quickens and reaches 90 beats per minute.
The skin becomes pale, chills develop.
On the 3rd day of illness, the neck swells, lymphadenitis develops. The first degree of its severity is characterized by swelling of the tissues reaching the middle of the neck, the 2nd degree of lymphadenitis is characterized by swelling up to the collarbones. With the third degree of lymphadenitis, the edema extends to the chest.
Other symptoms that occur in a person, starting from the 3rd day of diphtheria, include: slurred speech, wheezing during breathing, sweet smell from the mouth.
If an antitoxic serum is administered to the patient on time, then it is most often possible to avoid his death. When there is no treatment, death cannot be ruled out. It happens due to the development of complications.
Diphtheria pharynx hypertoxic
This form develops in those children who have not been vaccinated against the disease. Hypertoxic diphtheria is characterized by a severe course and often causes death.
Symptoms of the disease develop from the first day. Body temperature rises to a critical 40 ° C. An intoxication symptom is accompanied by fainting, delirium, intense vomiting (it happens up to 40 times a day), convulsions.
A few hours after the jump in body temperature, the organs begin to work intermittently. Blood pressure drops sharply, and the heart beats very fast. Blood rushes to vital organs to keep them functioning. This applies to the lungs, brain and heart. The skin becomes pale, cold and tight.
A characteristic film appears in the mouth, its size varies. Most often it spreads to the pharynx, tonsils and the palate.
A person dies in the first 2 days from the development of the disease. The cause of death is heart or kidney failure. It is not possible to cope with the hypertoxic form of the disease, since there are no effective therapeutic methods.
Diphtheria pharynx hemorrhagic
The disease develops acutely, accompanied by the appearance of a film on the tonsils. Complications from the heart and blood vessels develop slowly, so a person dies 12-21 days after the onset of the disease. Despite the treatment received, it is often not possible to save the life of the patient.
A distinctive feature of the disease is the appearance of bleeding, which have different localization. They appear on the 3-5th day of illness. The film on the tonsils and the skin over the lymph nodes becomes purple in color, as it is saturated with blood.
Diphtheria of the nasopharynx, localized
With diphtheria, a person’s nasopharynx is not disturbed by pain during swallowing food. Difficulties in nasal breathing come to the fore. This is due to the fact that the film does not cover the tonsils, but the nasal mucosa, but it is impossible to see it on your own.
Since the nasopharynx is abundantly supplied with blood vessels, bacteria easily penetrate the systemic circulation and provoke intoxication of the whole organism. At the same time, the body temperature rises to 39 ° C, weakness increases, the head begins to hurt, appetite worsens.
Sometimes the symptoms of intoxication of the body appear first, and only then a diphtheria film is formed. The prognosis for recovery is favorable.
Localized croup
Diphtheria of the larynx has the worldwide name “localized croup”. The disease occurs no more often than in 0,5% of cases. It only develops in people who have not been vaccinated.
Intoxication of the body with this form of the disease does not occur, but the danger of pathology lies in other symptoms. As a result of damage to the larynx by pathogenic flora, it narrows, which affects the breathing process.
Stages of development of diphtheria croup:
catarrhal stage. The voice becomes hoarse, the body temperature rises to 38 ° C, a cough with sputum appears. These symptoms appear 1-2 days after infection.
Stenosis stage. The voice disappears, the person can only speak in a whisper. Cough dry, no sound, weakness worsens. The thorax is retracted in the region of the subclavian fossae and between the ribs in the jugular fossa. The skin becomes pale. These symptoms occur on the second day of the development of the disease. They can last from several hours to several days.
preasphyxic stage. Breathing becomes weak, the heart begins to beat faster, the patient’s anxiety increases. The chest in the areas described above is retracted even more. The patient sweats, the skin becomes very pale. This stage lasts no more than 2 hours. If the patient does not perform tracheal intubation, then he will develop asphyxia.
stage of asphyxia. A person cannot move, as the body suffers from hypoxia, fainting develops, the heart begins to beat less frequently, after which it stops altogether and the patient dies. The skin becomes bluish in color, the pulse is not heard, the chest remains motionless. This stage lasts about 2 minutes, maximum – 20 minutes.
Widespread croup
With a common form of diphtheria croup, not only the larynx, but also the trachea, as well as the bronchi are involved in the pathological process. Pathology has a severe course.
Symptoms of respiratory failure appear already in the first days from the onset of the disease, among them:
Shortness of breath that occurs even when the person is at rest.
Pale skin.
Shallow breathing with a frequency of 40-60 breaths per minute.
The heart starts beating fast.
Then the patient begins to cough. Together with mucus, films and blood come out of the respiratory organs. The person does not suffer from the symptoms of intoxication. Death happens quickly, in a few days. It is very difficult to cope with a common croup, the chances of survival are extremely low.
Complications

The toxic and hypertoxic form of diphtheria can lead to complications such as:
nephrotic syndrome. This condition does not pose a threat to the life of the patient. It is manifested by changes in blood and urine parameters. No other pathological symptoms accompany nephrotic syndrome. After a person recovers, nephrotic syndrome completely disappears.
Nerve damage.
Complication can occur in 3 ways:
Paralysis of cranial nerves (partial or complete). It is difficult for the patient to swallow food, he chokes on liquids, drooping of the eyelid and double vision are possible.
Polyradiculoneuropathy. Hands and feet lose their normal sensitivity, arms and legs may be paralyzed. Symptoms of nerve tissue damage will be completely stopped 3 months after recovery.
Damage to the heart muscle. If the first signs of myocarditis occur 1 week after the development of diphtheria, then the patient quickly develops heart failure. It often causes death. When myocarditis occurs 2 weeks after the onset of diphtheria, it is often possible to completely cope with the manifestations of the pathology.
In addition to these health problems, a person can develop anemia, which is a companion of the hemorrhagic form of the disease. It can be identified by the results of a blood test.
Diagnosis of diphtheria
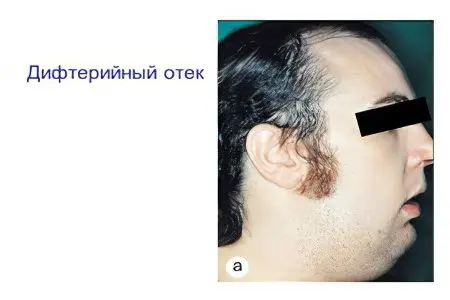
The first stage of diagnosis is the collection of anamnesis and examination of the patient. It is necessary to pay special attention to the condition of the cervical lymph nodes, as well as the presence of swelling of the neck. To do this, press on it with your finger for a few seconds, and then release it. If a hole appears in this place, which does not disappear immediately, then there is edema.
Investigations for which a person with suspected diphtheria is referred:
Donating blood for a general analysis. ESR and neutrophil levels increase significantly.
Urine for general analysis. This allows you to exclude kidney damage. The presence of a pathological process in the organs of the urinary system will be indicated by symptoms such as the appearance of protein in the urine, erythrocytes and renal cylinders.
Delivery of a smear from the nasopharynx. It is examined for the detection of bacteria in it. The results will be known after 5 days.
Conducting electrocardiography. This simple study allows you to evaluate the functions of the heart and detect deviations in its work in a timely manner.
Donating blood for biochemical analysis. Assessment of the functioning of the liver is carried out by the level of ALT, AST and bilirubin. urea and creatinine provide information about the state of the kidneys.
Blood index | Normal values |
AST | Up to 45 ME/l |
ALT | Up to 40 ME/l |
total bilirubin | 5,1-17 μmol/l |
Urea | 2,8-7,5 mmol/l |
Creatinine | Norm for a man: 74-110 µmol / l. The norm for a woman is 60-110 µmol / l. |
If required, the doctor will prescribe additional studies to the patient at his own discretion.
Diphtheria treatment

The sooner the antitoxic serum is administered to the patient, the better the prognosis for recovery. It is used in any form of diphtheria.
Antibiotics may not be used, but if the doctor deems it necessary, he may prescribe them. WHO recommends using a remedy called Josamycin for the treatment of children. Adults can take clindamycin. The frequency of administration and dosage is determined individually.
Be sure to direct efforts to remove intoxication from the body. To do this, intravenously administered physiological saline solution of sodium chloride or glucose. Hemodez or Reopoliglyukin can also be used. They are shown in the case when a person feels very bad.
If complications of the disease develop, then the therapeutic regimen is expanded. There are certain standards for the treatment of myocarditis and polyneuritis, which are sufficiently effective. However, the possibilities of medicine are still limited and severe forms of the disease with a pronounced intoxication syndrome can end in death.
Prevention of diphtheria
To prevent the development of the disease, it is enough to vaccinate the child on time. Two types of vaccines are currently used – DTP and ADM. They are highly effective and have a minimal set of side effects.
The DTP vaccine is administered at 3, 4.5 and 6 months. It is impossible to reduce the period between vaccinations, but it is permissible to slightly lengthen the interval. After the injection is made, you need to remain under medical supervision for half an hour. This is necessary in order to be able to get help if the child has an allergic reaction.
Another preventive measure that can reduce the likelihood of developing diphtheria is maintaining immunity at the proper level. In many ways, the health of the child depends on the parents. Therefore, it is necessary to be in the fresh air as often as possible, to temper, to give the child’s body physical activity. The baby must eat properly and fully.
Answers to popular questions

If a child once had diphtheria, can he get sick again? The chance of re-infection is 5%. The second time the disease will have an uncomplicated course.
Do I need to remove the film that forms in the mouth? No, it’s not allowed. After treatment, it will dissolve on its own. Under it, a fresh mucous membrane will be visible. If you remove it mechanically, then a wound will remain in its place, which will again be covered with a film.
Why do some patients develop a toxic form of the disease, while others develop a common one? It all depends on the state of the immune system of the child.
Vaccination is expensive, is it necessary to put it? On the Internet they write that it is ineffective. The DTP and DTP vaccine has proven effectiveness. The cost of one vaccination is 600-800 rubles. However, the funeral of a child will cost parents more. The chance of diphtheria in a child who has not received the vaccine is extremely high.
Are there any side effects from DTP? After the vaccine is given, the child’s body temperature may rise to 38 ° C, weakness increases. Redness and swelling appear at the injection site. This is where the side effects are limited.
Should an adult get the DTP vaccine? No, there is no such need. However, if you have contact with an infected person, you can get vaccinated. First you need to determine the level of antibodies to Corynebacterium in the blood.









