Contents
What is diffuse alopecia?
Diffuse alopecia – This is hair loss over the entire surface of the head, which occurs evenly. Pathology affects both men and women, but the weaker sex suffers from diffuse alopecia more often.
As for statistics, diffuse alopecia is less common than androgenetic. However, the analysis of modern publications indicates that recently there is a trend towards an increase in the incidence of diffuse alopecia among middle-aged women. Approximately 8% of women annually turn to medical and cosmetology institutions with this problem. It can be suggested that more people suffer from diffuse alopecia, since many of them do not seek medical help, considering hair loss to be a natural process. Most often, a trichologist is visited when there is a pronounced thinning of the parting, with the scalp clearly visible through the hair. In this case, pathological hair loss can be up to 1000 pieces per day, with a norm of 100 pieces. On average, the risks of experiencing diffuse alopecia throughout life are up to 1,7%.
According to current data, diffuse alopecia is an autoimmune disease that manifests itself in people with a genetic predisposition, as well as under the influence of exogenous triggers.
It is worth distinguishing between two types of diffuse alopecia – these are telogen and anagen. It is not advisable to classify androgenetic alopecia as a diffuse type of alopecia (although sometimes such theses are found in the literature of past years), since it differs in clinical and morphological characteristics: firstly, hair falls out in specific areas, and secondly, it occurs due to the excess content of androgens in the body and the processes associated with them. These differences are also mentioned in the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases.
Symptoms of diffuse alopecia
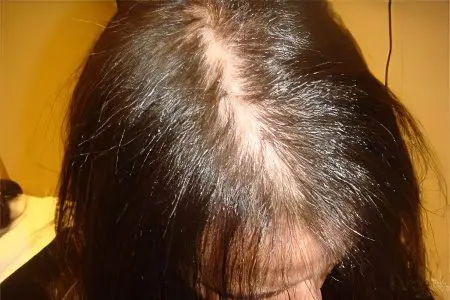
Diffuse alopecia is characterized by hair loss all over the head, among other symptoms:
The rods become brittle, weak. A little effort is enough to pull out the hair.
Hair fades, becomes unhealthy, confused. With increasing silicon content, they become wavy.
Hertog’s sign, when there is a parallel loss of eyebrows and eyelashes. This is especially often manifested due to hypothyroidism, syphilis and atopic dermatitis.
The parting becomes wider, as the disease progresses, the skin begins to shine through it. This is diffuse baldness in the form of a strip. Nest-type baldness can also be seen when the alopecia covers large areas. In any case, the hair falls out evenly.
It is impossible to consider the symptoms of alopecia separately from the main types of diffuse alopecia – anagen and telogen.
As for telogen alopecia, it can be acute and chronic. However, the complete loss of hair in any case will not occur. The acute phase lasts no more than six months, ends spontaneously due to therapeutic effects. Chronic telogen alopecia can disturb the patient for several years. It is characterized by severe and persistent hair loss that occurs in waves.
Anagen alopecia appears suddenly and is caused by the influence of chemical agents or radiation exposure. Hair begins to fall out, bypassing the resting stage. Baldness occurs suddenly, after an average of 2 weeks after the influence of the provocative factor: sometimes a week earlier, sometimes a week later. An example of such alopecia is hair loss during cancer therapy. The hairline, as a rule, has the property of self-healing, and they become stronger and healthier than those rods that have undergone loss.
Causes of diffuse alopecia

The etiological factors that affect the development of the disease can be as follows:
Transferred infectious diseases. After suffering a severe fever caused by a particular disease (especially with recurrent and prolonged course), after an average of 2 months, hair loss may begin. Damage to the follicles occurs in the same phase of their cyclic activity. Infections that can provoke diffuse alopecia: syphilis, tuberculosis, typhus, brucellosis, mononucleosis, influenza, pneumonia, malaria. Alopecia also develops against the background of progressive HIV infection.
Taking medications in high doses, it can cause anagen baldness. taking low doses of drugs can cause telogen effluvium. The danger is represented by the means included in these 7 groups: anticoagulants, antiparkinsonian drugs, retinoids, α-blockers and H2-receptor blockers, anticonvulsants and cytostatics.
Deficiency of nutrients, macro and micro elements, as well as vitamins. It is not only iron deficiency anemia known to most people that negatively affects the condition of the hair follicles. Lack of selenium and silicon leads to hair loss (without them, hair breaks, becomes thinner), zinc (without it, hair grows poorly), chromium, proteins, B vitamins. In this regard, protein-free diets are especially dangerous. The reaction of hair to the lack of this element will be instant: the rate of their growth will decrease, the rod will decrease in diameter. In addition to a protein-free diet, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, malabsorption syndrome, enteropathy, and metabolic disorders can lead to its secondary insufficiency. In addition, studies were conducted that made it possible to establish that all children suffering from diffuse alopecia have a selenium deficiency, and the ratio of manganese, copper, iron, potassium and zinc is also disturbed.
Chronic diseases One of the common causes of hair loss is the pathology of the endocrine glands, in particular hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. The danger in terms of the development of diffuse alopecia is lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, erythroderma and other pathologies.
Psychosomatic disorders. So, stress, surgical interventions, accidents lead to baldness. Scientists associate the increase in cases of baldness during wars with psychosomatic problems.
If the cause of diffuse alopecia could not be identified, then we speak of idiopathic chronic alopecia. However, there is evidence that patients with complaints of diffuse hair loss actually suffer from androgenetic alopecia, since after a thorough diagnosis, 40% of them had a high level of androgens in the serum part of the blood.
Treatment of diffuse alopecia
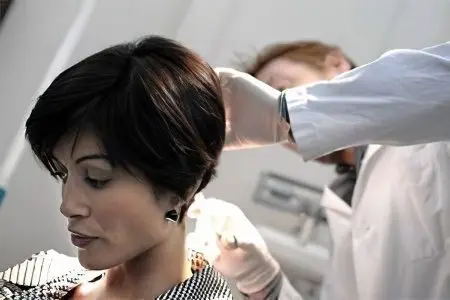
When a patient complains of hair loss, he will need to undergo a traditional examination scheme. Diseases of the central nervous system, thyroid gland, liver, adrenal glands, ovaries should be excluded, the state of the immune system, etc. should be assessed. As a result of complex diagnostics, the cause of hair loss is identified, and further baldness therapy is based on the results obtained.
Most often, treatment begins with the appointment of external agents. For this, patients are recommended to use balms, masks, gels containing zinc, alcohol, ether.
At this stage, the following drugs are recommended for patients inside:
Zinc in the composition of multivitamin complexes;
Injections of vitamins of group B – B1, B12, B6;
Vitamins PP, A and C orally.
If the ongoing therapy is ineffective, then trichologists recommend other, stronger means for treatment – Aminexil, Minoxidil, Tricosaccharide. So, Minoxidil is a drug for getting rid of androgenetic alopecia, in relation to which it shows the maximum effectiveness. However, we should not forget about the available data regarding the increase in the level of androgens in the blood serum in women with diffuse alopecia. Therefore, in 40% of cases, this drug can help in the treatment of this form of baldness.
In order to stimulate hair growth, trichologists in some cases recommend taking plant-based preparations. Among these: Beroxan, Psoberan, Ammifurin are photosensitizing agents that are prescribed only by a doctor. It is important to remember that the treatment of baldness with these drugs should be carried out not only taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and his sensitivity to the components included in their composition, but also taking into account the time of year.
If baldness was provoked by the intake of certain medications or radioactive exposure, then after the elimination of the provocateur factor, the hair begins to grow again. No specific treatment is required in this case. It is only possible to comply with general preventive recommendations regarding proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
Here is a list of the most popular treatments:
The best shampoo for hair restoration and growth
Medical treatment of alopecia (full list of drugs)
Minoxidil for hair loss
Finasteride for hair loss
Hair transplant: answers to basic questions
It is important to review the diet with a predominance of liver, seafood, cereals and cereals, mushrooms, it is important to exclude coffee and alcohol, since their intake is not combined with drugs used to treat alopecia. The diet must be balanced, the exclusion of any component from its scheme is unacceptable. The emphasis should be on products that can enrich the body with B, A, PP, C vitamins, iron, selenium, magnesium and zinc. It is always worth remembering that the nutrients contained in food are absorbed by the body much better than their vitamin supplements and complexes.
Often, patients with alopecia require the help of a psychologist and psychiatrist, even when the disease is not associated with psychosomatic problems. This is due to the formation of a sense of inferiority and a decrease in self-esteem as a result of a developed cosmetic defect. Therefore, in addition to conversations and trainings, sedatives are prescribed for the recovery period, for example, Novopassit, Persen and others.
So, the diffuse form of alopecia is a disease that has a multifactorial nature. It is based on a polygenic system, which is due to both hereditary predisposition and exogenous trigger factors. In this regard, the prognosis for recovery depends on whether it was possible to determine the true cause of the disease, which is not always possible.
Author of the article: Herman Olga Leonidovna, trichologist, specially for the site ayzdorov.ru









