Contents
- Proven content
- Dexamytrex – composition
- Dexamytrex – indications
- Dexamytrex – contraindications
- Dexamytrex – side effects
- Dexamytrex – dosage
- Dexamytrex – precautions
- Dexamytrex – side effect
- Dexamytrex – Price
- Pharmachologic effect
- Method of application and dosing regimen
- Overdose
- Precautionary measures
- Use during pregnancy and lactation
- Influence on the ability to drive a car and potentially dangerous mechanisms
- Interaction with other drugs
- Storage conditions
- Best before date
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of Healthy-Food makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Dexamytrex is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial eye conditions. The preparation is applied topically. Dexamytrex should not be used in case of hypersensitivity to any component of the drug. It should also not be used for more than 3 weeks. Long-term use can lead to glaucoma.
Dexamytrex is a topical antibiotic. It is composed of gentamicin. In some cases, Dexamytrex may cause a slight temporary burning sensation in the eye. Check when it is worth reaching for Dexamytrex.
Dexamytrex – composition
The active substance of the antibiotic Dexamytrex is gentamicin, which has antibacterial properties, and dexamethasone, which has anti-inflammatory properties. The preservative is cetrimide.
Dexamytrex – indications
The indication for the use of Dexamytrex is the treatment of bacterial eye infections with inflammation at the same time. The drug is active against gentamicin-sensitive bacteria. They trigger, among others:
- bacterial conjunctivitis;
- keratitis without damaging the corneal epithelium;
- allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva.
The antibiotic is applied topically. The gentamicin contained in the antibiotic Dexamytrex inhibits the synthesis of bacterial proteins. In turn, dexamethasone, a corticosteroid, has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties. In addition, this substance fights exudate.
Dexamytrex – contraindications
Hypersensitivity to this group of antibiotics is a contraindication to the use of Dexamytrex. The drug should not be used for more than 3 weeks as resistance may develop. In addition, the drug can not be used in the case of:
- infections of the cornea of the eye with herpes viruses;
- tuberculous or fungal infections of the eye;
- ulcer or wounds on the cornea;
- acute purulent infection of the anterior segment of the eye;
- glaucoma (narrow and open angle of filtration).
Dexamytrex – side effects
Among the side effects, there is a burning sensation in the eye that occurs in some patients.
Dexamytrex – dosage
Dexamytrex antibiotic should be used 4 to 6 times a day, 1 drop directly into the conjunctival sac.
Dexamytrex – precautions
Dexamytrex should only be used topically and topically into the conjunctival sac. Treatment with Dexamytrex must be under the supervision of an ophthalmologist. The drug used for a long time may lead to an increase in intraocular pressure, glaucoma, damage to the optic nerves, acuity disturbances and visual field limitation. Subcapsular cataracts may also appear.
Intraocular pressure should be monitored regularly during treatment with Dexamytrex. You should also not wear contact lenses. Immediately after administration of the drug, visual disturbances may occur which may affect the safety of driving and operating machinery.
The use of Dexamytrex during pregnancy should be consulted with the attending physician. The drug should not be used during breastfeeding.
In the event of using other eye preparations, a distance of min. 15 minutes.
Dexamytrex – side effect
Mild and short-term knowledge problems may arise while taking Dexamytrex. If the preparation is applied to a wounded cornea, wounds may take longer to heal. As a result of long-term use, e.g. glaucoma may appear. There are also cases of pupil dilation.
Dexamytrex – Price
Dexamytrex costs about 10 USD.
Before use, read the leaflet, which contains indications, contraindications, data on side effects and dosage as well as information on the use of the medicinal product, or consult your doctor or pharmacist, as each drug used improperly is a threat to your life or health.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VZynHzxFSQM
Pharmachologic effect
Method of application and dosing regimen
After reducing inflammation, Dexamethasone eye drops are instilled 1-2 drops into the conjunctival sac 3-5 times a day.
Recommendations for the use of dropper tubes:before using the drug, remove the protective cap from the dropper tube, cut off the membrane of the neck of the body with scissors without damaging the threaded part. Turn the body of the tube-dropper with the drug neck down and gently press the body of the tube-dropper, using it as a pipette. To avoid infection of the contents of the dropper tube, do not touch the open tip of the tube to the eye or any other surface. If, for any reason, a drop of the drug immediately after instillation flows out of the conjunctival sac, it is necessary to repeat the instillation again. After using the dose recommended by the doctor or indicated in the instructions for medical use of the drug, turn the body of the dropper tube with the threaded part up and screw on the protective cap.
Before instillation of drops:
• wash your hands thoroughly;
• take a comfortable position (sit down, lie on your back, stand in front of a mirror).
Application of eye drops:
1. Open the vial. To avoid contamination of the contents of the bottle – do not touch the tip of the bottle to the eyelids, eyelashes and do not touch it with your hands.
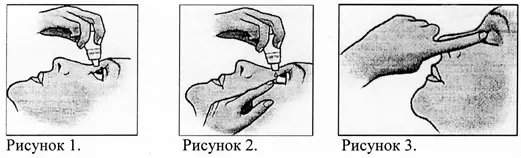
2. Tilt your head back. Place the vial over the eye (Figure 1).
3. Pull the lower eyelid down and look up, squeeze the vial lightly and place the eye drops into the eye (Figure 2).
4. Close the eye, lightly press its inner corner with your finger for 1 minute. This will increase the effectiveness of the drops and reduce the risk of adverse systemic side effects (Figure 3).
Close the vial tightly.
If you forget to take Dexamethasone eye drops, it is not recommended to take a double dose to make up for the missed one. If you have any
questions about this drug, you should consult your doctor.
Overdose
Treatment: the drug should be discontinued and symptomatic therapy prescribed. There is no specific antidote.
Precautionary measures
Before starting treatment with dexamethasone, make sure that the eyes are not infected.
Cases of corneal perforation have been described with topical application of corticosteroids in diseases that cause thinning of the cornea or sclera.
Corticosteroid therapy may mask an ongoing bacterial or fungal infection. In the presence of infection, the use of drops should be combined with appropriate antimicrobial therapy.
Fungal infections should be suspected in patients with persistent corneal ulceration who are using or have used drugs with corticosteroids. In the event of a fungal infection, drug therapy should be discontinued.
Do not use the drug for more than one week. If more prolonged use of dexamethasone is necessary, the patient should be under the supervision of a physician. Long-term use of topical ophthalmic corticosteroids can lead to glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, decreased visual acuity, visual field defects, and subcapsular cataract formation. Patients receiving long-term corticosteroid therapy should regularly monitor intraocular pressure and the condition of the lens, especially patients at high risk of developing glaucoma. Such patients may require dose adjustment of dexamethasone. Long-term use of the drug may increase the risk of developing a secondary eye infection.
Topical application of corticosteroids in ophthalmology may delay the healing of corneal wounds.
Contact lenses should not be worn during treatment with corticosteroid eye drops due to an increased risk of infection.
Systemic absorption can be reduced by squeezing the lacrimal sac in the medial angle for a minute after instillation of drops (this prevents dexamethasone from penetrating through the nasolacrimal canal to the extensive absorption surface of the nose and pharyngeal mucosa; especially recommended in children).
Excipients
Dexamethasone contains the preservative benzalkonium chloride, which can be absorbed by soft contact lenses and cause discoloration and adverse effects on eye tissues.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Influence on the ability to drive a car and potentially dangerous mechanisms
Interaction with other drugs
The risk of increased intraocular pressure associated with long-term corticosteroid therapy is increased by the concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs, especially atropine and related compounds, in patients predisposed to anterior chamber angle closure.
The risk of corneal opacification is more likely in patients with weakened corneas who are receiving concomitant phosphate-containing eye preparations.
The following drug interactions are possible but are of very low clinical significance when using Dexamethasone Eye Drops.
The therapeutic efficacy of dexamethasone may be reduced by phenytoin, phenobarbital, ephedrine, and rifampicin.
Glucocorticoids may increase the need for salicylates.
If more than one topical ophthalmic medicinal product is used, then the medicinal products must be applied with a time interval of at least 5 minutes.
Eye ointments should be applied after applying eye drops.









