Contents
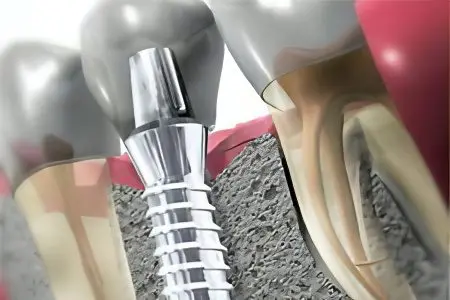
Dental implants – these are artificially created structures, consisting of several components, designed to be inserted into the intramaxillary bone tissue. Subsequently, the implant fuses with bone tissue (the process of osseointegration) and prosthetics are performed using a crown, bridge or other type of prosthesis. An implant is an artificial replacement for lost teeth.
Modern dentistry offers the patient a choice, as there are many types of implants.
However, they all have approximately the same structure and consist of the following components:
The head or abutment is located above the neck and is necessary for fixing various designs of dental prostheses on it. Abutments can be twisted and lockable.
The neck is located between the body and the head of the implant and is in direct contact with the gingival mucosa.
The body is inserted into the bone tissue and serves as a base for fixing the head and neck of the implant. The body is the infrastructure of the implant; it can be presented as a solid plate, as a plate with holes, as a self-tapping or screw cylinder, as a machine tool or a tape.
The gingiva former is a type of abutment. It looks like a screw with a cylinder head. The shaper is screwed in for a while and serves to give the gum an attractive and natural shape. It is also called a healing support, healing, gingival cuff.
Types of dental implants
The types of dental implants are as follows:
Endosseous implants or lamellar intraosseous. Lamellar intraosseous implants are most often installed in those patients who have thin bone tissue. In this regard, they do not have the opportunity to implant the screw of a traditional implant. The endosseous implant looks like a thin plate, which subsequently becomes the base for the installation of the abutment and the prosthesis. The doctor bends it so that it fits under the patient’s jaw. To increase reliability, such an implant is implanted deep into the bone tissue.
The advantages of installing a plate implant are as follows:
Low price for a lamellar implant compared to classic root-shaped implants.
No need to increase bone tissue.
Disadvantages of installing an endosseous implant:
Less reliable compared to root implants.
The complexity of the installation procedure.
The inability to withstand heavy loads while chewing food, which requires some caution from the patient. The same factor determines the unreliability of the implant and their weak stability.
Due to the fact that the reliability of plate implants suffers, they are installed only if indicated.
Root implants. The peculiarity of root implants is that their design is as similar as possible to the natural root of the tooth, which is the reason for their name. Root implants, in turn, can be cylindrical and screw.
Cylindrical root implants have a porous surface, which allows bone tissue to grow deep into the implant, forming a reliable grip. There is no thread on such implants, so the area of contact between them and the bone is small compared to the screw design. Cylindrical implants are most often designed for classical implantation, so the process of their implantation can take up to six months.
Screw implants are the most common. They are equipped with a thread that is firmly attached to the bone hole. Implants are literally screwed into the bone, for which it must first be drilled. If there are no contraindications, then specialists always prefer this particular type of implants, since their main advantage is reliability and a high degree of survival.
subperiosteal implants. This type of implant is implanted under the gum with attachment to the jawbone. The implant is simply placed on the bone, no drilling is required. The design is openwork, thin, more massive compared to classic implants.
There are two methods for installing such an implant. The first is to take a cast from the jaw bone. To do this, the periosteum is carefully separated from the bone and its imprint is made, according to which the implant is subsequently made. Then it is installed, and the soft tissues are sutured.
The second method is more technological. So, to remove an imprint from the bone surface of the jaw, there is no need to make an incision. It is enough for the patient to undergo the procedure of computed tomography, according to the results of which a metal structure will be made.
The advantages of subperiosteal implants include:
The possibility of installation for those patients who have thin bone and for some reason they do not have the opportunity to build it.
They can be installed even for those people who have severe atrophy of the alveolar process, which greatly expands the possibilities of fixed prosthetics.
The disadvantages of installing subperiosteal implants include:
The design is less reliable compared to screw implants implanted into the jaw bone.
The complexity of manufacturing and planning the design.
High failure rate.
Endodontic stabilized implants. This type of implant is placed in order to strengthen your own loose tooth. They are not used when it is completely lost, since implantation takes place directly in the root of the tooth, through which the pin is screwed. The term endodontic means intradental.
These implants are designed to strengthen loose and severely damaged teeth. However, a prerequisite for its installation is the presence of at least 3 mm of healthy periodontium around the tooth root. Otherwise, it will not be possible to achieve reliable fixation of the tooth.
The advantages of such implants are:

No need to perforate the gums and mucous membranes.
Preservation of one’s own tooth.
One-step approach to treatment. That is, the implant is installed in one visit to the dentist’s office.
The installation technology is simple and fairly painless for the patient.
The implant allows not only to strengthen the root of the tooth, but will also serve as a crown in the future.
The chewing load is evenly distributed on the root of one’s own tooth without leading to atrophy of the bone tissue.
There are practically no drawbacks to the procedure, except that it is necessary to contact the dentist’s office in a timely manner, until the periodontal remains at least partially healthy.
Combined implants. Combined implants can differ greatly from each other in design, as they are made for each individual patient on an individual basis.
The following types of combined implants can be distinguished:
Traditional or lamellar. It is a combination of a root and lamellar implant and looks like a thin plate on which a screw is located in the middle. This is an intraosseous implant, which is recommended for installation with severe atrophy of bone tissue in the lower jaw (its height should not be less than 6 mm, and the thickness of the alveolar process should be less than 3 mm).
Disk. It can be installed in almost any jaw bone, since the degree of its atrophy does not matter in this case. Disc implants quickly take root, they can be attached to the prosthesis after a week.
Transosseous or clinical. These implants are placed through an incision made in the chin. They are recommended for use when the atrophy of the lower jaw is extremely pronounced.
Combined implants are widely used in modern dental practice. They are used when classic root-shaped implants cannot be installed. This is their main advantage.
intramucosal implants. Intramucosal implants are designed for those patients who have removable dentures in the upper jaw, but suffer from its excessive mobility due to atrophy of the alveolar process.
The intramucosal implant has two parts: one of the parts is attached to a removable prosthesis, and the second is implanted into the oral mucosa. For their adhesion, designs are used that, in their structure, resemble clothes buttons.
The advantage of such implants is that for their installation there is no need to have bone tissue of a certain thickness. However, the mucosa should not be thinner than 1,1 mm. Intramucosal implants allow you to stop worrying about the fact that a removable prosthesis will be unreliably fixed and fly off during its use. They also provide an opportunity to get rid of possible speech and taste disorders that could be caused by wearing removable dentures.
Mini implants. Mini-implants are their main distinguishing feature are small in size. They are represented by thin screws and a removable prosthesis. There are practically no contraindications to their installation, they are implanted into the gum bone. The purpose of such implants is to maintain a removable prosthesis, which is installed on them.
Their advantages:
Removable prosthesis on mini-implants will be securely fixed.
It is possible to install a prosthesis even in the complete absence of teeth.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and does not take much time (from 30 minutes to 1 hour 30 minutes).
The prosthesis can be installed immediately after implantation of the implants.
You can chew with implants on the same day.
The minimum set of contraindications.
There is no need to increase bone tissue.
No age restrictions.
Low cost compared to classical implantation.
Although these implants do not need to be removed, they must be cleaned regularly and with great care. The disadvantage of mini-implants is that permanent prostheses cannot be placed on them, as they are not designed for high loads.
How are dental implants placed?
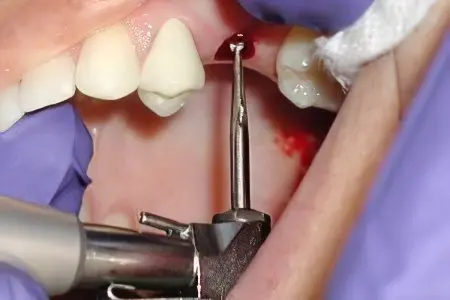
You can learn about how dental implants are placed in the dentist’s office, since depending on the specific situation, this procedure will vary. Some methods make it possible to install them without incisions in the gums, other methods allow you to implant the implant immediately after tooth extraction, etc.
However, in general, the procedure of dental implantation is reduced to five successive stages:
Definition of indications and contraindications for the procedure. To do this, the doctor fully examines the patient, prescribes the delivery of the necessary tests. At this stage, all possible diseases that may be an obstacle to implantation should be identified. It is important to pay attention not only to the state of the oral cavity, but also to the state of the organism as a whole. Blood is given for sugar, hepatitis, HIV, X-ray examinations are performed.
If there are no contraindications, then you can proceed to the second stage, which consists in preparing for implantation. At this time, it is necessary to cure all diseased teeth, replace old crowns, get rid of gum disease, etc. After that, the doctor directs the patient to undergo computed tomography and to perform a panoramic X-ray of the jaw. This allows you to identify the presence or absence of hidden diseases, such as granulomas or cysts. The pictures also provide an opportunity to choose the best place to place the implant.
The surgical intervention is performed in the third stage. If there is a lack of bone tissue, if its mass is insufficient, then an open or closed sinus lift procedure is performed. This allows you to increase the gingival bone. The extension procedure itself lasts up to several hours, and the engraftment process can take three or more months. However, if the patient does not want to build up the bone, some types of implants allow this procedure to be dispensed with. The process of surgical implantation itself is reduced to making an incision or puncture of the gums with the subsequent implementation of the structure. After that, a plug is placed on the implant, and the gum is sutured. The engraftment process takes up to six months, although some techniques can reduce this time to several days.
The penultimate stage is the installation of the abutment. A prosthesis will be attached to this element. 14 days before its installation, a temporary gum shaper is built in, giving it the desired shape.
The final stage of the dental implantation procedure is orthopedic. At this time, the manufacture of a tooth or bridge takes place, their color is selected, a prosthesis is made and installed. This may take up to several hours. Immediately after the installation of the prosthesis, the patient can return to their usual way of life and start chewing food with the help of new artificial teeth.
This sequence of actions is common to all implantation techniques. This scheme must be followed by all dentists practicing in implantology.
Answers to popular questions:

How long do dental implants last? No specialist can say exactly how long dental implants last, since this indicator is influenced by many factors, ranging from correct installation to proper care of implants. On average, the guaranteed service life of an implant is from 5 to 10 years, although there are cases when they served without replacement for 15 years or more.
How much does 1 dental implant cost? The price of an implant depends on the manufacturer, the material from which it is made, as well as the complexity of the work. If we calculate the average price for the implantation of one tooth, then it will vary from 12 to 000 rubles.
Is prosthetics on implants possible in the complete absence of teeth? Prosthetics on implants in the complete absence of teeth is possible.
There are several methods of implantation:
«all-on-4»;
full implantation with implantation of 12-14 implants in both jaws and subsequent prosthetics with dental crowns;
it is possible to install a bridge prosthesis on implants supported by artificial teeth;
removable prosthetics using mini-implants;
installation of a removable prosthesis with implantation of a minimum number of implants.
Does it hurt to put a dental implant? The implant installation process itself is painless for the patient, as it is performed under the influence of local or general anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the operation. However, soreness is an inherent sensation in the postoperative period, when the action of anesthesia is completed. Such pains will normally disturb the patient for no more than five days and should respond well to traditional analgesics.
How long does a dental implant take? The surgical phase of the implant placement procedure will vary on average from half an hour to 1 hour and 30 minutes. This time will be enough for the dentist to implant the artificial root into the prepared bed.
Is an implant placed immediately after a tooth extraction? Immediately after tooth extraction, an implant can be placed thanks to the one-stage implantation technique. However, for this it is necessary to pass a qualitative preliminary examination.
Contraindications to the installation of dental implants

Any surgical intervention, including dental implantation, has its own contraindications. However, not all of them are absolute, that is, some of them can be eliminated with the help of the therapy, some are temporary, etc.
Absolute contraindications to the installation of dental implants:
Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs. It will be impossible to perform the operation, for example, in case of a violation of blood clotting, as this threatens the development of bleeding.
Acquired and congenital diseases of the central nervous system: depressive mood of the patient, psychosis, hypochondria, psychopathy. In the presence of such diseases, patients are often unable to adequately perceive information regarding the rules of conduct during and after treatment.
The presence of a malignant oncological formation. In this case, the prohibition is due to the fact that any surgical intervention can affect the growth and development of the tumor.
Diseases of the immune sphere. In this case, the ban is due to the fact that implantation, as a surgical intervention, will require enhanced immunity, which is impossible.
Connective tissue pathology. After the process of implantation, the implantation will require enhanced formation and growth of the connective tissue around it. The body will not be able to fully start this process in the presence of such diseases as: systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, rheumatoid disorders, etc.
Tuberculosis, gonorrhea, AIDS and other seropositive infections, as well as complications caused by them.
Diseases of the oral mucosa: aphthous stomatitis, prone to relapse, pemphigus, lupus erythematosus, Sjögren’s syndrome and some others.
Diabetes mellitus of the first type.
Bruxism and hypertonicity of the muscles responsible for chewing.
Increasing the size of the tongue.
Relative contraindications that can be reviewed when certain conditions are created are:
Unsatisfactory condition of the oral cavity, for example, the presence of carious teeth.
Poor compliance with the rules of oral hygiene.
Infectious and non-infectious gingivitis.
Inflammatory process in the tissues surrounding the teeth (marginal periodontitis).
Diseases of the temporomandibular joint.
Violations of the structure of the alveolar process or severe atrophy of bone tissue.
Abuse of bad habits, in particular, smoking, alcoholism and drug addiction.
The period of bearing a child and the period of breastfeeding.
In addition, there are general contraindications in a separate row, including:
General surgical provisions that are the basis for refusing to perform a surgical procedure.
Intolerance to painkillers.
Some general somatic diseases that can progress during implantation, for example, heart disease, endocarditis, rheumatic diseases, etc.
The passage of therapy with immunosuppressants, anticoagulants, cytostatics and other drugs.
Cachexia.
Less than a year after exposure.
Postoperative rehabilitation period.
The patient’s age is over 55 years.
Exacerbation of any chronic diseases.
The presence of a metal endoprosthesis.
Author of the article: Muravitsky Boris Viktorovich, dentist, specially for the site ayzdorov.ru