Contents
Skin diseases most often deliver only cosmetic discomfort to a person. They rarely pose a serious threat to life. It is to such diseases that demodicosis belongs. Any parts of the body that have sebaceous glands can be affected by this pathology. In this case, the internal organs will not be affected by the infection. Despite the fact that demodicosis does not pose a threat to life, it should be treated immediately after detection.
The disease negatively affects the appearance of a person, as a result of which his self-esteem decreases. He begins to close himself off from people, becomes nervous and quick-tempered. To cope with the disease, you need to consult a doctor, confirm the diagnosis and undergo the prescribed therapy.
What is demodicosis?

Demodecosis – This is a skin lesion with a microscopic mite. This tick is called Demodex. The demodex mite lives in the sebaceous glands, in the hair follicles, for this reason, the places of its distribution are the eyelids, facial skin, the superciliary arches, forehead, nasolabial folds and chin, and the external auditory canal. Places with abundant sebaceous secretion are most favorable for ticks to live. Demodex mites can also live in the body of a healthy person – in the skin, feeding on dead cells. However, in order to penetrate into the deeper layers, they need to wait for the weakening of immunity, after which they cause an inflammatory process.
Demodicosis in its manifestations is very similar to rosacea and acne. Very often, these diseases are combined, because acne vulgaris and rosacea suppress the skin’s natural defenses.
In their naivety, people do not even assume such a neighborhood, although a malfunction occurs in the body, and ticks “attack”.
Men suffer from demodicosis twice as rarely as women, and women with white, delicate skin. The reason for the development of this disease can be: a malfunction of the endocrine and digestive systems, stress, decreased immunity, and sometimes the use of expensive cosmetics with hormonal or other biological additives. A peaceful life with a tick can be disturbed by excessive consumption of black coffee, alcohol, spicy spices, prolonged exposure to a computer, frequent visits to a bathhouse or a solarium.
If it were possible to look into the hair follicles from which hair grows, or into the glomeruli of sebaceous glands located right there, then one could see small colorless, bristle-covered “worms”. This is exactly what mites from the Demodex family look like.
The tick is very easy to detect in the laboratory, carried out directly in the presence of the patient in the office. To do this, take 8 cilia from each eye – four from the upper eyelid, the same number from the lower. These cilia are placed on a glass slide by dropping an alkaline solution or a mixture of 1 ml of glycerol and 9 ml of saline. Then cover with a blanket and examine the cilia under a microscope.
Who is the causative agent of demodicosis?
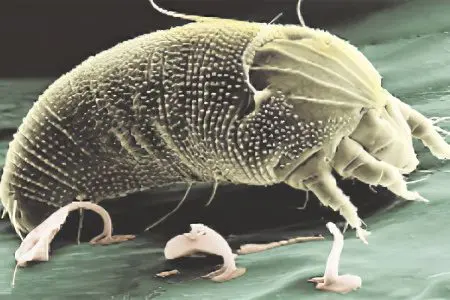
Demodicosis provokes a tick. This microscopic organism is called Demodex folliculorum/brevis (D. folliculorum/brevis). The tick parasitizes in the sebaceous glands of a person, in which there are favorable conditions for its reproduction. From animals, a person cannot become infected with a tick, it is transmitted only among a population of people. Ticks live on the skin of dogs and cats, but they cannot exist on the human body.
The tick has sufficient mobility for a microscopic organism. It can move at a speed of 13-18 mm/hour. It is not difficult for him to move across the skin and conquer new “habitats” of habitat. Moreover, ticks migrate all the time and in large quantities, but it is impossible to notice their movements without a microscope. Therefore, it is very easy to become infected with demodicosis, it is enough to use the household items of an infected person or to be in close contact with him. The tick will quickly find a sebaceous gland and master it. It will exist in it until the patient receives treatment.
The tick can settle on the eyelids, in the armpits, in the perineum, that is, in those parts of the dermis where there are sebaceous glands. Therefore, the characteristic symptoms of infection will appear in these places. The optimal temperature for the existence of a tick is 37-40 ° C. It actively increases its population in hot climates and in warm rooms. In such conditions, demodicosis manifests itself especially intensively.
Who can get demodicosis?

According to statistics, by the age of 30, about 60% of the population is infected with a tick. In this case, the symptoms of the disease will appear only in some individuals. The parasite is activated when the human immune system fails. Tick infestation does not cause allergies or tissue damage if the body inhibits its activity.
In people whose immune system is weakened, or there is a genetic tendency to hypersensitive reactions, demodicosis will manifest characteristic symptoms.
The following categories of citizens are at risk:
People with immunodeficiency pathologies, for example, diabetes mellitus, HIV, tuberculosis, cancerous tumors.
People whose close relatives are infected with a tick and suffer from severe symptoms of pathology.
People who are regularly exposed to stressors.
People prone to allergic reactions.
People working in hazardous enterprises.
In such patients, demodicosis manifests itself brightly.
The first signs of demodicosis

acne, acne vulgaris, rash, rosacea, pustules, sores, etc., appearing on the face, may indicate the presence of demodicosis. When neglected, these pimples cover the skin of the back, chest and thighs;
red spots on the face;
very oily skin and enlarged pores. The areas affected by demodicosis look moist, greasy, and have a characteristic sheen. The skin on the nose and cheeks is especially affected;
skin of the face is bumpy. Rough “scar” tissue and many small calcium clots form inside the skin, and this gives an unhealthy complexion and bumpy skin;
the nose increases in size, it happens that it is quite strong: the nose becomes like a large blue-red plum (rhinophyma);
feeling of crawling, slight tickling and itching. Very often, people do not pay attention to tickling at all, but scratch themselves automatically. By evening, the itching becomes stronger and continues to disturb throughout the night. This indicates the most active activity of ticks and the time of their mating.
the scalp itches, hair loss occurs. Early baldness can also talk about the vigorous activity of the demodex mite;
itchy eyelashes. Loss of eyelashes is also most often the result of the vital activity of the demodicosis mite, which lives in the roots of the eyelashes. At the base, the eyelashes begin to itch, the eyelashes become thinner and fall out;
itching of the ears
Symptoms of demodicosis
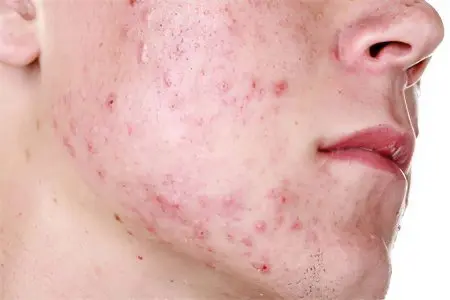
Almost any area of the skin, with the exception of the feet and hands, can be susceptible to infection. Demodicosis of the eyelids can cause severe eye allergies, which exacerbates the symptoms of the lesion. This disease is called ophthalmodemodecosis.
Risk factors that can lead to the activation of the disease:
Temperature changes. Therefore, demodicosis often makes itself felt in autumn and spring.
Weakening of the immune forces of the body. This happens as a result of the influence of stress factors, chronic diseases, taking hormonal steroid drugs, etc.
Violation of the rules of personal hygiene. At the same time, the sebaceous glands become clogged, which causes active reproduction of the tick.
Alcohol abuse, smoking.
Symptoms appear first of all in those parts of the body where there is a large accumulation of parasites. Localization of ticks can be the body, eyelids and eyes.
Damage to the skin
Blockage of the sebaceous gland cannot occur asymptomatically. Often, signs of demodicosis occur on the face, on the back and in the armpits (or popliteal fossae). In these parts of the body, the maximum number of parasites accumulates.
Symptom | Causes | Exterior changes |
Redness of the affected area | Fat stagnates in the gland, and ticks provoke an inflammatory reaction. Seal on the skin appears due to the fact that neutrophils (cells of immunity) arrive at the site of inflammation. | In the area inhabited by the tick, red spots appear that have an irregular shape. The more active the pathological process, the larger the spots will be. As they merge, one large spot is formed. |
Thickening of the dermis | The seal is in the area of inflammation and can be palpated. | |
Itching | Itching is aggravated by being in warm rooms, in the heat, if the rules of hygiene are not observed. On a permanent basis, he does not bother a person. | |
The appearance of nodules or vesicles | The exit of the sebaceous gland is clogged with parasites, so the fat will have nowhere to go. It accumulates in the duct of the gland, due to which a bubble forms. | Nodules are represented by dense formations that are small in size. They rise slightly above the surface of the dermis. Bubbles look the same as nodules, but they are denser and more elastic in consistency. Their contents are visible through the skin, which can be transparent or yellow. Less commonly, these nodules have a reddish color. |
peeling skin | A chronic focus of inflammation leads to the fact that the horny scales of the dermis begin to exfoliate faster. | There are many scales, their size is 1-2 mm. Some of them stick to the skin, others fall off when scratched. |
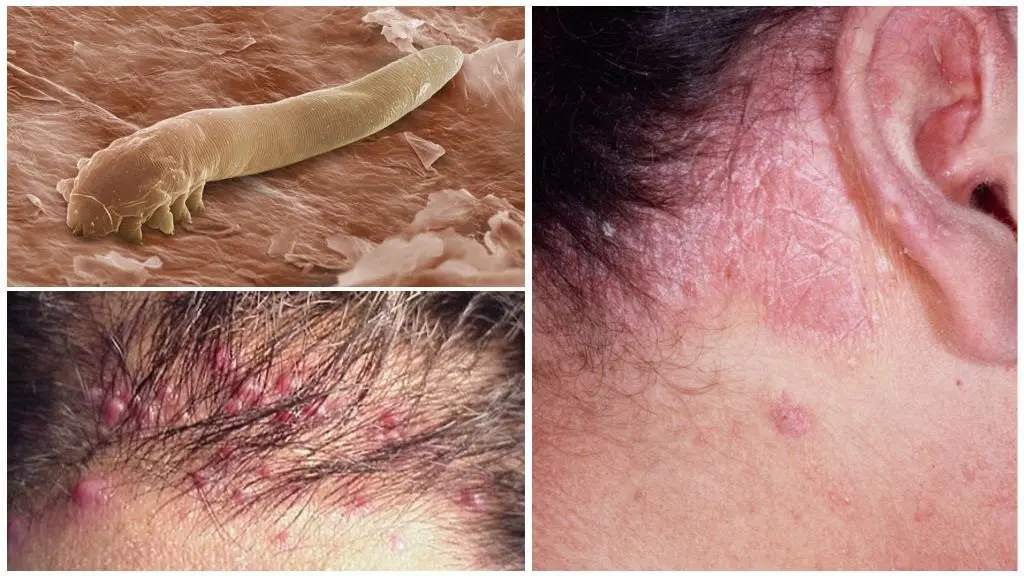
After a person has the first symptoms of demodicosis, he becomes dangerous to the people around him. The tick is transmitted even with a normal touch. However, the presence of a parasite in the sebaceous gland does not always lead to the development of the disease. In order for its symptoms to appear, provoking factors must act on the body.
Symptoms of blocked meibomian glands
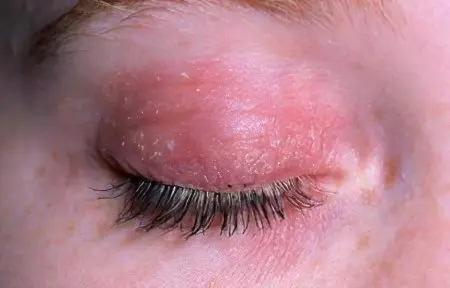
Blockage of the meibomian glands by parasites is called blepharitis.
Symptoms of blepharitis against the background of demodicosis are:
Redness.
Peeling skin.
Sealing of the eyelid and the formation of a crust on it. If you try to remove it, the person will experience pain.
The appearance of white growths on the eyelashes, the so-called “clutches”. They are represented by exfoliating skin.
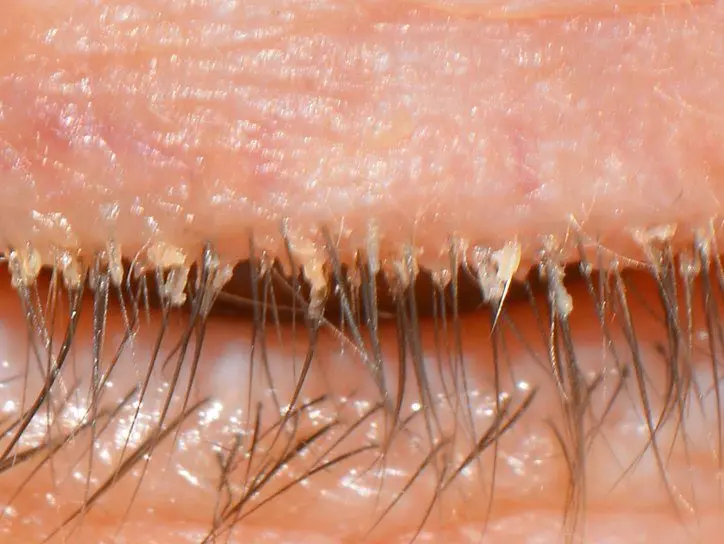
If the tick accumulates in significant quantities in the upper part of the face, then the likelihood of damage to the organs of vision increases. Although this does not threaten with serious consequences, it gives a certain discomfort to a person.
Eye damage (ophthalmodemodecosis)
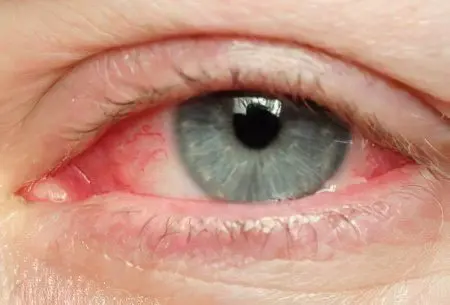
Ticks have the ability not only to clog the sebaceous ducts, but also to provoke allergies. Most often, it occurs locally, without leading to such severe pathologies as Quincke’s edema or urticaria. However, tissues adjacent to the site of infection may be affected. For this reason, a person develops ophthalmodemodecosis.
Symptoms of the disorder appear a few weeks after the development of blepharitis or skin demodicosis. By this time, antibodies are produced in the body, which are responsible for the development of allergies.
Eye symptoms are as follows:
Redness of the eyes, growth of the capillary network on the conjunctiva.
Increased eye fatigue, feeling as if sand had been poured into them.
Itchy eyes. To reduce discomfort, a person often rubs them with his hands, but this does not bring noticeable relief.
Swelling of the eyelids, their heaviness. After sleep, it is difficult for the patient to open his eyes wide. The appearance of the eyes changes.
Excessive dryness of the conjunctiva.
To get rid of the symptoms that have arisen, treatment is needed. Its timely start allows you to fully cope with the existing problem.
Demodicosis diagnosis
To confirm the diagnosis, you will need to donate blood for a general analysis, as well as skin particles for examination under a microscope. It is not advisable to use other diagnostic methods; they will not give additional information.
Changes in the blood picture with demodicosis:
Constituent unit of blood | Indicators of the norm | Disease indicators |
ESR | For women, the variant of the norm is ESR up to 16 mm / s, and for men – up to 11 mm / s | Values are rising |
leukocytes | 4-9,1*109/l | Increase by 1-2 points |
Neutrophils | 2,0-5,4*109/l | |
Eosinophils | Up to 0,3*109/l | Increase many times |
Basophils | Up to 0,65/109/l |
Microscopic examination of tissues or other materials will be required to confirm the diagnosis. The tick can be found in the contents of the vesicles, in the skin, in the horny scales, in the fat secreted from the glands or in the eyelashes.
To identify the tick, the collected material is treated with gasoline, glycerin or cyanoacrylate. This allows the tick to be detected. It takes 1-2 days to diagnose.
Treatment of demodicosis
To cope with demodicosis, you need to make adjustments to your lifestyle. Without this, treatment will be ineffective. Symptoms will periodically remind of themselves.
Recommendations for patients with demodicosis:
Immunity boost. To do this, you need to eliminate those factors that negatively affect the body’s defenses: stress, overwork, chronic diseases, etc. Sometimes it happens that you cannot completely get rid of them, for example, when it comes to severe chronic pathologies (HIV, sugar diabetes, cancer). In such situations, you need to see a doctor. The doctor will prescribe a treatment that will achieve a stable remission.
Compliance with hygiene rules. Cosmetics, dust, etc. can clog the sebaceous glands. Therefore, you need to take care of your skin regularly, use gels, masks, foams, tonics, etc.
Give up bad habits, from taking alcohol and smoking.
Do not visit places where the air temperature is too high, such as saunas, baths.
To cope with the symptoms of demodicosis, you need to use medicines. Acaricides destroy the tick, antiseptics disinfect the surface of the skin, and vitamin A promotes its regeneration. If inflammation of the eyes develops, you need to use special drops and ointments.
Place of impact | Preparations | How the drugs work |
Leather | Acaricides – Benzyl benzoate, Trichopolum, Sulfur ointment, Metrogyl jelly | The drugs are detrimental to parasites, they destroy adults, but the eggs remain viable. |
Antiseptics – Acerbin, Argosulfan, Betadine, Hexicon | Preparations cleanse the skin of pathogenic flora. They are used to prevent secondary infection. | |
Vitamin A applied topically – Retinol, Acnetin, Roaccutane | These drugs normalize metabolic processes in the skin. | |
Eyelids | Drops – Vitabact, Okomistin, Picloxidine | Antiseptics disinfect the treatment area and prevent the disease from spreading |
Ointments with antiseptic effect – Calendula, Glycoderm, Metrogyl jelly | ||
Acaricides, which are similar to those used in the treatment of skin demodicosis | Drugs kill ticks | |
Eyes | Preparations for stopping the inflammatory reaction – Tobrazon, Tobradex, DexaTobropt | They reduce the negative manifestations of the organs of vision. |
Allergy drugs – Loratadine, Clemastine, Desloratadine, Azelastine. | Stop an allergic reaction. |
All of these funds are most often not prescribed to patients with demodicosis. The doctor selects drugs depending on the severity of the disease and its specific manifestations.
How to get rid of demodicosis in 4 days?

It is believed that the treatment of demodicosis takes 1-2 months. In 2014, scientists from Orenburg developed a new exposure scheme that allows you to get rid of the disease in 4 days. The therapy has been proven in practice.
The scheme of treatment of demodicosis:
For the destruction of ticks, benzyl benzoate ointment with a concentration of 10% is used.
Uniderm cream is used to relieve inflammation and symptoms of the disease.
Emolium cream is used to eliminate skin peeling.
All these drugs are applied to the affected tissue, maintaining an interval of 20 minutes. They must be used in the order in which they are listed. To prevent a recurrence of the disease, the course must be repeated after 14-18 days.
The proposed scheme can be practiced if no bacterial infection has occurred (the use of antimicrobials is required).
Forecast
The prognosis is always favorable. Persistent changes in the dermis with demodicosis are not observed. To cope with parasites, you need to strictly follow medical recommendations.









