Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
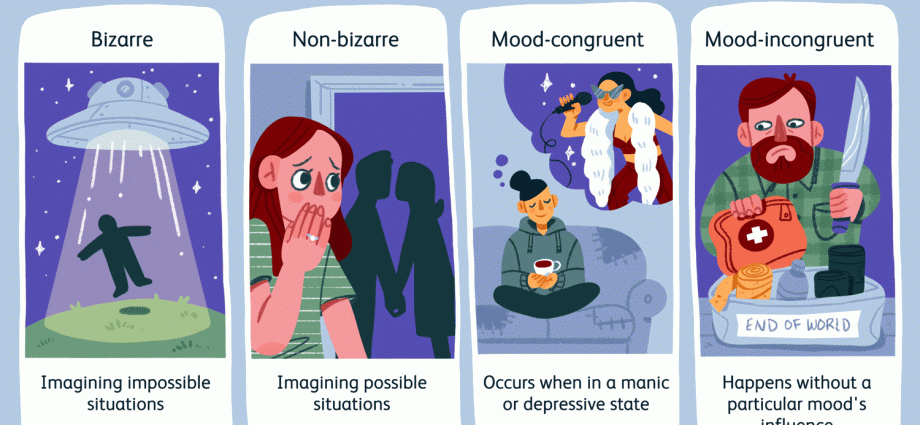
Delusions are unconfirmed and imaginary beliefs, events, situations that the sick person perceives as real. Mental illness is the most common cause, but it can also include Alzheimer’s, alcohol, and drugs. Find out what exactly delusions are.
What are delusions?
Delusions are imaginary beliefs of a sick person about something or about someone despite the existence of real arguments proving their untruth. The patient may think that he is terminally ill or his life is threatened by someone. In other cases, betrayal may be imaginary, i.e. the patient is overly jealous of his / her partner for no real reason.
Most often, a delusional person does not allow himself to think that he is sick. They consider their relatives or people explaining this fact (e.g. doctors) to be in need of help. The patient cannot explain the reality, no rational arguments appeal to him.
- Here are 7 mental disorders that can destroy us
The causes of delusions
The causes of delusions may be a mental illness, e.g. paranoid schizophrenia, otherwise known as delusional schizophrenia. The disease consists of auditory, olfactory, tasting and visual hallucinations, as well as delusions.
Other causes of delusions may include:
- biological, mental, genetic and environmental factors;
- abuse of alcohol or psychoactive substances (e.g. drugs, legal highs);
- excessive stress (although confirmatory studies are still ongoing),
- confusional syndrome, i.e. a disorder of consciousness manifested by a lack of contact with the world, impaired thinking and movement, hallucinations and delusions.
Delusions – types
Delusions have many causes, and therefore there are also many types of delusions. Specialists distinguish, among others:
- persecution,
- book,
- size,
- hypochondriacal,
- jealousy
- erotic,
- frowning.
Persecutory delusions
They are based on the belief that someone or something is a constant threat to the sick person. The patient is convinced that his relatives, family or even institutions (e.g. a hospital) do their best to destroy him and cause suffering. I feel watched, under surveillance, restricted, trusting no one.
Delusional delusions
The patient pays special attention to himself and believes that others are also doing it. All glances, conversations, jokes, etc. he relates to himself. He lives with the feeling that everyone is looking at him, talking about him, wanting to rob him, etc.
Delusions of size
Convincing the patient about his superior role in society. Seeing yourself as a particularly influential and important person. The relatives of the patient may confuse this type of delusion with an excessively overactive ego.
Hypochondriac delusions
According to the patient, he is incurably ill. Most often for AIDS, cancer, leukemia, as they are known incurable diseases. Long-term delusions can lead to symptoms of the patient. Here it is necessary to distinguish hypochondriac delusions from various types of neuroses. With the second disease, somatic disorders occur normally, but they are not the result of an imaginary disease, but a disorder of the nervous system.
Delusions of jealousy
The sick person is overly jealous of his / her partner. The so-called scenes of jealousy, he follows and monitors. He considers every conversation or glance of his partner to be an act of betrayal and infidelity.
Erotic delusions
The belief that the sick person is an object of erotic and sexual desire. Therefore, the patient seeks contact with an admirer. In fact, the person who is perceived as lust may not pay attention to the sick person or even avoid him.
Delusions of foamy
Continuous presumption of harm. Seeing yourself as a victim, testing your rights even in court.
Delusions – diagnosing
Delusions very often occur between the ages of 35 and 45. According to statistics, delusions occur in 0,05% of the population, but this result is underestimated due to the lack of treatment by many patients.
The diagnosis of delusional diseases consists mainly in cooperation with a psychiatrist, e.g. interviews with the family and the patient, analysis of the environment, examination of the frequency of delusions, as well as diagnosis of somatic and mental diseases (in which delusions may be one of the symptoms).
Treatment of delusions
People with delusional disorders do not have to be excluded from social, family and professional life. The most important thing in this situation is appropriate professional help that will help in the fight against the disease.
In some situations, however, delusions are so strong that they do not allow the normal functioning of the patient or the family – then the help of a psychiatrist should be initiated as soon as possible. Unfortunately, in many cases the patient does not want to be treated, believing that his delusions are real.