Contents
- What is dehydration?
- The body’s need for water
- The first symptoms
- Types of dehydration
- Dehydration levels
- Causes of dehydration in adults
- When to seek medical help?
- Diagnosis of dehydration
- What to drink with dehydration at home?
- Drugs prescribed for dehydration in medical settings
- Effects of dehydration on various body systems
- Dehydration prevention
- If you don’t like drinking clean water, what should you do?
Water takes part in all processes occurring in the body. Dehydration is dangerous, as it leads to metabolic disorders and the development of various diseases. However, dehydration itself can be a symptom of pathology. Therefore, it is so important to know the maximum information regarding this condition. Doctors call dehydration dehydration.
What is dehydration?
Dehydration – This is the loss of fluid by the body, when water supplies are rapidly running out and do not have time to meet all its needs. Water leaves the body during breathing, it leaves the body with sweat, urine, feces. Together with it, a certain amount of minerals is displayed. Normally, these losses are restored during the day. If this does not happen, then the balance is disturbed, dehydration develops. Its severe form can be fatal.
The body’s need for water

The human body can not only accumulate, but also retain nutrients for a long time. This is possible only if he does not experience a shortage of water. In general, a person without it will not be able to survive longer than 3 days. Of the total body weight, liquid accounts for about 2/3 of the part. Even a slight decrease in the water level causes serious disturbances. The fact is that cells cannot maintain their existence in an excessively viscous environment.
The system that ensures the balance of biochemical processes in the body is called homeostasis. If it is violated, then the normal functioning of organs and systems becomes impossible.
Fluid in the human body can be in 3 states:
Blood that circulates through blood vessels.
Intercellular fluid, which is located in the intercellular space.
Intracellular fluid, inside which are all the structures of living cells.
For cells, water is very important, as it is a nutrient medium for them.
As the body ages, the volume of water in it begins to decrease. In children who have just been born, it is 80% of the total body weight. In adults, this figure drops to 60%. Children lose fluid much faster than adults. This is due to the fact that the system that controls the water-salt metabolism is poorly debugged in them.
By the age of 70, the indices of intracellular and intercellular fluid decrease from 1,1 to 0,8. This negatively affects the functioning of all internal systems. Therefore, doctors strongly do not recommend people to bring themselves to thirst. You need to drink water as often as possible. Water provides nutrition to cells, and dehydrated cells cannot function normally.
The first symptoms

Early symptoms of dehydration include:
Thirst.
Drying of mucous membranes.
Fatigue and weakness.
Slimming. A person with dehydration loses at least 5% of their body weight.
Older people do not suffer from thirst as severely as younger people.
Therefore, it is important to pay attention to other signs of dehydration:
Lack of desire to eat.
Inexplicable feeling of tiredness.
Drowsiness.
Increased body temperature.
Types of dehydration
Depending on the nature of fluid loss and how long ago dehydration developed, there are 3 types of it:
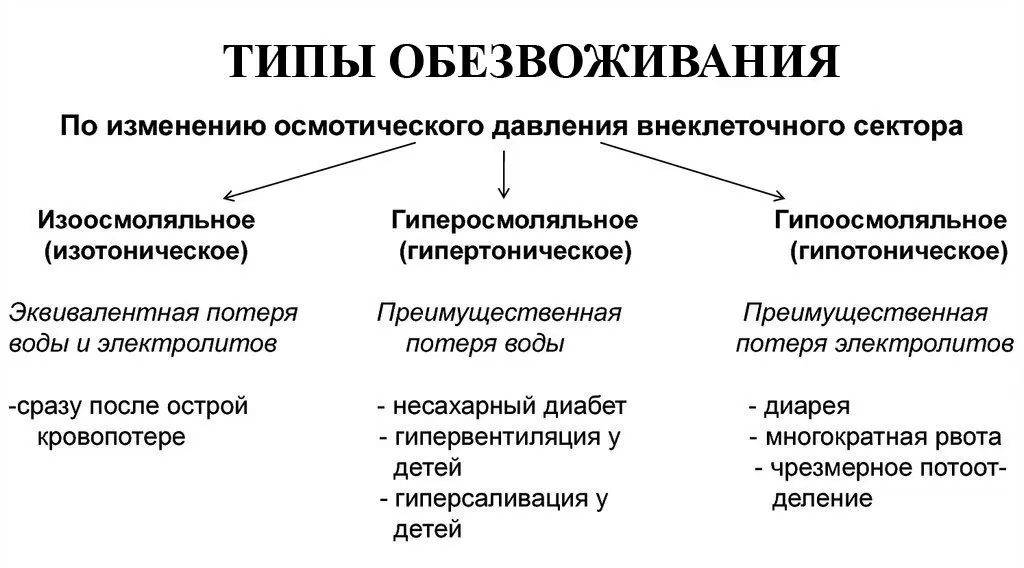
Hypertonic (water-deficient, intracellular) dehydration. This type of dehydration occurs when excess water is removed from the body. This situation is observed with severe diarrhea, against the background of elevated body temperature, with dyspnea and hyperhidrosis. At the same time, the level of electrolytes in the blood plasma increases (sodium salts become the most).
To make up for the loss of water, intercellular fluid begins to flow into the bloodstream, which leads to an increase in osmotic pressure. To normalize it, the cells themselves begin to release water into the intercellular space. As a result of this process, dehydration of the body develops.
Its main symptoms are:
Thirst and dryness in the mouth.
Dryness of the skin.
Consciousness.
Muscle spasms.
Increased body temperature.
Decrease in the amount of urine produced.
Hypotonic (hypoosmotic, extracellular) dehydration. This type of dehydration of the body develops due to the fact that it loses more electrolytes than water. The osmotic concentration of blood at the same time begins to decrease. This situation is observed with profuse vomiting, which is much stronger than diarrhea.
To normalize hemostasis, the body directs sodium salts from the intercellular space into the bloodstream. In this case, water from the bloodstream passes into the interstitium of cells. As the osmolar concentration of the intercellular fluid decreases, it begins to penetrate into the cells. Potassium electrolytes are displaced from the cells and excreted in the urine. There is too much water in the cells, as most of the fluid rushes inside them.
Symptoms of this type of dehydration include:
Laxity of the skin.
Dry eyes.
Lack of desire to drink water.
Dyspnea.
Increased heart rate.
Vomiting that develops after drinking water.
Isotonic dehydration. This type of dehydration of the body occurs due to the fact that both water and electrolytes are removed from it at the same time. They become equally small in the lymph flow, blood and tissues. Osmolarity and the level of sodium ions in the blood is normal. Isotonic dehydration is the most common. The patient’s state of health can reach moderate severity, but sometimes there is severe dehydration of the body.
The symptoms of isotonic dehydration are as follows:
Increased heart rate.
Light thirst.
Deafness of heart sounds.
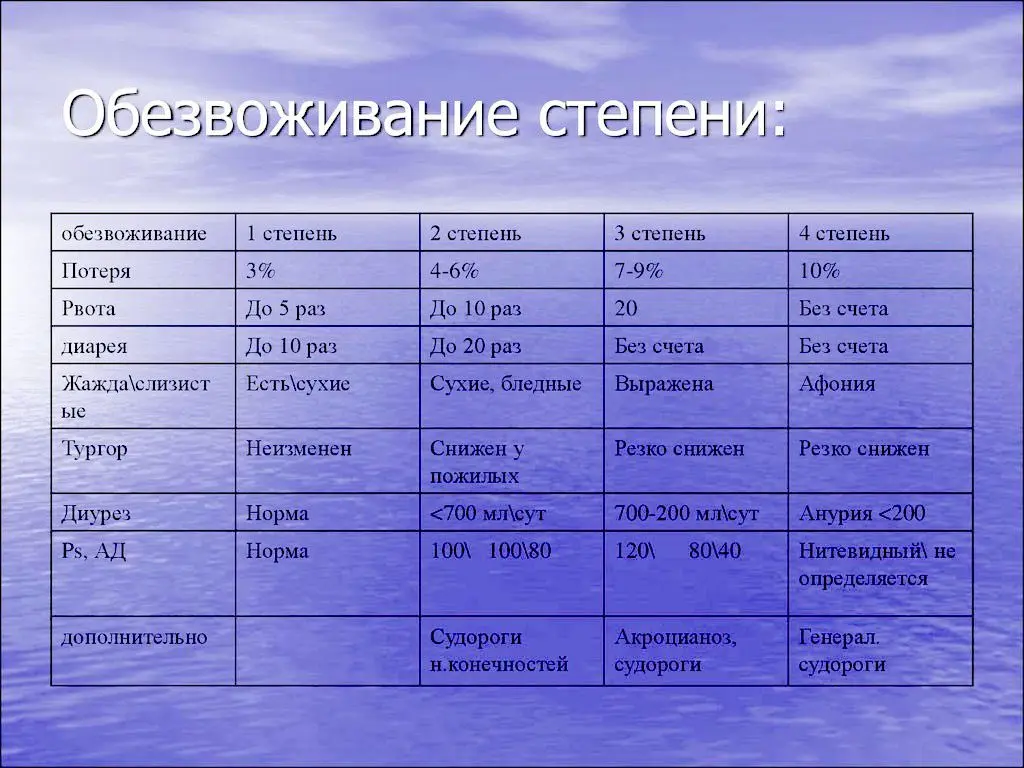
Dehydration levels
There are 4 degrees of dehydration, which depend on the amount of fluid lost:
Mild dehydration. The body loses 1-3% of water, but not more than 1,5 liters. Hospitalization is not required, the replacement of lost fluid is carried out by oral dehydration. It is recommended to take a few tablespoons of water every 15 minutes. Recovery is fast and no medical assistance is required.
Moderate dehydration. Water losses are 3-6%, but not more than 3 liters. If at home it is not possible to restore the fluid lost by the body, then medical assistance is required. The doctor recommends taking Regidron, since it will not be possible to stabilize the patient’s condition with water alone.
Severe dehydration. Fluid losses are 6-9%. The patient is urgently hospitalized, in the hospital ward he is put on a drip. Self-medication threatens with serious complications.
Significant dehydration develops when water losses exceed 10%. In such a situation, the patient develops problems in the work of internal organs, a fatal outcome may occur.
Causes of dehydration in adults

Dehydration can be caused by the following reasons:
Acute intestinal infections, accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting. If the patient develops vomiting, then the digestive juices and fluid that is contained in the upper parts of the digestive system come out. Together with it, the body leaves sodium, potassium and chlorine ions. During vomiting, the patient cannot replenish fluid reserves by mouth. When a person develops diarrhea, the fluid leaves the body very quickly, since the pressure of the blood plasma is higher than the pressure inside the intestines.
Diseases in which the body temperature rises greatly. Dehydration against the background of infectious diseases occurs due to high body temperature and shortness of breath. Sometimes the loss of water is increased by opening vomiting and diarrhea. High body temperature always leads to fluid loss. Patients direct efforts to achieve sweating. To do this, they take as much tea as possible, but the loss of water in this case will be even more significant.
Consumption of large volumes of coffee, tea, carbonated drinks. If a person drinks a lot of coffee, tea, beer or alcoholic beverages, then he supplies the body not only with water, but also with components that contribute to dehydration, such as caffeine. It has been proven that when taking these drinks, the loss of water is higher than its intake into the body.
Taking drugs: indapafon, diuretics and some others. As for taking medicines, the body will spend water on the assimilation of any drug. This contributes to increased dehydration. Moreover, in 90% of cases, people take drugs without real need and without medical advice. Fighting the symptoms of the disease, and not its root cause, leads to the fact that the state of health worsens even more.
Water comes out of the body every day through sweat. Actively a person sweats during sports. Therefore, going to training, you must definitely take water with you.
Frequent urination. It is observed in people with diabetes mellitus, in which the process of assimilation of glucose in the body is impaired. If the pancreas produces little insulin, then the person will suffer from intense thirst. The more he drinks, the more often he goes to the toilet. Similar symptoms can occur with diabetes insipidus. This disease develops due to a deficiency in the body of the antidiuretic hormone of the pituitary gland. The patient also suffers from intense thirst and urinates frequently.
Situations in which water does not enter the body for a long time.
Children lose a lot of water when they are actively moving and playing. Physical activity for children is the norm, but fluid volumes must be replenished in a timely manner. This should be supervised by adults.
When to seek medical help?

You need to seek medical attention in the following cases:
Abundant diarrhea does not stop within 2 days.
Vomiting continues for more than a day.
Body temperature rises to 39 ° C and above.
The patient has a loss of strength.
Little urine comes out, a person rarely goes to the toilet.
The weight is dropping fast.
Sometimes there are situations in which you need to call an ambulance:
Body temperature reaches 40 °C.
No urination for 12 hours.
The patient’s orientation in space worsens, fainting occurs, or he becomes lethargic and apathetic, his head hurts badly or pains appear in the chest.
The pulse becomes thready, breathing becomes difficult, convulsions occur.
If in such a situation a person is not provided with medical assistance, then he may die.
Diagnosis of dehydration

Diagnosis of dehydration is reduced to examining the patient, performing various tests, blood and urine tests. It is important not only to state the fact of dehydration of the body, but also to find out the cause of its occurrence.
Assessment of health indicators:
If the patient has a high body temperature, lowered blood pressure, breathing and heart rate is rapid, then these are symptoms of dehydration.
Assessment of pulse and blood pressure level in the supine position and in the standing position. When a person lies down and then gets up, the pressure decreases slightly, then the heart rate increases and the pressure returns to normal. When a person develops dehydration, there is not enough blood in the body to circulate. Therefore, the heart will always beat faster, the head will begin to spin when lifting, the person will experience weakness.
Passing urine for analysis:
Evaluation of the color and transparency of urine, its specific gravity and the presence of ketone bodies in it. All these signs allow diagnosing dehydration.
If glucose is present in the urine, this may indicate developing diabetes mellitus.
Kidney disease is indicated by the presence of protein in the urine.
Sometimes urine allows you to suspect certain infections.
Blood analysis:
In terms of diagnosing dehydration, the assessment of the level of salts, electrolytes, glucose, protein and creatinine in the blood is important.
A biochemical blood test allows you to clarify the presence of an infectious process.
The blood may be sent for further research. The need for them is carried out by a doctor.
What to drink with dehydration at home?
To replenish the body’s water and salt reserves, you need to add saline solutions to the water, or prepare them separately.
Drugs that are used for rehydration:
Gastrolit.
Hydrovit.
Orasan.
Orsol
Regidrare.
They are available in the form of powder or granules, which dissolve quickly in water. Salt solution can be prepared independently by adding a spoonful of salt to the water (a teaspoon of sodium chloride is required per liter of liquid). You need to drink not because you are thirsty, but because it is a necessity. The closer the temperature of the liquid to the temperature of the human body, the faster it will be absorbed.
Dehydration in children at home can only be treated if it is mild. The child is offered the same drugs as an adult. They are drunk in those quantities in which the liquid is excreted from the body. If the child is an infant, then he must be given water through a syringe without a needle.
You can only cope with mild dehydration at home. In other situations, you must consult a doctor.
Drugs prescribed for dehydration in medical settings

Moderate dehydration and severe dehydration should be treated with drips. This is the only way to quickly restore fluid loss and lost blood volumes. For this, Ringer’s solution, saline, glucose, trisol, disol are used. Hemodez and Poliglukin are prescribed when it is necessary to remove the symptoms of intoxication from the body. They are indicated for bleeding, as they prevent further removal of fluid from the body.
If the patient’s body temperature rises, then it must be knocked down using antipyretic drugs.
To eliminate vomiting, antiemetics are prescribed, for example, Sturgeon.
Preparations such as Gastrolit, Regidron, Oralit or other powdered salt preparations are used only as an adjunct treatment.
Effects of dehydration on various body systems
If severe vomiting and diarrhea lead to dehydration, then, in addition to water, electrolytes are excreted from the body in significant volumes. This causes the movement of water from the intercellular space into the bloodstream. Therefore, there is even less fluid in the general bloodstream.
dehydration for the brain
The brain suffers from hypoxia, as its blood supply deteriorates. Its natural defenses in the form of the blood-brain barrier are reduced. Under the blood-brain barrier understand the barrier between the capillary network and the neurons of the nervous system. It is they who, normally, do not allow harmful substances to enter the central nervous system.
Dehydration and a decrease in barrier function leads to the fact that toxins enter the brain, which can later cause the development of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis.
Against the background of dehydration, the level of intracellular fluid first decreases to 66%, then the level of intercellular fluid decreases by 25%, after which 8% of water is extracted from the blood. The body launches such a mechanism in order to provide nutrition to the brain. After all, it is 85% water. If the brain loses even 1% of fluid, it will lead to irreversible damage.
Dehydration and blood cells
Against the background of dehydration, processes such as:
The blood is getting thicker.
The lumen of the vessels narrows.
The blood becomes viscous.
Increases the likelihood of blood clots forming.
When dehydrated, blood cells lose their natural activity and stick together. Such associates are not able to perform their functions correctly, they cannot seep through cell membranes, so blood fluidity deteriorates. It must be remembered that the adhesion of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets is the main factor leading to the development of atherosclerosis.
The immune system
Immunity to dehydration reacts with the launch of chronic immunodeficiency diseases, such as bronchial asthma or scleroderma. This also includes infertility, bronchitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.
Metabolism
Obese people may not even suspect that their excess weight is a consequence of dehydration. The less water in the cells, the more they need the energy they take from food. This promotes the accumulation of fat. Moreover, the source of such energy is often starches and proteins. Therefore, dehydration and obesity are closely related.
Dehydration prevention

To prevent the development of dehydration, the following preventive measures must be observed:
If a person knows that he will sweat, you need to provide yourself with drinking water. Stress and physical activity lead to its removal from the body. You need to drink as much as you want.
Do not exercise in the heat or in a hot room.
It is necessary to ensure that children and the elderly receive sufficient water. They must have constant access to fluid. It is recommended to drink more water for people with poor hearing.
Do not drink alcohol in the heat
In hot weather, always carry a bottle of water with you. Clothing should be light so that the body does not suffer from heat.
If you don’t like drinking clean water, what should you do?
Sometimes drinking a lot of plain water is not tasty. To make this task easier for yourself, you can add fruits or berries to it. Water with citrus fruits makes a person more cheerful.
If you add pineapple to the water, you will be able not only to improve its taste, but also to lose weight. It contains antioxidants that prevent free radicals from damaging human cells. They help fight atherosclerosis, arthritis and cancerous tumors.
Vivacity adds apple water with ginger. You need to drink it in the morning.









